What Is an NGFW?
The Next Generation Firewall (NGFW) is the next-generation product of traditional stateful firewalls and unified threat management (UTM) devices. In addition to all functions (such as basic packet filtering, stateful inspection, NAT, and VPN) of traditional firewalls, it integrates more advanced security capabilities, such as application and user identification and control and intrusion prevention (IPS). Compared with UTMs, NGFWs have faster processing efficiency and stronger external expansion and association capabilities.
Definition of NGFW
Back to 2007, Gartner, a well-known consultative firm, proposed the concept of NGFW based on changes in the enterprise service workflow and IT architecture and emerging trends in security threats. In 2009, Gartner officially released Defining the Next-Generation Firewall.
Gartner defines an NGFW as "a wire-speed integrated network platform that performs deep inspection of traffic and blocking of attacks." According to Gartner, the NGFW must provide the following capabilities:
- Traditional Firewall Functions
The NGFW is a substitute for traditional firewalls in the new environment and must be backward compatible with traditional firewall functions, including packet filtering, protocol status detection, NAT, and VPN.
- Application Identification and Control Technologies
Application awareness, refined security policies based on applications, and hierarchical bandwidth control are the most important capabilities introduced by NGFWs. Traditional stateful inspection firewalls merely work at Layer 2 through Layer 4 and do not inspect packet payloads. The NGFW can inspect information at Layer 2 through Layer 7, providing visibility into and control over network services.
- In-Depth Integration of IPS and Firewall Functions
The NGFW must support the IPS function and integrate it with firewall functions for convergence. In this case, one plus one equals more than two. Gartner specially emphasizes more integration between the IPS and firewall than mere their interworking in NGFWs. For example, a firewall should be able to automatically update and deliver security policies when malicious traffic is detected by the IPS, without manual involvement. In other words, a firewall with IPS integrated is more intelligent. Gartner finds that the NGFW and IPS markets are converging, particularly in enterprise boundary-specific deployment scenarios, in which the NGFW encroaches on the market of standalone IPS products.
- Using Information Outside the Firewall to Enhance Management and Control
The NGFW can use the user, location, vulnerability, and network resource information provided by other IT systems to improve security policies. For example, to address the changeable IP address-induced control challenges in mobile working scenarios, the NGFW can be integrated with a user authentication system to enforce security policies based on user information instead of IP addresses.
NGFWs vs. Traditional Firewalls vs. UTMs
Firewalls have evolved with network development since their emergence.
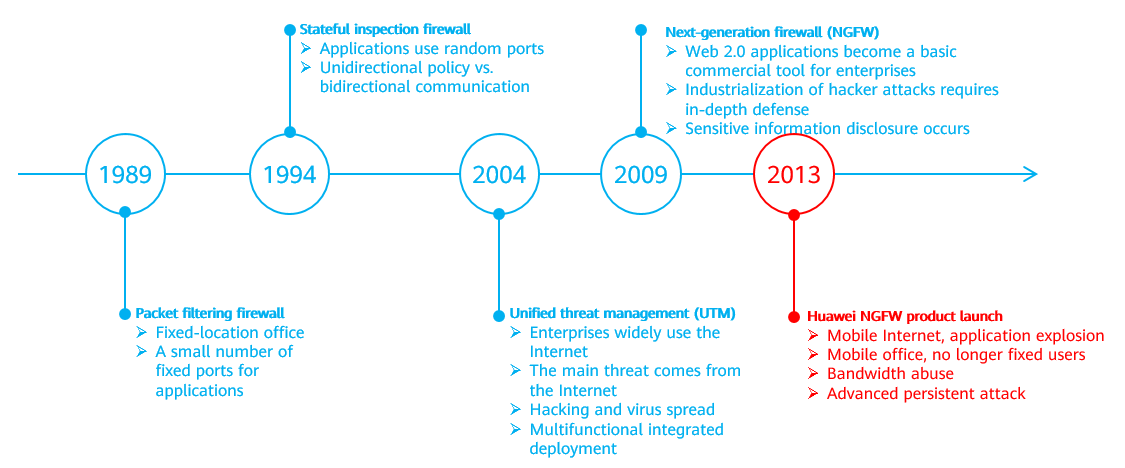
Development history of packet filtering firewalls, stateful inspection firewalls, UTMs, and NGFWs
- Early packet filtering firewalls isolated networks only by implementing access control.
- A stateful inspection firewall (also called a traditional firewall) integrated the TCP/UDP and application status detection capabilities to implement Layer 3 and Layer 4 protection. On the stateful inspection firewall, the concept of policy was introduced and what was to be processed was changed from packets to flows, improving processing efficiency.
- In 2004, UTMs were developed to integrate traditional firewall, content security (antivirus, IPS, and URL filtering), and VPN functions. Each functional module ran separately, requiring that packets be parsed repeatedly for detection by each module. As such, detection efficiency was not improved. The UTMs simplified security product deployment to some extent and were suitable for small- and medium-sized enterprises.
- As the number of web applications increased, the relationships between applications, ports, and protocols became more complex. For instance, some people may use HTTP during their studies, and some may use it to play games. Therefore, traditional firewalls that identify traffic based only on 5-tuple information cannot clearly identify network traffic. Through this, the NGFW with application identification technology emerged. It can distinguish applications corresponding to traffic, even if these applications use the same protocol and port. In addition, the NGFW deeply integrates multiple security services, such as IPS and antivirus, with the firewall services for parallel processing. This addresses the issue in which the UTM device is required to process packets module by module with low performance. However, in most cases, the UTM and NGFW do not provide the web application firewall (WAF) capability.
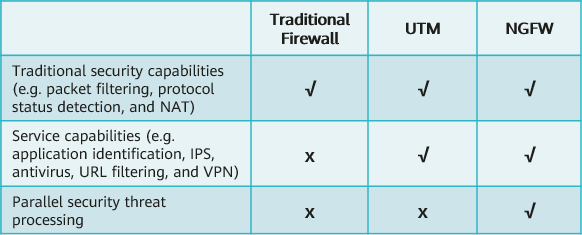
Capability comparison among traditional firewalls, UTMs, and NGFWs
Which Type of Firewall Is Needed Now?
With the development of mobility, socialization, cloud, and big data, the ICT network environment is being reshaped. The NGFW must satisfy the strict requirements of the network security environment.
High Performance
As the NGFW is a real-time protection device, its performance is the top consideration for possible purchasers. Huawei's NGFW relies on the advanced integrated intelligent awareness engine to perform integrated processing on packet content. In other words, data extracted at a time is eligible for being processed by all content-based security features, delivering high detection performance.
Comprehensive Threat Prevention Capabilities
- In addition to inheriting and improving traditional security functions, the NGFW effectively identifies applications and defends against application-layer threats and attacks.
- It integrates the user authentication system and supports user identification to address the challenges associated with mobile access.
- It supports content protection and filters content of web pages, emails, and files.
- It supports SSL-encrypted traffic detection. It can decrypt SSL traffic and detect content in decrypted traffic.
- It interworks with a sandbox and can send suspicious files to the sandbox for detection to identify unknown threats.
Refined Detection Granularity
The NGFW supports flow-based integrity detection, real-time monitoring, and cache-free technology. By using only a few system resources, the firewall uses these technologies to detect fragments and packets to identify applications, intrusion behavior, and virus files in real time.
Cloud Computing and Data Centers
The NGFW supports virtualization in terms of route-based forwarding, configuration management, and security services. A single NGFW can be virtualized into multiple independent virtual firewalls, which can be used by tenants of cloud computing and data centers.
Simplified Management
- The NGFW provides the visualized management UI and various log reports.
- It supports intelligent policy optimization and agile cloud management.
- It provides open RESTful and NETCONF APIs for northbound management.
Future of NGFW
- As the volume of encrypted traffic swells, problems cannot be resolved just by improving processing performance.
- Various new attack approaches, such as using DGA malicious domain names and C&C traffic, emerge one after another, presenting a trend of three-dimensional attacks and rapidly increasing variant attacks.
- Mass attack events make security O&M analysis more and more complex.
From traditional firewalls to NGFWs, they protect against network attacks from the network layer to the application layer. In the era of big data and artificial intelligence (AI), NGFWs must evolve towards platformization and intelligence. In 2018, Huawei proposed the concept of AI firewall to implement advanced threat defense based on AI capabilities. The AI firewall continuously improves automated handling and knowledge collaboration capabilities by virtue of the big data security platform.
- Author: Wang Haoda
- Updated on: 2021-09-30
- Views: 13778
- Average rating:







