What Is Intelligent Traffic Analysis?
Intelligent traffic analysis is a network traffic monitoring and analysis technology. It allows the device to perform in-depth analysis on a specified service flow to obtain data about high-precision performance indicators such as the packet loss rate and delay (nanosecond-level) of the service flow. The analysis result can be exported to iMaster NCE-FabricInsight for display or further analysis. It helps O&M personnel monitor the network running status or quickly locate network faults, and provides support for network-wide traffic visualization.
Why Is Intelligent Traffic Analysis Required?
As the digital transformation of industries accelerates, a growing number of important services and applications are being deployed on user networks, resulting in larger networks and more complex application types and data flows. Some problems that may occur during service flow forwarding, such as TCP connection establishment failures and abnormal delay of service flows, bring great challenges to network O&M and pose new requirements. It is important to quickly detect and accurately locate faults, quickly restore services, and effectively improve O&M efficiency. In addition, network traffic visualization has become a trend to implement refined service management in complex network environments.
- This technology is implemented using the built-in chip of the device, does not affect the forwarding performance of the device, and reduces the processing load of the remote analyzer.
- Intelligent analysis is performed based on different characteristics of service flows, implementing in-depth analysis based on each service flow. In addition to measuring the packet loss rate and delay, it also allows the device to calculate the round-trip time (RTT) in nanoseconds.
- The network running status is monitored in real time, and faulty nodes can be quickly and accurately located, improving network stability and reducing network maintenance costs.
- The analysis result can be exported to iMaster NCE-FabricInsight, providing strong support for implementing network-wide visualized traffic management.
What Are the Components of the Intelligent Traffic Analysis System?
A typical intelligent traffic analysis system consists of the traffic-analysis data exporter (TDE), traffic-analysis processor (TAP), and traffic-analysis data analyzer (TDA).
- The TDE is a device configured with the intelligent traffic analysis function. It determines which service flows are to be detected and sends them to the TAP.
- The TAP is a built-in chip on the CPU of a device. It processes and analyzes the service flows received from the TDE, and exports analysis results to the TDA.
- The TDA is iMaster NCE-FabricInsight, which is a network traffic analysis tool. It provides a graphical user interface (GUI) for users to easily obtain, view, and analyze collected data.
In actual applications, the TDE and TAP are deployed on the same device. On the network shown in the following figure, the intelligent traffic analysis function is configured on DeviceA.
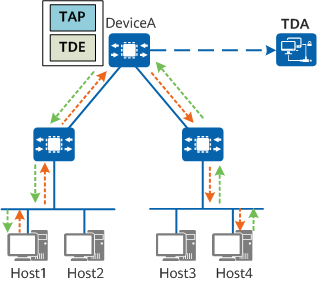
Components of the intelligent traffic analysis system
How Does the Intelligent Traffic Analysis System Work?
The working process of the intelligent traffic analysis system includes flow matching, flow analysis, and flow table export, as shown in the following figure.
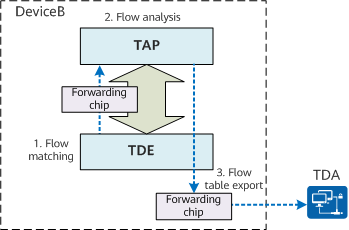
Working process of the intelligent traffic analysis system
Flow Matching
A service flow to be detected is specified on the TDE and an ACL rule is delivered to match the service flow. A matched service flow is mirrored and sent to the TAP through the forwarding chip. If the TAP cannot process the packets sent by the TDE, for example, the TAP does not support the packet type or the number of received packets exceeds its processing capability, the TAP discards the packets.
Flow Analysis
- Based on 5-tuple information (source IP address, source port number, destination IP address, destination port number, and transport layer protocol of a service flow) and key values in the packets, the TAP generates flow tables.
- The TAP collects statistics on some key fields in the flow tables. Based on the statistics, the TAP can analyze the characteristics of flows, including the number of discarded packets, delay, number of packets, and flow creation time.
Flow Table Export
Intelligent traffic analysis allows users to view service flow characteristics analyzed by the TAP. However, flow tables need to be sent to the TDA for visualized and user-friendly display of analysis results. Currently, only iMaster NCE-FabricInsight can be used as the TDA. iMaster NCE-FabricInsight consists of the FabricInsight collector and FabricInsight analyzer.
As shown in the following figure, intelligent traffic analysis flow tables that contain flow analysis results are first stored in the cache of the device. When the intelligent traffic analysis flow tables in the cache meet the aging conditions, the TAP in the device adds the statistical fields of the flow tables to the NetStream V9 extended template for encapsulation. The forwarding chip searches for routes for the encapsulated packets and forwards them to the FabricInsight collector. After receiving the exported packets from the intelligent traffic analysis system, the FabricInsight collector summarizes the characteristics of service flows based on packet information such as source addresses, and sends the characteristics to the FabricInsight analyzer for final processing and display.
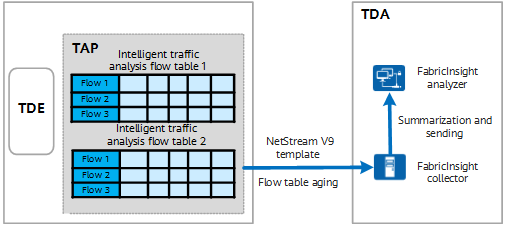
Exporting intelligent traffic analysis flow tables
Application of Intelligent Traffic Analysis
Intelligent traffic analysis can be applied to complex network environments, helping O&M personnel implement visualized network management. As shown in the following figure, different services are deployed in the data center of an enterprise, and an application is deployed on VM1 and VM3. Packets in a service flow carrying this application are sent and received along the same path between VM1 and VM3. In this case, every switch on the path can capture bidirectional traffic of this service flow. To monitor the application traffic, O&M personnel can deploy the intelligent traffic analysis function on one or more switches that the application traffic passes through to monitor and analyze service flows. Once an exception such as packet loss or long delay is detected, O&M personnel can quickly and accurately locate the fault. In addition, the analysis result can be sent to iMaster NCE-FabricInsight for further analysis and display.
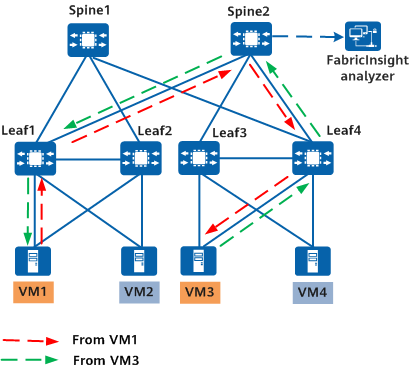
Application of intelligent traffic analysis
- Author: Li Huike
- Updated on: 2024-02-27
- Views: 8989
- Average rating:






