What Is AAA?
Authentication, Authorization, and Accounting (AAA) is a security management framework for network access control. It determines which users can access the network and which resources or services are available to authorized users. This document introduces the three elements of AAA and its implementation, used protocols, as well as applications.
Three Elements of AAA
Authentication
Authentication: confirms the identities of users accessing the network and determines whether the users are authorized.
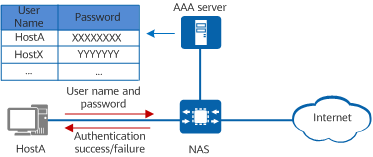
Authentication
The AAA server compares a user's authentication credentials with those stored in a database. If the credentials match, the user passes identity authentication and is permitted access to the network. If the credentials do not match, the user fails identity authentication and is denied access to the network. The following lists the typical authentication credentials:
- Password
- User name and password
- Digital certificate
Authorization
Authorization: assigns differentiated rights to authorize users to use specific services.
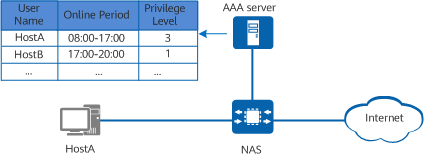
Authorization
After a user passes identity authentication, the following items are authorized to the user:
- Commands
- Resources
- Information
Authorization follows the least privilege principle. That is, users are granted only the permissions required for executing required functions to prevent any accidental or malicious network behavior.
Accounting
Accounting: records all the operations of a user during the network service process, including who, when, and what has been performed.
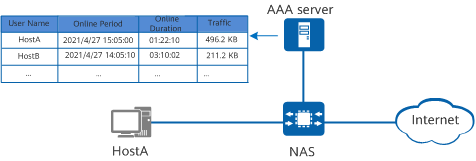
Accounting
Accounting records the used service type, start time, and data traffic to collect and record the network resource usage of the user for implementing time- or traffic-based accounting and network monitoring.
How Does AAA Work?
AAA uses the client/server structure, which is simple, scalable, and facilitates centralized user information management.
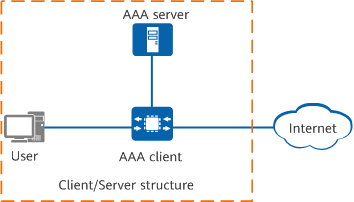
AAA framework
As shown in the preceding figure, the basic AAA implementation process is as follows:
- The user establishes a connection with the AAA client before accessing the network.
- The AAA client sends the user's authentication credentials to the AAA server.
- The AAA server authenticates and authorizes the user based on the user's authentication credentials and returns the authentication and authorization results to the AAA client.
- The AAA client determines whether to allow the user to access the network based on the received authentication and authorization results.
In the AAA framework:
- The AAA client runs on a network access server (NAS), which can be a router or switch that provides network access services for users.
- The AAA server is responsible for user authentication, authorization, and accounting, as well as centralized user information management. Depending on the communication protocols used in AAA, AAA servers are classified into Remote Authentication Dial-In User Service (RADIUS) servers and Terminal Access Controller Access Control System (TACACS) servers.
What Protocols Are Used in AAA?
AAA implements authentication, authorization, and accounting through multiple protocols.
RADIUS
RADIUS is a standard protocol supported by almost all mainstream device vendors. Therefore, RADIUS is most widely used on live networks.
In RADIUS, authentication and authorization are defined in RFC 2865, while accounting is defined in RFC 2866. RADIUS was defined earlier than the AAA framework model, and RADIUS combines authentication and authorization. Therefore, when AAA is implemented through RADIUS, the user may not know whether the access is denied because of an authentication failure (for example, the password is incorrect) or an authorization failure (for example, the user does not have the permission).
TACACS, TACACS+, and HWTACACS
TACACS is an AAA protocol originated in the 1980s. In later development, vendors extended TACACS. For example, Cisco developed TACACS+, whereas Huawei developed Huawei Terminal Access Controller Access Control System (HWTACACS). TACACS+ and HWTACACS are proprietary protocols. They gradually replaced TACACS and are no longer compatible with TACACS.
HWTACACS is compatible with TACACS+. HWTACACS and TACACS+ define the same packet structure and types. The main difference is that the meanings or types of attributes carried in the authorization and accounting packets are not exactly the same.
Compared with RADIUS, HWTACACS and TACACS+ are more suitable for identity authentication of login users (such as STelnet users). This is because HWTACACS or TACACS+ is more secure in data transmission and encryption, and provides advantages such as command authentication and event recording.
LDAP and AD
The Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) is implemented based on the TCP/IP protocol suite. LDAP can be considered as a database, which can store various types of hierarchical, structured, and associated data, such as email addresses, human resources data, and contact lists. LDAP implements authentication and authorization through bind and query operations. It is typically used in single sign-on (SSO) scenarios. For example, an enterprise user can access multiple mutually trusted application systems after logging in to a PC.
Active Directory (AD) is an application instance of LDAP. It is a component that provides directory services to store user information on the Windows operating system. Compared with LDAP, AD integrates the Kerberos protocol into the LDAP authentication process and uses the symmetric key mechanism of Kerberos to prevent user passwords from being disclosed.
Diameter
Diameter is a next-generation AAA protocol defined by the IETF. It evolves from RADIUS. Diameter overcomes many disadvantages of RADIUS. For example, Diameter supports authentication, authorization, and accounting of mobile IP, multiple interfaces, and mobile agents. With the maturity and standardization of the Diameter protocol and its applications, it will play a great role in promoting the development of the future mobile communication system and broadband access system.
What Are the Applications of AAA?
Based on the user access mode, AAA can be applied in the following scenarios:
- Login user management
A login user refers to a user who directly logs in to a device through various methods (such as a console port or STelnet) to perform operations. These users have high security requirements. AAA can be used to determine the users who can log in to the device and the commands that can be executed after login, and record the operations performed by users.
- NAC user access control
Network Admission Control (NAC) users refer to the users who access the network through 802.1X authentication, MAC address authentication, or Portal authentication. These users can be wired or wireless users, and may access enterprise campus networks, education networks, medical networks, or shopping mall/supermarket networks. Such users have complex access types, frequently changing physical locations, and different privilege levels. AAA can work together with NAC to effectively ensure the security of these users.
- Author: Dou Cuicui
- Updated on: 2024-02-27
- Views: 19796
- Average rating:







