What Is HACA?
The authentication server is deployed on the Internet, so packets between the device and server may need to traverse a NAT device. However, Portal protocol packets cannot traverse the NAT device. To address this issue, Huawei Agile Cloud Authentication (HACA) allows the device and server to establish a connection for Portal authentication.
Why Do We Need HACA?
Small- and medium-sized enterprises are characterized by small network scale, a small number of concurrent online users, and dispersed network sites. To support these enterprises, Huawei proposes the CloudCampus Solution to provide services through the public cloud. This solution realizes centralized multi-tenant management, plug-and-play network devices, and batch deployment of network services. Compared with the traditional network architecture and deployment mode, this solution provides a shorter network deployment period, lower maintenance costs, and better network scalability.
The authentication server is deployed on the Internet, so packets between the device and server may need to traverse a NAT device. However, Portal protocol packets cannot traverse the NAT device. To address this issue, Huawei Agile Cloud Authentication (HACA) allows the device and server to establish a connection for Portal authentication.
How Does HACA Work?
When HACA authentication and authorization are used, the authentication and authorization information must be configured on the HACA server.
When a user requests to access the Internet, the access device forwards authentication information to the HACA server. The HACA server then decides whether to allow the user to pass based on the configured information. If the user is allowed, the HACA server sends an access-accept message carrying authorization information to the access device. The access device then authorizes network access rights to the user according to the access-accept message.
Similar to the RADIUS protocol, the HACA protocol uses the client/server model to authenticate access users.
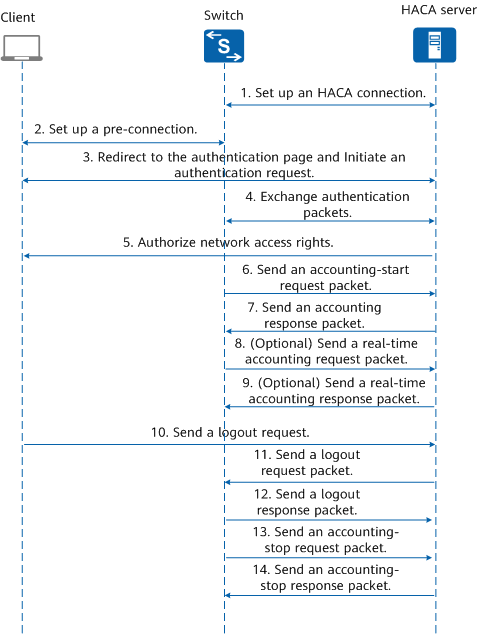
iMaster NCE-Campus deployed on the cloud acts as an external Portal server and an HACA server to provide authentication and accounting services. A switch acts as a user authentication point to provide the user authentication function together with the HACA server. User authorization information is configured on the HACA server. After a user passes authentication, the HACA server authorizes network access rights to the user. Figure 1-2 shows the HACA authentication, authorization, and accounting process.
- An access device sets up a persistent connection and register with the HACA server using HTTP/2.
- The client and device set up a pre-connection before authentication.
- The client initiates an authentication request using HTTP. The HACA server provides a web page for the client to enter the user name and password for authentication.
- The device and HACA server exchange authentication packets.
- After the client passes authentication, the HACA server sends an authorization packet to authorize network access rights to the client.
- When the client starts to access network resources, the access device sends an accounting-start request packet to the HACA server.
- The HACA server sends an accounting response packet to the access device and starts accounting.
- (Optional) If real-time accounting is enabled, the access device periodically sends real-time accounting request packets to the HACA server, preventing incorrect accounting results caused by unexpected user disconnection.
- (Optional) The HACA server returns real-time accounting response packets and performs real-time accounting.
- The client sends a logout request.
- The HACA server sends a logout request packet to the access device.
- The access device sends a logout response packet to the HACA server.
- The access device sends an accounting-stop request packet to the HACA server.
- The HACA server sends an accounting-stop response packet to the access device and stops accounting.
- Author: Zhu Yue
- Updated on: 2022-01-20
- Views: 5551
- Average rating: