What Is SPN FGU?
Inheriting the highly efficient Ethernet kernel of SPN, SPN Fine Granularity Unit (FGU) provides low-cost, refined, and hard-isolated FGU transport pipes by integrating fine-grained slicing into the SPN architecture. Specifically, FGU refines the granularity of hard slicing from 5 Gbit/s to 10 Mbit/s to meet differentiated transport requirements (such as small bandwidth granularity, high isolation, and high security) of 5G vertical industry applications and private line services. This technology will become a key force in accelerating their deployment.
Why Is SPN FGU Needed?
5G construction is in full swing toady, and vertical industry applications — such as those in the electric power, transportation, government, and financial sectors — have become the focus of the 5G industry chain. For these vertical industries, carriers need to create multiple isolated virtual networks on the public physical network infrastructure. These virtual networks must be able to provide isolation of different levels and run independently, with their lifecycles also being able to be managed independently. To securely transmit various services of different industries, SPN hard-isolated slicing technology can be used.
As 5G vertical industry applications evolve from single scenarios to systematic and complex scenarios and computing networks gain popularity, industry user requirements are becoming increasingly different and application scenarios more complex. Along with this, massive data and efficient computing bring about a large number of transport requirements for deterministic latency, high-security, and bandwidth of 1 Gbit/s or lower. In addition, a large number of government, financial, and large enterprise private line services also pose different requirements on the slice isolation degree and granularity of SPN.
According to the survey in the SPN FGU Technical White Paper released at the OptiNet China Conference 2021, the minimum bandwidth required by 5G vertical industries (including computing services) and government and enterprise private lines can be 2 Mbit/s, and services requiring bandwidth of less than 10 Mbit/s account for a large proportion. The granularity of existing slicing technologies, however, is usually at the Gbit/s level. This means a bandwidth waste when services that require only a small-bandwidth granularity are being transported. In addition, as the number of such services increase, the overall network bandwidth they require increases accordingly. In this context, FGU slicing that more closely matches service bandwidth requirements becomes a preferred SPN technology.
SPN FGU integrates fine-grained slicing into the SPN architecture, providing low-cost, refined, and hard-isolated FGU transport pipes.
What Are the Advantages of SPN FGU?
SPN FGU inherits the SPN technology architecture while making only some enhancements at the Slicing Packet Layer (SPL), Slicing Channel Layer (SCL), and Slicing Transport Layer (STL), as shown in the following figure.
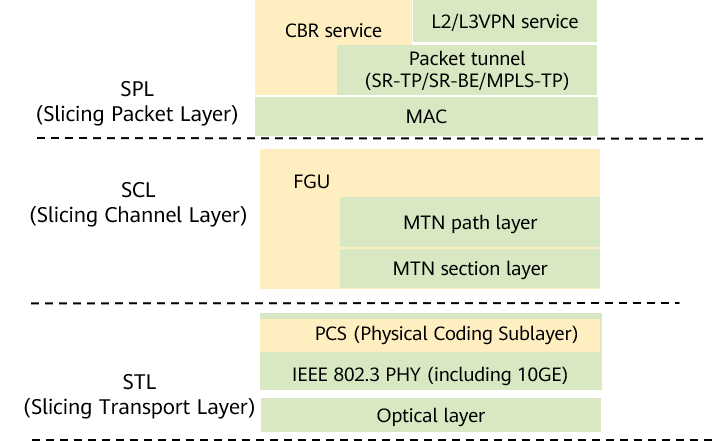
SPN architecture that supports FGU
- SPL: newly supports the Constant Bit Rate (CBR) service type. The SPL layer provides fine-grained CBR service mapping based on E1, STM-1, and the like, implementing full-process timeslot switching from the ingress to egress and ensuring hard service isolation.
- SCL: newly supports the FGU layer to provide 10 Mbit/s hard slicing for services. The FGU layer is an independent sublayer and decoupled from the service layer. It can be flexibly carried over the MTN path layer, MTN segment layer, or Ethernet physical layer as required.
- STL: newly supports 10GE ports for industry applications in addition to supporting SPN-defined high-speed Ethernet physical-layer interfaces, such as 50GE, 100GE, 200GE, and 400GE. The Ethernet Physical Coding Sublayer (PCS) uses 64/66B blocks that are compliant with the requirement of the Ethernet bottom-layer protocol stack to ensure seamless compatibility between FGU and this protocol stack.
SPN hard slicing is unaware of and does not identify service packet data or change user packet data. FGU inherits this characteristic. It allows packets to be transparently transmitted in FGU hard slices, thereby implementing compatibility with packet technologies.
In addition, SPN FGU maximally reuses existing technologies while simplifying the processing mechanism. It is applicable to multiple types of devices, such as CPEs, hubs, access devices, aggregation devices, and core devices, enabling E2E FGU deployment on live networks.
Huawei's existing SPN devices on live networks can smoothly support FGU functions through software upgrades and insertion of FGU processing boards. Huawei's newly developed compact SPN devices natively support FGU slicing, SDN management and control, and standard southbound interfaces, without the need for any additional operation. This means that they can seamlessly interconnect with all series of devices on an SPN transport network.
Furthermore, the SPN Mbit/s-granularity slicing technology improves FGU OAM, slice timeslot, and bandwidth adjustment mechanisms. It offers the following technical advantages:
- High security: FGU channels exclusively use specified timeslots to provide strict TDM features. The timeslots of the egress and ingress ports on any node of a channel are allocated and fixed in advance at the management and control layer. This ensures hard isolation while improving service and computing data security.
- High reliability: FGU OAM is compatible with SPN/MTN path OAM and provides E2E OAM monitoring capabilities for each FGU channel. Users are unaware of OAM insertion and extraction. Furthermore, 1+1 protection for FGU channels meets carrier-class switching performance requirements in scenarios involving device power-off and link faults.
- Deterministic latency: E2E non-blocking timeslot switching achieves nanosecond-level service jitter and ensures stable service transmission latency.
- Hitless slice bandwidth adjustment: The comprehensive timeslot and bandwidth adjustment mechanism ensures zero packet loss of existing services when the timeslots and bandwidth of an FGU slice decrease or increase.
Where Can SPN FGU Be Used?
5G Vertical Industry Scenario
As the basic enabler of 5G vertical industries, network slicing can ensure SLAs of different industries and services as well as service security, reliability, and software and hardware isolation. Control services in 5G vertical industries require networks to provide low latency and high reliability. This is where SPN FGU comes in. It will become a key force in facilitating the deployment of 5G vertical industry applications.
Take the electric power industry as an example. To match the power security requirements of "secure partitioning, dedicated networks, horizontal isolation, and vertical authentication", power grid services can be divided into four zones based on security partitions: production control service zone (security partition I), production non-control service zone (security partition II), production management service zone (security partition III) and management information service zone (security partition IV). The following table lists the typical service examples of each partition.
Electric Power Security Partition |
Typical Service |
|---|---|
Production control service zone (security partition I) |
Energy management, wide-area phasor measurement, power distribution automation, and substation automation |
Production non-control service zone (security partition II) |
Fault recording information management and energy metering |
Production management service zone (security partition III) |
Dispatch/production management, construction site monitoring, robot inspection, drone inspection, smart power distribution room, and smart quality control |
Management information service zone (security partition IV) |
The following table lists the key communication indicators of production control services in 5G smart grid scenarios.
Application Scenario |
E2E One-Way Latency |
Bandwidth |
Reliability |
|---|---|---|---|
Distributed power distribution automation |
≤ 15 ms |
2 Mbit/s to 10 Mbit/s |
99.999% |
Centralized power distribution automation (from terminals to the main station) |
≤ 50 ms |
< 2 Mbit/s |
99.999% |
Power Monitoring |
≤ 50 ms |
10 Mbit/s |
99.999% |
Precise load control |
≤ 50 ms |
10 kbps to 2 Mbps |
99.999% |
To meet the network security requirements of the electric power industry, 5G transport networks need to be constructed following the three-layer (access, aggregation, and core) network architecture, and E2E MTN slices need to be deployed to implement hard service isolation. Specifically, grid services requiring high security, high reliability, and ultra-low latency are carried by independent network slices through the MTN hard isolation technology; services requiring a small-bandwidth granularity are carried using the 10 Mbit/s FGU technology.
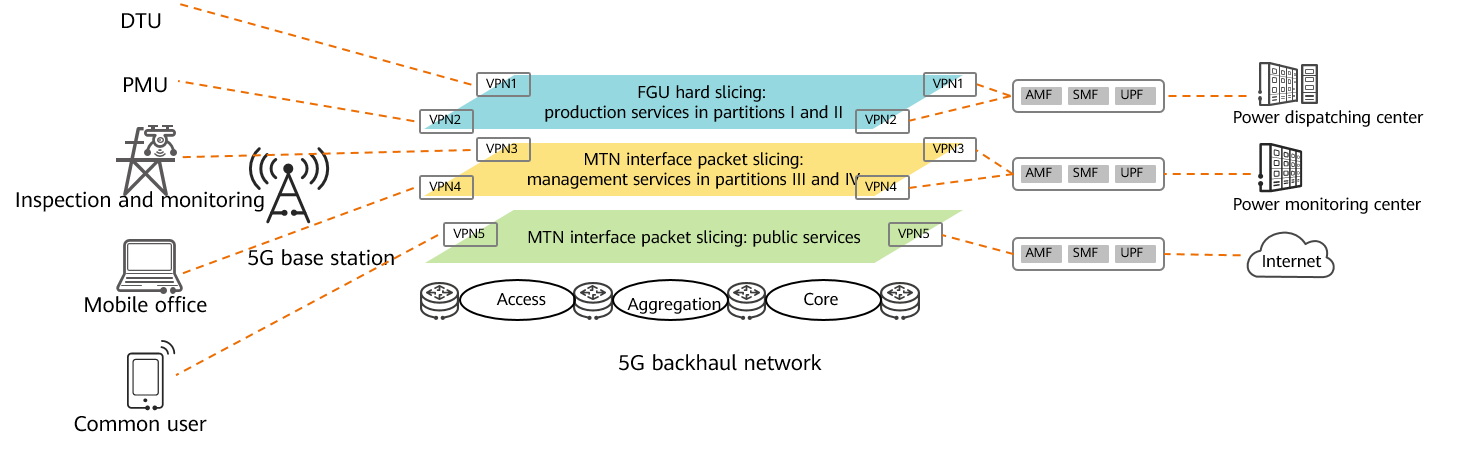
FGU used in 5G smart grid scenarios
Government and Enterprise Private Line Scenarios
Government and enterprise private lines mainly used by important customers, such as government departments, financial institutions, and large enterprises. Their service requirements vary significantly.
The following table lists their requirements on networks.
Scenario |
Private Line |
Typical Application |
Network Requirement |
|---|---|---|---|
Government and enterprise private line |
Government private line services |
Government information transmit, video conferencing, and video surveillance |
High security, high reliability, and strict isolation |
Premium financial private line services |
Financial transaction services |
Security, reliability, ultra-low latency, and flexible connection |
|
Premium private line services for large enterprises |
Cloud services, voice/video, office, and production |
High security, flexible connection, and convenient access |
As a comprehensive transport network, the 5G backhaul network can use FGU channels with the TDM hard isolation feature to carry private lines of government and financial customers and some large enterprises, use MTN interface packet slicing to carry enterprise private lines without hard isolation requirements, and use a combination of soft and hard slicing technologies to provide differentiated private line services.
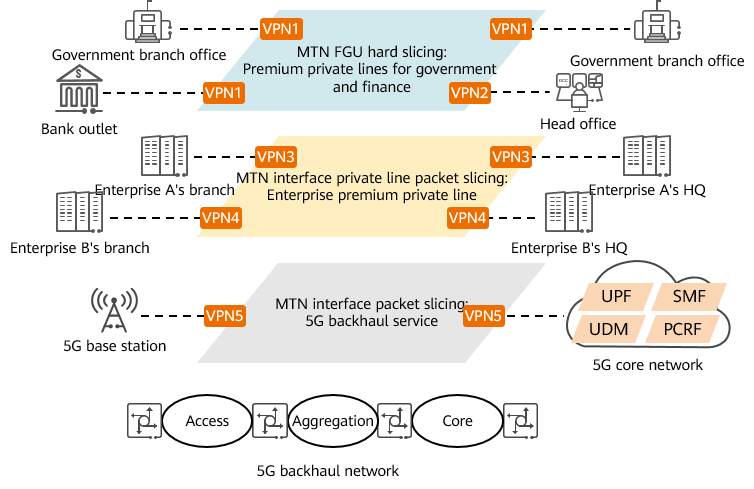
FGU application in government and enterprise private lines
- Author: Xilv Li
- Updated on: 2022-08-05
- Views: 2273
- Average rating:







