What Is Edge Computing?
Edge computing, a distributed open platform integrating core capabilities of network, computing, storage, and application, provides edge intelligence services at the network edge close to devices or data sources. To put it simply, edge computing directly analyzes data collected from terminals at or near the device or network where data is generated. This eliminates the need to transmit data to the cloud data processing center.
Why Do We Need Cloud Computing?
With the rapid development of loT technology, more and more common objects with independent functions are interconnected. IoT enables a massive, ever-growing number of industry terminals to be connected through networks, accelerating digital transformation across industries.
However, IoT is a huge and complex system, with application scenarios varying according to industry. Statistics from third-party analysis organizations indicate that there will be more than 100 billion devices connected to the Internet and the device data volume will reach 300 ZB by 2025. In the traditional data processing mode, all obtained data needs to be transmitted to the cloud computing platform for analysis. Due to such a vast amount of data, the cloud computing platform faces the following challenges: high network latency, large number of devices to be connected, difficult processing of massive data, insufficient bandwidth, and high power consumption.
This is where edge computing comes in. Edge computing, a distributed open platform integrating core capabilities of network, computing, storage, and application, provides edge intelligence services at the network edge close to devices or data sources. To put it simply, edge computing directly analyzes data collected from terminals at or near the device or network where data is generated. This eliminates the need to transmit data to the cloud data processing center.
Edge Computing vs. Cloud Computing
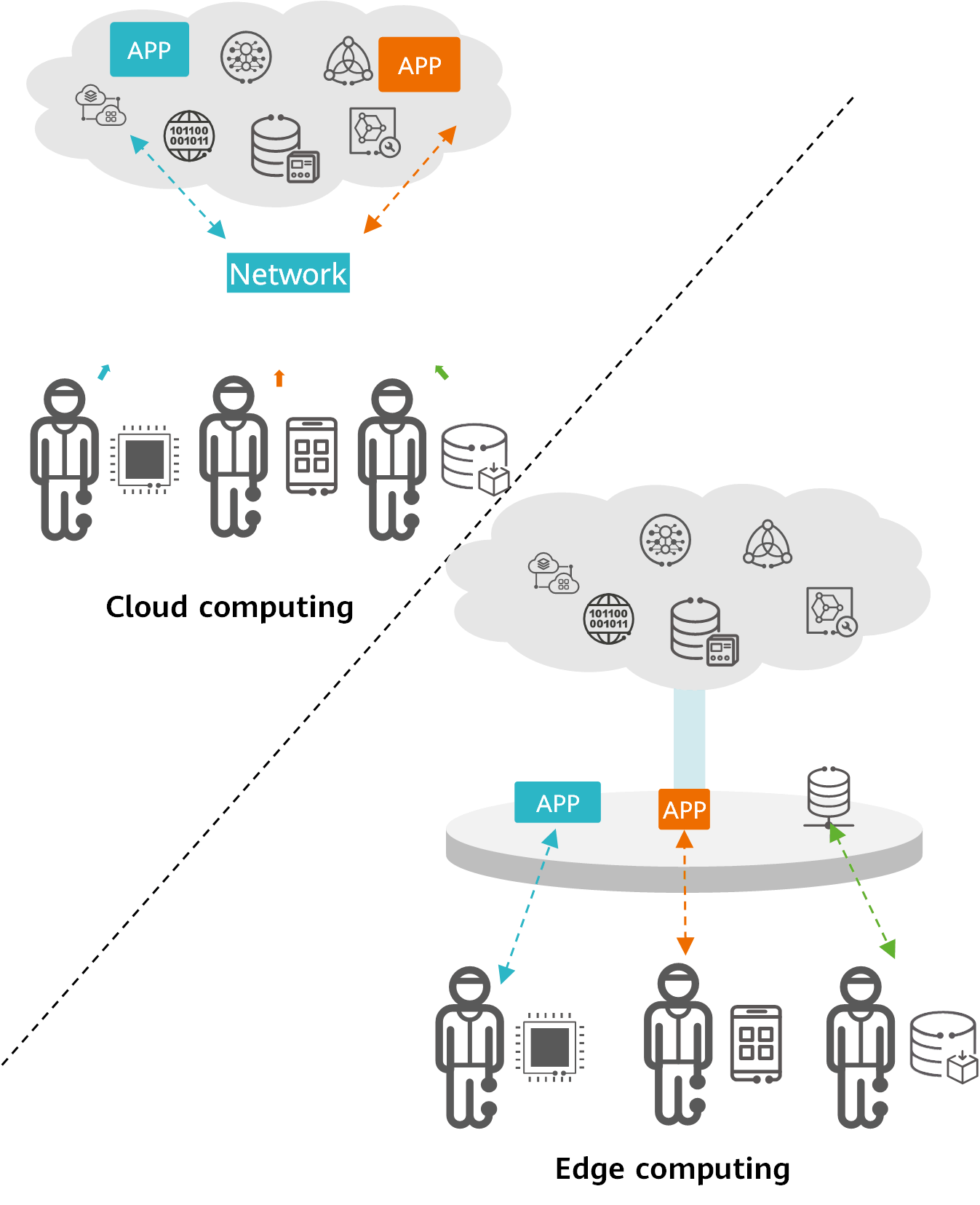
Edge computing is a concept relative to cloud computing. Cloud computing uploads all data to the computing resource-intensive cloud data center (DC) or servers for processing, and all requests for access to the data must be transmitted to the cloud.
The explosive growth of data brought about by IoT magnifies these disadvantages of cloud computing:
- Cloud computing cannot efficiently process increasingly massive volumes and sources of data.
With the integration between the Internet and various industries, especially after the popularization of IoT, the demand for computing power is increasing exponentially, which is beyond the current processing capability of the traditional cloud computing architecture.
- Cloud computing cannot implement real-time data processing.
In the traditional cloud computing architecture, terminals collect IoT data and then transmit the data to the cloud computing cluster in a faraway DC. The computing cluster then sends back the result. This inevitably results in a long response time. However, some emerging application scenarios, such as unmanned driving and smart mining, have demanding requirements on the response time. As such, cloud computing is unsuitable for them.
Edge computing can solve these problems to some extent. As shown in flowing figure, data generated by IoT terminals does not need to be transmitted to remote cloud DCs for processing. Instead, data is analyzed and processed at the network edge, which is more efficient and secure than cloud computing.
Edge Computing vs. Cloud Computing
Item |
Edge Computing |
Cloud Computing |
|---|---|---|
Calculation method |
Distributed computing, focusing on real-time and short-period data analysis |
Centralized computing, depending on cloud DCs |
Processing location |
Close to data-generating terminals or loT gateways |
Cloud DC |
Latency |
Low latency |
High latency |
Data storage |
Only useful information is transmitted to the remote end. |
All collected information is stored. |
Deployment cost |
Low |
High |
Privacy and security |
Relatively high privacy and security |
Relatively low privacy and security, which calls special attention |
How Does Edge Computing Work?
The figure shows the edge computing architecture. In this architecture, data is processed near terminals without the need of transmitting data to the centralized cloud computing center for processing.
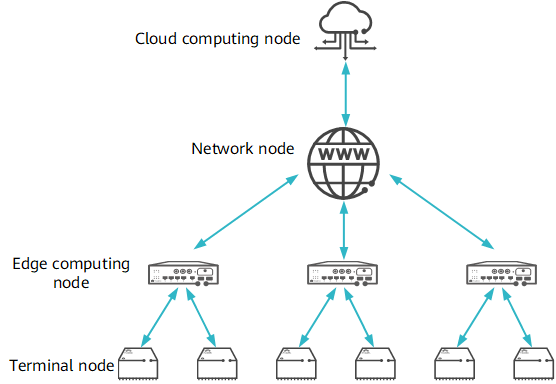
Edge computing architecture
- Terminal: The terminal layer consists of various loT devices, such as sensors, RFID tags, cameras, and smartphones, which collect and report raw data. At this layer, IoT devices need to provide only sensing capabilities but not computing capabilities.
- Edge computing node: Edge computing nodes enable the response to basic services by properly deploying and allocating the computing and storage capabilities at the network edge.
- Network node: A network node uploads useful data obtained through edge computing nodes to cloud computing nodes for analysis and processing.
- Cloud computing node: The data reported by the edge computing layer is permanently stored on cloud computing nodes. The analysis tasks and comprehensive processing tasks beyond the capabilities of edge computing nodes are still processed by cloud computing nodes. In addition, cloud computing nodes dynamically adjust the deployment strategies and algorithms at the edge computing layer based on the network resource distribution.
Typical Applications of Edge Computing
Edge computing features more real-time data processing and quicker response and therefore is ideal for the loT field. loT gateways with edge computing abilities (known as EC-IoT gateways) deployed near network edge nodes provide services such as device management and control to resolve the "last mile" problem in loT communication. This implements smart connection and efficient management of loT devices.
The figure shows the edge computing IoT architecture. Designed for the industrial IoT field, edge computing supports a wide range of industrial protocols and IoT interfaces, making it ideal for device connection scenarios across industries. The open edge computing capabilities and cloud management architecture meet the intelligent data processing requirements of different industries:
- Connectivity: EC-IoT gateways offer diverse IoT interfaces, for example, IP-based Power-line Communication (PLC), radio frequency (RF), RS485, and RS232, for connecting to sensors and terminals, enabling massive numbers of terminals to connect to IoT networks.
- Cloud-based management: Using cloud computing technologies and Huawei's loT platform, customers can implement centralized cloud-based management of edge IoT resources (such as networks, devices, containers, and applications). Additionally, the platform offers open northbound application programming interfaces (APIs) to support flexible integration with other industry application systems.
- Customization of industry applications: The IoT platform provides standard open APIs for integration with partners' industry application systems, extending its adaptability across industries and enabling in-depth customization.
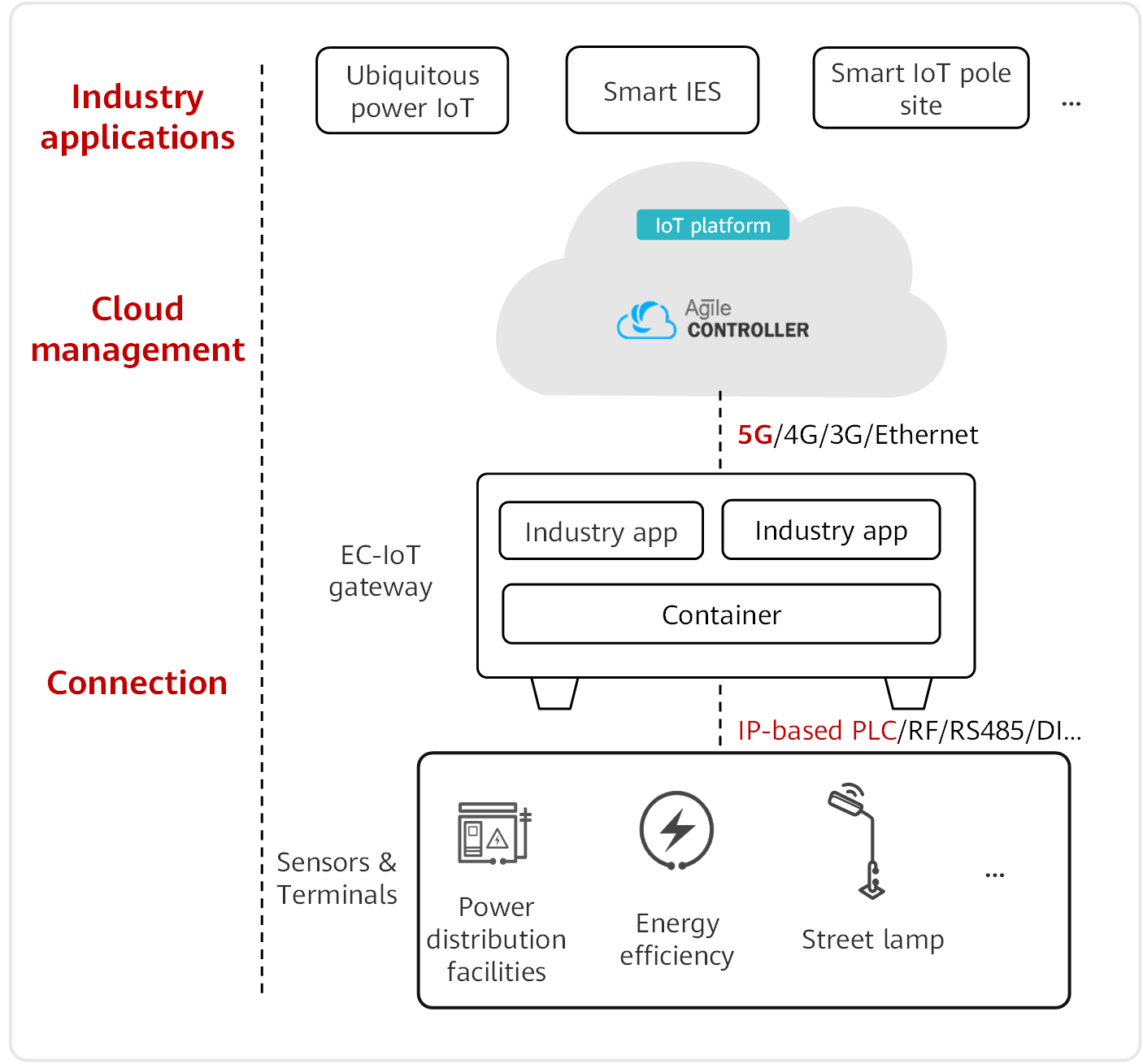
Edge computing-IoT
- Author: Cui Yunlong
- Updated on: 2021-11-23
- Views: 5348
- Average rating:







