What Is a Private Cloud?
A private cloud is a cloud computing service constructed exclusively for an organization. It can effectively control data, security, and quality of service. The private cloud owner has infrastructures and can control the network and application services deployed on the infrastructures. The private cloud can be built by the organization's ICT department or by a dedicated private cloud provider. The resources of the private cloud are exclusive to the owner of the private cloud.
Features and Benefits of a Private Cloud
Enterprises can deploy cloud computing services in three modes: public cloud, private cloud, and hybrid cloud. A private cloud is a dedicated cloud computing system built in an organization. The private cloud system is deployed inside firewalls of the organization's data center (DC) or is deployed in a secure hosting place to provide services only for the organization.
A private cloud has the following features and benefits:
- Security: A private cloud is exclusive to a specific organization rather than the general public. It is deployed inside the firewall of the organization. Therefore, the private cloud can provide a higher security and privacy level and forbid third party access to sensitive data.
- Guaranteed Service Level Agreement (SLA): The private cloud is usually deployed in the organization's DC. The SLA can be guaranteed when organization users access resources in the private cloud.
- Full autonomy: Private cloud customers can purchase the hardware and software as desired, while public cloud customers must use the hardware and software provided by public cloud service providers.
- Flexible customization: During private cloud construction, customers can customize computing, storage, and network resources on demand, and run their own customized software and management platforms.
Private Cloud Architecture
The following figure shows a common private cloud architecture, which includes Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and O&M platform.
- IaaS: provides computing, storage, and network resource service capabilities. Customers can flexibly select services based on their service requirements. The private cloud system needs to be simplified while meeting service requirements to reduce O&M complexity and investment costs.
- PaaS: is considered as a capability subset of the public cloud PaaS. Different from the public cloud PaaS, the private cloud PaaS provides services only for the private cloud owner and is inaccessible to third parties.
- O&M platform: Private cloud customers can use the O&M platform provided by IaaS and PaaS providers, or customize their own O&M platforms based on service characteristics.
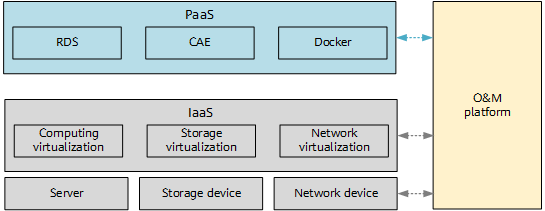
Common private cloud architecture
Comparison Between Private and Public Clouds
Overall Comparison
Compared with the public cloud, the private cloud has higher security but higher costs. In addition, the average utilization of the private cloud infrastructure is lower than that of the public cloud.
Compared with a private cloud, a public cloud has the following advantages:
- Higher flexibility and scalability: With the public cloud, customers can quickly purchase computing, storage, and network resources to cope with surging service requirements without purchasing and deploying new hardware.
- Lower costs: Most customers can use public cloud services without adding any physical infrastructure.
- Faster access to the latest technologies: In many cases, public cloud providers can provide the latest hardware and software and upgrade them more quickly.
Construction and Operation Modes
- Private cloud assets belong to the organization that builds the cloud. The organization takes the lead in building, managing, and maintaining the cloud and deploys the cloud in the DC. A private cloud requires high initial investment and a long construction and commissioning period. The O&M of the private cloud needs to be performed by the organization.
- The public cloud mode is a new IT capability consumption mode. It enables users to focus on the capabilities and SLAs of cloud services instead of paying attention to the resource locations, construction, delivery, and O&M. Users can quickly rent resources to deploy their own services, lowering the initial investment costs and shortening the service TTM. In terms of O&M, public cloud providers deliver most O&M services, and public cloud users only need to focus on their own applications.
Architecture
Generally, the IaaS and PaaS capabilities of a private cloud are part of those of a public cloud. The private cloud is constructed to meet the specific service requirements of an organization. Therefore, only the IaaS and PaaS capabilities required by the organization need to be deployed. For example, if the organization uses only the VM service rather than the BMS service, the BMS service does not need to be deployed in the private cloud.
In addition to IaaS and PaaS, the public cloud also provides SaaS, operation, and other key capabilities.
- A public cloud typically provides the SaaS capability, which however may not be deployed in a private cloud. If the SaaS software is deployed in a private cloud, the private cloud owner needs to consume a vast number of resources to maintain the SaaS software. As such, the use of the SaaS capability in a private cloud causes high costs. Actual SaaS deployment depends on the customer's requirements in terms of security, cost, maintenance, and so on no matter whether SaaS is deployed in a public, private, or hybrid cloud.
- A private cloud does not involve operation because the use of the private cloud is not charged within the organization. A public cloud must provide the operation capability because the public cloud provider needs to charge users in various modes.
Service Type
- Core services and services requiring high information security levels of an organization are deployed in the organization's private cloud.
- Non-core services, services that require fast iteration, and external services are deployed in the public cloud.
The following table lists the differences between the public and private clouds.
Item |
Public Cloud |
Private Cloud |
|---|---|---|
User type |
Startups, small enterprises, and individuals |
Government agencies and large enterprises |
Service type |
External services |
Internal services |
Security |
Security isolation among hosts |
Security isolation at the network layer |
Cost |
The cost is low at the initial stage and gets higher with the growth of service volume. |
The initial cost is high. As the service volume increases, the average cost becomes low. |
Customization |
Rarely customized |
Flexibly customized and can be integrated with legacy systems |
Technical architecture |
Self-developed architecture, focusing on distributed and large clusters |
Open-source architecture, focusing on high availability and flexibility |
Compatibility |
Services are modified based on public cloud requirements. |
Proactive compatibility with and adaptation to the organization's services |
O&M |
O&M is performed by public cloud service providers in a unified manner. |
O&M is performed by the organization or a third party. |
Private Cloud Service Providers
Large-scale private cloud service providers in China include:
- Huawei
- H3C
- Huayun
- China Telecom
- China Unicom
- Author: Zhang Fan
- Updated on: 2021-12-06
- Views: 4312
- Average rating:







