What Is DCI?
Data Center Interconnect (DCI) enables multiple data centers to communicate with each other. Data centers are important infrastructure for digital transformation, and as cloud computing, big data, and artificial intelligence continue to develop, enterprise data centers are becoming increasingly popular. To meet requirements such as cross-region operations, user access, and remote disaster recovery, increasingly more organizations and enterprises are deploying multiple data centers in different regions. This gives rise to the need for data center interconnection. Huawei's CloudFabric solution uses key technologies such as VXLAN and EVPN to provide two DCI solutions: E2E VXLAN and segment VXLAN.
What Is a Data Center?
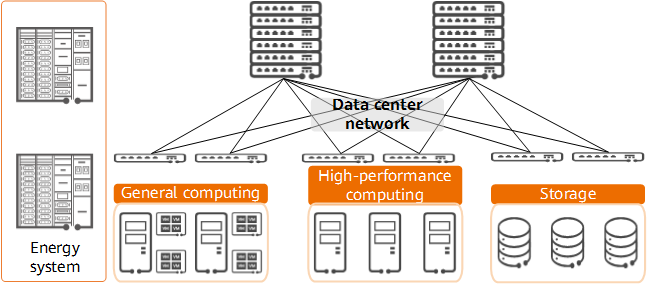
As industry digital transformation continues to develop, data has become a key production factor. Data centers, which are responsible for data computing, storage, and forwarding, are the most critical digital infrastructure in the new infrastructure initiative. A modern data center comprises the following core components:
- Computing system, including general-purpose computing modules used for service deployment and high-performance computing modules that provide super computing power
- Storage system, including the mass storage module, data management engine, and dedicated storage network
- Energy system, including the power supply module, temperature control module, and IT management module
- Data center network, which connects general-purpose computing modules, high-performance computing modules, and storage modules in the data center for data exchange
Composition of a data center
User services are directly deployed on general-purpose computing modules, which rely on large numbers of servers as their basic physical units. The data center network functions like arteries in a human body to transmit data between servers in a data center.
Why Is DCI Required?
Data center construction is becoming a growing trend among various organizations and enterprises. However, one data center alone cannot meet service requirements in the new era. Interconnection between multiple data centers is in urgent need due to the following reasons.
Rapid Service Growth
At present, emerging services such as cloud computing and intelligence are developing rapidly, and related applications are growing rapidly in number. These applications depend heavily on data centers, giving rise to the rapid expansion of services carried by data centers. As such, the resources provided by a single data center will soon become insufficient. Limited by factors such as footprint and energy supply, a single data center cannot be expanded infinitely. When services grow to a certain scale, multiple data centers need to be constructed in the same city or different cities. In this case, multiple data centers need to be interconnected to collaboratively support services.
Against the backdrop of economic digital transformation, enterprises in the same industry or different industries often need to share data and cooperate with each other at the data layer to achieve joint business success. This also requires interconnection between the data centers of different enterprises.
Cross-regional User Access Becoming the Norm
In recent years, data centers have shifted focus from web services to cloud and data services. The user scope of related organizations and enterprises is no longer restricted by regions. In particular, with the increasing popularity of the mobile Internet, users want high-quality services anytime and anywhere. To meet the preceding requirements and further improve user experience, enterprises often build multiple data centers in different regions if conditions permit to facilitate the nearby access of cross-region users. This requires service deployment across data centers and interconnection between multiple data centers.
Cross-regional user access
Rigid Requirements for Remote Backup and Disaster Recovery
Nowadays, people rely more and more heavily on various application systems in daily work. The continuity of these application systems depends on the stable running of data center systems. Furthermore, data security, service reliability, and service continuity are drawing increasingly more attention, and backup and disaster recovery have become rigid requirements. The real-world environment is full of uncertainties and risks. Given the vast amount of uncertainties and risks in today's world, data centers face various potential threats, such as natural disasters, accidents, and human-crafted attacks. One solution aimed at improving service continuity, robustness, and data reliability and availability is to deploy multiple data centers in different cities. This is an effective solution and one that has been widely recognized in the industry. To deploy backup and disaster recovery solutions between different data centers, you first need to interconnect these data centers.
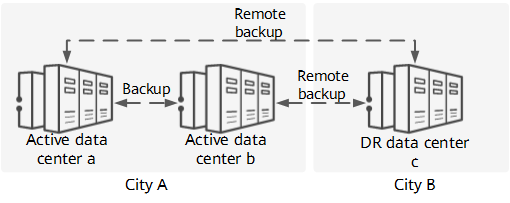
Remote backup and disaster recovery
Trends of Data Center Virtualization and Resource Pooling
As the cloud computing business model reaches maturity, various applications and traditional IT services are being cloudified, and cloud services are becoming a new driver of revenue. As such, the transformation from traditional data centers to cloud data centers has become a mainstream trend. Virtualization and resource pooling are key features of a cloud data center, in which the core idea is to change the minimum functional unit of a data center from a physical host to a virtual machine (VM). VMs are irrelevant to physical locations, and their resource usage can be flexibly adjusted. In addition, VMs can be freely migrated across servers and data centers to integrate resources within a data center or across data centers. This helps form a unified resource pool and significantly improves resource utilization flexibility and efficiency. Because interconnection between data centers is the prerequisite for VM migration across data centers, DCI is also an important part of data center virtualization and resource pooling.
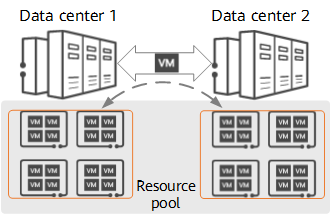
Virtualization and resource pooling
What DCI Solutions Are Available?
To better meet the requirements of cloud data centers, Huawei provides the CloudFabric solution. This solution consists of Huawei's data center switches (CloudEngine series), data center controller (iMaster NCE-Fabric), intelligent network analysis platform (iMaster NCE-FabricInsight), and security solution (HiSec). It offers customers a simplified operation experience throughout the lifecycle of cloud data center networks and provides the following two recommended DCI solutions.
E2E VXLAN Solution
In E2E VXLAN tunnel-based DCI, the computing and network resources of multiple data centers are in the same resource pool and centrally managed by a cloud platform and a set of iMaster NCE-Fabric. These data centers form a unified E2E VXLAN domain, and the user Virtual Private Clouds (VPCs) and subnets can be deployed across data centers while allowing service interworking. The following figure shows the deployment architecture.
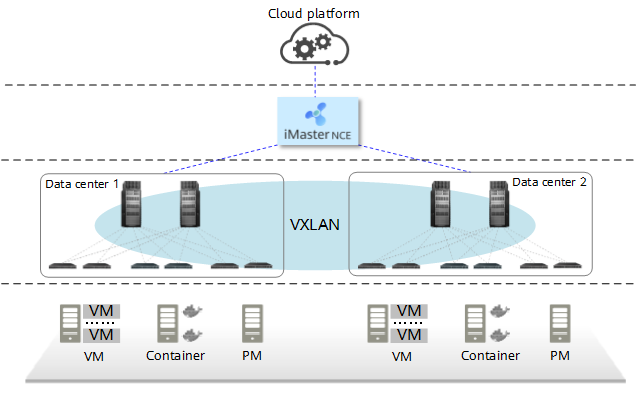
E2E VXLAN solution architecture
In this solution, an E2E VXLAN tunnel must be established between data centers. As shown in the following figure, the data centers must be routable to each other on the underlay network and have EVPN deployed between their leaf nodes on the overlay network. The leaf nodes at both ends use EVPN to discover each other and use EVPN routes to transmit VXLAN encapsulation information to each other, triggering E2E VXLAN tunnel establishment.
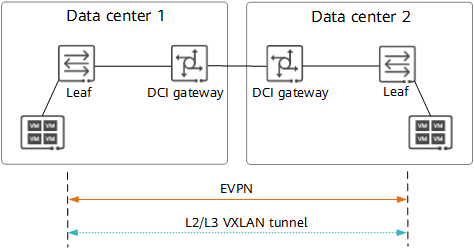
E2E VXLAN tunnel
This solution mainly applies to scenarios with multiple points of delivery (PODs). A POD is a group of relatively independent physical resources. In a multi-POD scenario, one set of iMaster NCE-Fabric manages multiple PODs, and these PODs form an E2E VXLAN domain. Specifically, this solution applies to scenarios where small-scale data centers are deployed close to each other in the same city.
Segment VXLAN Solution
In segment VXLAN tunnel-based DCI, the computing and network resources of each data center belong to independent resource pools and are independently managed by the corresponding cloud platform and iMaster NCE-Fabric. Each data center is an independent VXLAN domain, and these data centers can communicate with each other only after a DCI VXLAN domain is established between them. Moreover, the VPCs and subnets of each user are deployed in the corresponding data center. As a result, service interworking between data centers requires unified orchestration by an upper-layer cloud management platform. The following figure shows the deployment architecture.
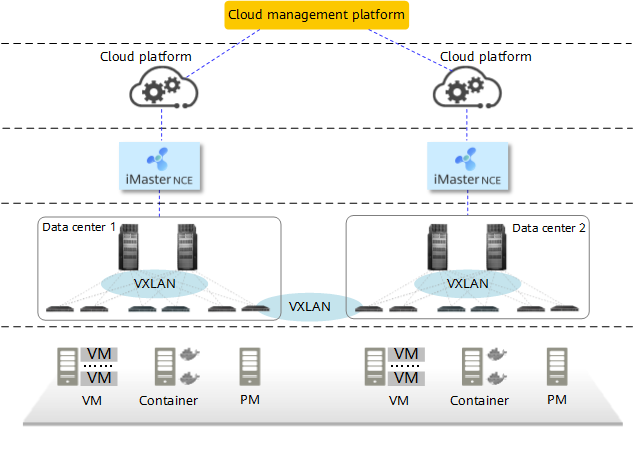
Segment VXLAN solution architecture
In this solution, VXLAN tunnels must be established within and between data centers. As shown in the following figure, the data centers must be routable to each other on the underlay network and have EVPN deployed between the leaf node and DCI gateway in each DC and between the DCI gateways in different data centers on the overlay network. The related devices use EVPN to discover each other and use EVPN routes to transmit VXLAN encapsulation information to each other, triggering segment VXLAN tunnel establishment.
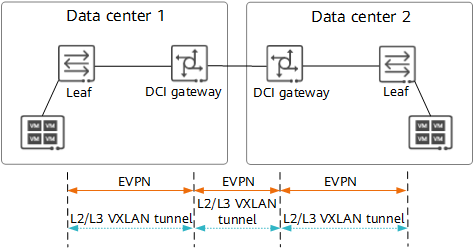
Segment VXLAN tunnel
This solution mainly applies to multi-site scenarios where interconnection is required between data centers that cannot be managed by the same set of iMaster NCE-Fabric (due to being located in different regions or are far away from each other).
What Are the Key Technologies Required for DCI?
As described in the previous section, VXLAN and EVPN are the key technologies used by Huawei's CloudFabric solution to interconnect data centers.
VXLAN is essentially a tunneling technology and can be used to build a Layer 2 virtual network over any network with reachable routes. VXLAN uses VXLAN gateways to implement communication within a VXLAN network and between VXLAN and non-VXLAN networks. VXLAN uses the MAC-in-UDP encapsulation technology to extend Layer 2 networks, encapsulating Ethernet packets into IP packets and transmitting these IP packets over IP routes. Intermediate devices do not need to be aware of VM MAC addresses. Moreover, an IP routing network is free of network structure limitations and has large-scale scalability, allowing VMs to be flexibly migrated regardless of the network architecture. For more information about the VXLAN technology, see VXLAN.
EVPN is a next-generation all-service bearer VPN solution. It unifies the control planes for various VPN services and uses BGP extensions to transmit Layer 2 or Layer 3 reachability information, separating the forwarding plane from the control plane. With the in-depth development of data center networks, EVPN and VXLAN are gradually converging. For example, VXLAN makes up for its lack of a control plane by using EVPN as the control plane, and EVPN uses VXLAN tunnels as public network tunnels to adapt to more scenarios, such as DCI. For more information about the EVPN technology, see EVPN.
- Author: Guo Fenghai
- Updated on: 2021-09-30
- Views: 5620
- Average rating: