What Is Smart Policy Routing?
Smart policy routing (SPR) is a route selection mechanism that proactively detects link quality and selects the optimal link to forward service data according to service quality requirements, implementing intelligent traffic steering.
SPR protects user services from being affected by network quality, ensuring user experience.
Why Do We Need SPR?
As network services become increasingly diverse, it is vital to guarantee link quality. Against this backdrop, users are shifting their focus from network connectivity to service availability, such as service response speed and service quality. But such factors cannot be guaranteed using conventional routing protocols, which are unable to detect the link quality. Such routing protocols only care that a route is reachable, not whether the corresponding link is poor in quality or even unable to forward packets. This can affect or even fully interrupt services. SPR overcomes these challenges by proactively detecting link quality and selecting the optimal link to forward service data. This minimizes the impact of network quality on user experience.
How Does SPR Work?
Using the link quality detection function, a device monitors the delay, jitter, packet loss rate, and composite measure indicator (CMI) of service links in real time. Different services have different requirements on these indicators, and you only need to set thresholds for those that the service has high requirements on. If any of the set indicators reaches its threshold, link switchover is triggered. The following figure shows the traffic steering process.
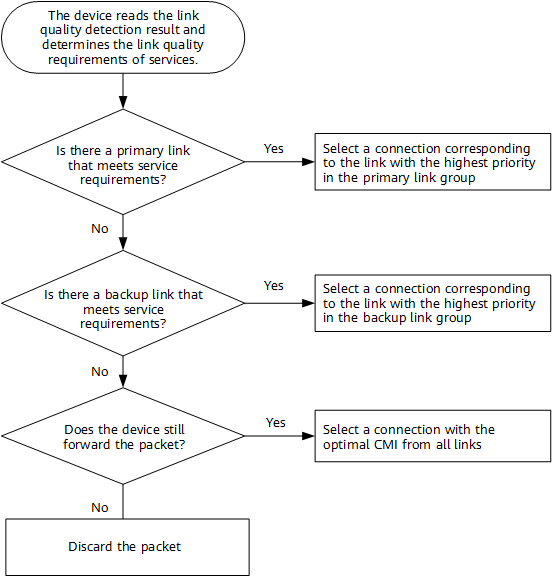
Traffic steering process
If no link is available, the device uses an ordinary route to forward traffic.
Application of SPR
As shown in the following figure, an enterprise branch connects to a data center over two Internet service provider (ISP) networks (ISP1 and ISP2), and a 3G outbound interface is configured to provide an emergency link. RouterA connects to ISP1 through the link group named group1 and connects to ISP2 through the link group named group2. ISP1 provides high-quality network services, which are expensive; ISP2 provides cost-effective network services with relatively low quality. The branch exchanges voice, video, FTP and HTTP services with the data center. As voice and video services require high link quality, group1 and group2 function as the primary and backup link groups respectively for them. As FTP and HTTP services do not have high requirements on link quality, group2 and group1 function as the primary and backup link groups respectively for them.
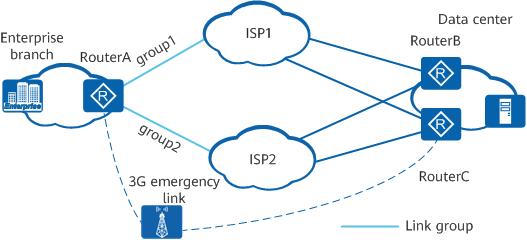
Network diagram of SPR
An SPR-enabled device performs the following operations to process voice and video services:
- When link quality provided by group1 cannot meet voice and video service requirements but link quality provided by group2 does, the SPR-enabled device switches voice and video services to group2 after the flapping suppression timer expires.
- If group1 meets service requirements again, the SPR-enabled device switches services back to group1 after the flapping suppression timer expires and an additional switchover period elapses.
- If both group1 and group2 cannot meet service requirements later but group1 provides better link quality than group2, the SPR-enabled device switches services back to group1 after the flapping suppression timer expires and an additional switchover period elapses.
- If group2 cannot meet service requirements later but provides better link quality than group1, the SPR-enabled device continues to use group2 to transmit services.
- When the link quality provided by both group1 and group2 cannot meet voice and video service requirements but their links are available, the SPR-enabled device selects the link with the optimal CMI from all links in group1 and group2 to transmit services.
- When all links in group1 and group2 are unavailable, the SPR-enabled device uses the 3G emergency link to transmit services.
- Author: Tang Dandan
- Updated on: 2021-09-30
- Views: 3313
- Average rating:






