What Is Route Monitoring Group?
Route monitoring groups monitor the connectivity of network-side IPv4 routes, and their status is associated with IPv4 static routes. By leveraging route monitoring groups, access-side service modules can perform active/standby link switchovers upon changes to the connectivity status of network-side IP routes, preventing network congestion or traffic loss.
Why Do We Need Route Monitoring Group?
To improve network reliability, device-level redundancy is used on live networks. This involves two devices that back up each other and operate in load balancing mode. If one device fails, the other device takes over services from the faulty device. Inter-device link reliability and load balancing issues need to be resolved when one device is dual-homed to two devices that operate in active/standby mode.
In a two-node hot standby scenario, if some or all network-side links fail, the bandwidth of the network-side links decreases accordingly. Network congestion or traffic loss will occur if the access side cannot promptly detect link failures. To prevent these problems from arising, you can configure a route monitoring group and associate its status with the status of IPv4 static routes. This allows status changes of network-side routes to trigger switching between the active and standby links of access-side service modules.
What Are Application Scenarios of Route Monitoring Group?
Preventing Network Congestion
On the network shown in the following figure, AGG_Switch_A and AGG_Switch_B back up each other, and several ACC_Switches are dual-homed to the two AGG_Switches to implement load balancing. If some network-side links between AGG_Switch_A and the core network fail, the available bandwidth of links between them decreases accordingly. However, ACC_Switches cannot detect link failures and still forward packets destined for the core network to AGG_Switch_A. In this scenario, congestion will occur on the links between AGG_Switch_A and the core network.
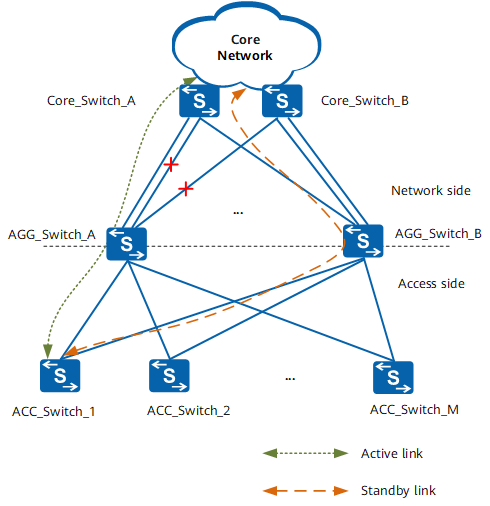
Typical networking diagram of route monitoring groups
Preventing Traffic Loss
On the network shown in the following figure, AGG_Switch_A and AGG_Switch_B back up each other, and several ACC_Switches are dual-homed to the two AGG_Switches to implement load balancing. If all the links between AGG_Switch_A and the core network fail, only the links between AGG_Switch_B and the core network are available on the network side. However, ACC_Switches cannot detect link failures and still forward packets destined for the core network to AGG_Switch_A. In this scenario, the packets transmitted from ACC_Switches are lost because all the links between AGG_Switch_A and the core network are unavailable.
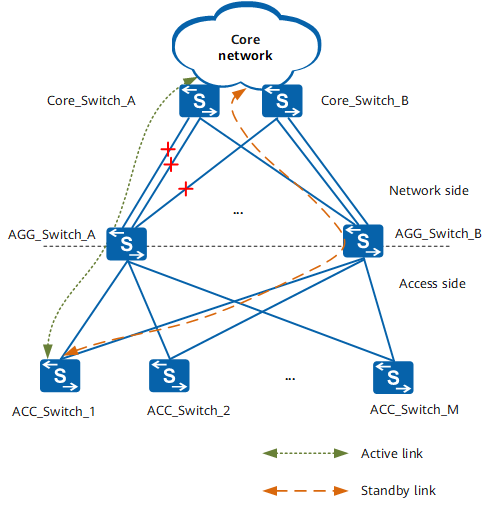
Typical networking diagram of route monitoring groups
How Does Route Monitoring Group Work?
Monitored routes of the same type on the network side can be added to a route monitoring group. Each route monitoring group is identified by a unique name. The status of a route monitoring group depends on the status of its member routes. Service modules will switch links if the status of the route monitoring group changes.
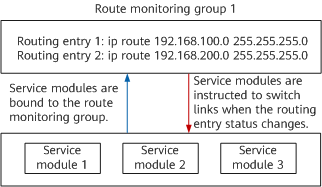
Route monitoring group workflow
A route monitoring group monitors the status of all its member routes. You can set the logical relationship between the monitored routes in a group to AND or OR.
- When the logical relationship between the monitored routes in a route monitoring group is set to AND, the group status changes to Down as long as one route in the group goes Down. The route management (RM) module then instructs the service modules to switch links.
- When the logical relationship between the monitored routes in a route monitoring group is set to OR, the group status only changes to Down when all the routes in the group go Down. The RM module then instructs the service modules to switch links.
- Author: Gu Suqin
- Updated on: 2021-09-30
- Views: 2717
- Average rating:






