What Is a Hybrid Cloud?
A hybrid cloud, as a cloud computing form, enables private and public clouds to collaborate with each other to improve cross-cloud resource utilization. It is an integrated system that contains resources and products in public and private clouds and helps users manage IT infrastructure across clouds and locations.
Hybrid Cloud Background
Currently, the enterprise IT architecture has been migrated from the centralized mainframe architecture to the current distributed virtualization architecture and is evolving to the multi-site and multi-cloud architecture. Based on service characteristics, services can be classified into stable services and agile services, which are deployed on private or public clouds as required.
- Stable services: are typically deployed on physical machines (PMs) of traditional networks or private clouds to meet the requirements of bare metal servers (BMSs), databases, and core services. Stable services require high reliability and low latency.
- Agile services: are typically deployed on VMs of public clouds to meet the agility and elasticity requirements for resources. Applications of agile services are iterated in DevOps mode.
Customers can flexibly select the cloud computing mode based on their service characteristics. For example, customers can store private data in their private clouds for security purposes and deploy testing services (frequently changed and upgraded) and services frequently accessed by external users on public clouds because a public cloud delivers high reliability, professional O&M, and fast resource expansion.
Hybrid cloud is the primary mode and development direction of cloud computing in recent years, and is listed as one of Gartner's top 10 strategic technology trends in 2020.
Features and Benefits of a Hybrid Cloud
Enterprises can deploy cloud computing services in three modes: public cloud, private cloud, and hybrid cloud. A hybrid cloud is an integrated system that contains various resources and products in public and private clouds. It helps customers manage IT infrastructure across clouds and locations.
A hybrid cloud is more than a mix of private and public clouds. It delivers the following capabilities:
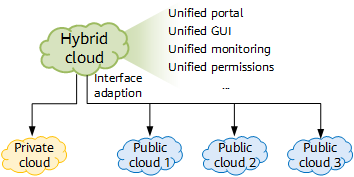
- Interconnection between private and public clouds: ensures data exchange across clouds and provides a flexible service deployment mode. Common interconnection modes include private line-based and VPN-based interconnections.
Hybrid cloud - Consistent services between public and private clouds: includes the unified service portal, resource monitoring GUI, and account permissions.
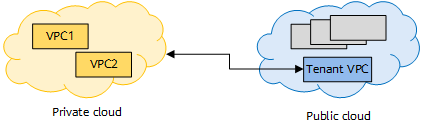
Consistent service experience - VPC interconnection across public and private clouds: implements service interworking across public and private clouds.
Communication between VPCs of the private cloud and public cloud
A hybrid cloud offers the following benefits:
- Enhanced service flexibility: Customers can deploy enterprise core data on their own private cloud to ensure data security and stability, and deploy new applications on a public cloud for iterative development and testing to enjoy flexibility and agility of the public cloud.
- Lower costs: Cloud storage costs less than local storage and can be used to back up data. When services need to be expanded, especially when the temporary service volume increases sharply, enterprises can purchase public cloud resources instead of purchasing or deploying local ICT facilities. After the service volume recovers, they can release purchased public cloud resources to reduce costs.
- Improved availability and access capability: Public clouds in hybrid cloud environments are usually deployed in multiple DCs across a country or even around the world, providing ubiquitous connections. As such, customers can access cloud services anywhere.
- Convenient service migration: Public cloud service providers usually provide dedicated tools for customers to migrate and test services between private and public clouds.
- Promoting service innovation: Customers can use the public cloud to develop and test new services. In this way, the customers can focus on services without worrying about costs caused by failures and ICT resource exhaustion. In addition, they can easily obtain and try new services and tools on the public cloud without deploying those services and tools locally.
Hybrid Cloud Application Scenarios
- Service burst and application load expansion
An enterprise deploys its applications in the private cloud. To cope with service peaks caused by seasonal or unexpected events, the enterprise rents public cloud resources, quickly improving service response capabilities.
- Disaster recovery
The hybrid cloud generally uses the master/slave architecture for disaster recovery (DR). With this architecture, users can store standby service data in the public cloud and use the technical advantages, DR experience, and O&M management resources of public cloud providers to quickly implement data recovery and ensure service continuity. In addition, compared with the private cloud, DR for the hybrid cloud requires less O&M workload and lower DR system costs. When a disaster occurs in the private cloud data center (DC), users can use cloud hosts on the public cloud to quickly perform switchover and use backup data, greatly reducing the recovery time objective (RTO) and achieving high service availability.
- Data backup
The purpose of data backup is to store the data or applications at a certain time point in a secure and reliable place. Generally, applications run on the public cloud or private cloud, and data is backed up on the private or public cloud to ensure data security.
- Front-end services close to users, and back-end services processed in a centralized manner
For an enterprise with multiple branches, especially a multinational enterprise, if all its services are processed by the DC at the headquarters, the processing capability and access bandwidth of the headquarters will become a bottleneck as the service volume increases. In the hybrid cloud solution, front-end services are deployed on the public cloud. The multi-region and content delivery network (CDN) advantages of the public cloud enable services to be deployed as close to end users as possible. The back-end services are still deployed on the private cloud at the headquarters. After front-end processing is complete, only a small amount of front-end and back-end interaction is required to complete the entire service processing.
- Development, testing, production, and deployment
For an application, the development and testing process usually requires flexible and quick environment setup, and the environment is often reconstructed during this process. The public cloud is ideal for this requirement. Once the application is launched, it is expected to run in a secure and stable environment. In this case, the private cloud will be considered. By building a hybrid cloud, you can employ the DevOps to use the public cloud or private cloud in different phases of an application as required.
- Access from private cloud applications to public cloud services
Applications deployed in the private cloud can use private IP addresses to access services provided by the public cloud through the VPN or private line, simplifying the development and deployment of local application systems.
Hybrid Cloud Service Providers
In the hybrid cloud market, the original public cloud and private cloud service providers have launched their own hybrid cloud products to meet customers' increasing requirements for hybrid clouds.
Common hybrid cloud service providers include HUAWEI CLOUD, Alibaba Cloud, Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud Platform (GCP), VMware, and Red Hat.
- Author: Zhang Fan
- Updated on: 2021-12-06
- Views: 3305
- Average rating: