What Is a Virtual Router?
A virtual router is a software router. It is a cloud-based router deployed on VM instances of x86 hardware servers to provide routing, switching, security, VPN, and other functions through a virtualization platform and offer network communication services for users.
Why Do We Need Virtual Routers?
As enterprise services become more diversified, more and more enterprises deploy virtual private clouds (VPCs) on private or public clouds to cloudify and virtualize enterprise networks and IT infrastructure, thereby reducing network costs and implementing fast service rollout. In addition, application providers gradually provide enterprises with mission-critical applications (such as office and Salesforce) in Software as a Service (SaaS) mode on clouds. According to related statistics, 85% of enterprises will migrate their applications onto the cloud in the future.
As cloud-based services develop, applications and traffic surge. Traditional enterprise WANs cannot satisfy the requirements of enterprise infrastructure and service cloudification, and face the following challenges:
- Branches need to access cloud applications through the headquarters or data center, causing a long delay and performance bottlenecks.
- Enterprise service cloudification poses high requirements on WAN bandwidth, leading to a year-by-year increase of private line costs.
- Enterprises cannot implement consistent security and management policies on public cloud networks and enterprise internal networks.
- The traditional enterprise WAN status cannot be detected, making management and O&M difficult.
Virtual routers address these challenges and cope with trends of network device cloudification and virtualization . Virtual routers are deployed in Network Functions Virtualization (NFV) mode and can convert traditional functions that rely on hardware network devices into software that can run on existing standard hardware devices. Virtual routers save hardware costs because no dedicated hardware platform is required. Virtual routers decouple IP routing functions from specific hardware and allow the functions to be flexibly deployed on the network. Virtual routers can be deployed in the enterprise headquarters, Point of Presence (PoP), and cloud environments to extend the enterprise network to the cloud and implement consistent security and management policies on the cloud and enterprise network. In addition, virtual routers can access WANs through hybrid links, and provide application-based intelligent traffic steering for optimizing enterprises' cloud access paths and improving experience of enterprise users in accessing cloud services.
How Does a Virtual Router Work?
A virtual router works similarly to a traditional router. It runs routing protocol instances, has its own dedicated I/O ports, buffer, address space, routing table, and network management software, and connects to devices to forward data packets between networks. With the development of networks, the basic architecture of virtual routers is evolving.
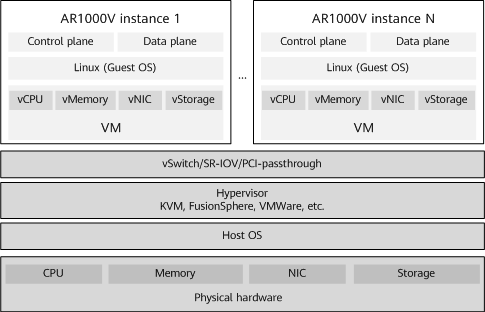
Huawei AR1000V is deployed in VNF mode. Figure 1-2 shows the system architecture of Huawei AR1000V, which consists of the following key components:
- Physical hardware and host operating system: A universal x86 hardware platform provides hardware resources such as the CPU, memory, NIC, and storage medium, and basic operating system services.
- Hypervisor: It supports mainstream virtualization platforms, such as KVM, FusionSphere, and VMware. As the intermediate software layer between physical servers and VM instances, Hypervisor manages VMs, allows multiple VM instances to share hardware resources, and isolates and protects VMs.
- vSwitch/PCI-passthrough: It enables information exchange between VM instances and between VM instances and external networks.
- VM instance: It uses the Linux operating system, has independent vCPU, memory, storage, and vNIC resources, and carries VNF instances, and provides routing, switching, security, and VPN functions.
Typical Applications of Virtual Routers
In the SD-WAN Solution, the AR1000V can function as an interworking gateway (IWG) to connect to a PoP gateway. It can also be deployed on the cloud as a cloud gateway to implement one-hop cloud access for enterprises.
Enterprise Aggregation in the SD-WAN Solution
In the SD-WAN Solution, Huawei AR1000V can be deployed as a hub at the headquarters of an enterprise or used as an aggregation node of an enterprise network. It functions as the aggregation router of an enterprise to implement interconnection and interworking between the headquarters and branches. It implements software functions using the same software platform as AR series physical routers. This ensures consistent GUIs and user experiences. The AR1000V features high forwarding performance, good scalability, and numerous VPN functions. It can be deployed with VNF instances such as the virtual firewall (vFW) and virtual WAN optimization controller (vWoC) on servers to implement multiple network functions. As such, it provides secure and reliable network services for enterprise customers and reduces network investments.
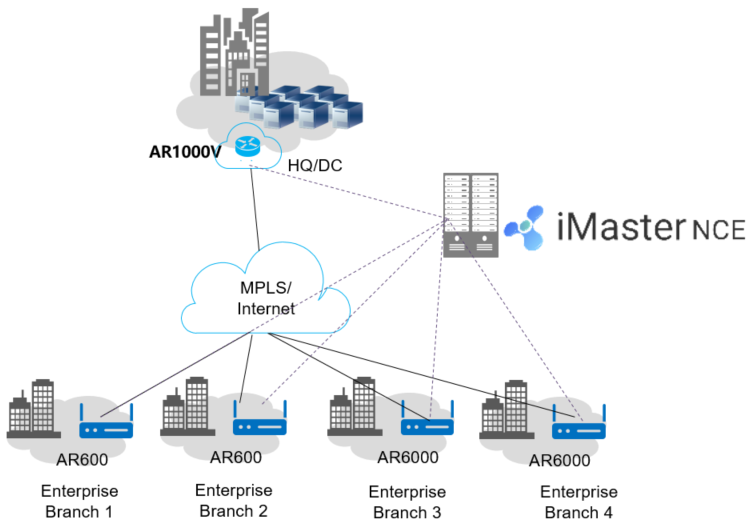
AR1000V functioning as the hub of the headquarters
Cloud Access in the SD-WAN Solution
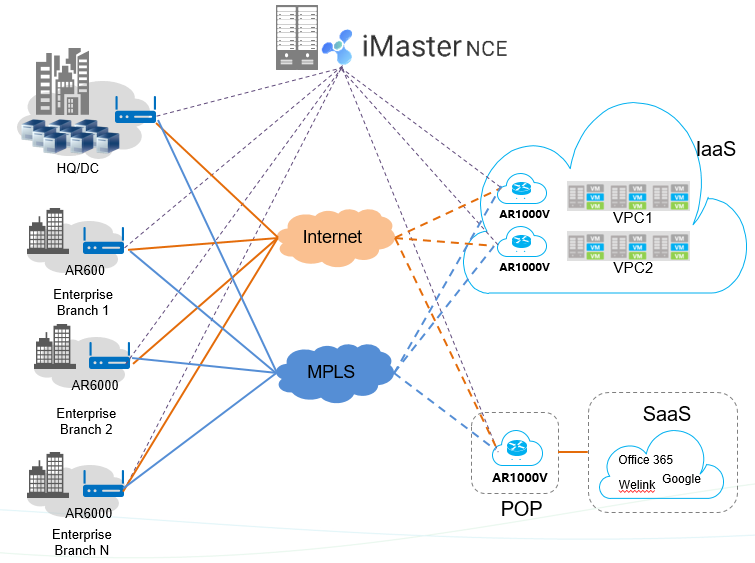
Huawei AR1000V is a software product. It is deployed on a VM as a VNF instance and functions as a virtual CPE (vCPE) on an SD-WAN network. It uses hybrid links to connect to the WAN, monitors the link status in real time, intelligently selects the optimal path based on the application and link status, optimizes cloud access paths of enterprise branches, and improves cloud access efficiency. In addition, the SD-WAN controller is deployed to implement centralized management as well as service and performance visualization and controllability, reducing WAN interconnection costs and improving O&M efficiency. Figure 3 shows the AR1000V functioning as a cloud access gateway in the SD-WAN Solution.
In the public cloud IaaS scenario, the AR1000V is deployed in a VPC of a public cloud and establishes a secure connection with the IaaS VPC of an enterprise. As a node on the enterprise network, the AR1000V extends the enterprise network to the cloud and adopts unified security, management, and QoS policies. It allows the enterprise to securely access IaaS services. In addition, cloud access traffic does not need to pass through the headquarters. This shortens the response delay, reduces the performance pressure of the hub node at the headquarters, and improves the IaaS cloud service experience.
In the public cloud SaaS scenario, the AR1000V is deployed on the server of a PoP or in the cloud environment and accesses SaaS services through the nearest PoP, improving the cloud access efficiency. Security and management policies are executed at PoPs to mitigate the security risks of enterprise branches in access to SaaS services and improve the SaaS access experience of enterprise users.
- Author: Li Jiaojiao
- Updated on: 2021-11-19
- Views: 14438
- Average rating: