What Is PFC?
Priority-based Flow Control (PFC) is the most widely used flow control technology that can effectively prevent packet loss and serve as the basis for intelligent lossless networks. A PFC-enabled queue is a lossless queue. When congestion occurs in such a queue on a downstream device, the downstream device instructs the upstream device to stop sending traffic in the queue, implementing zero packet loss.
Why Do We Need PFC?
Disadvantages of Traditional Flow Control Technologies
The most fundamental flow control technology is the Ethernet Pause mechanism defined in IEEE 802.3. When a downstream device detects that its receive capability is lower than the transmit capability of its upstream device, it sends Pause frames to the upstream device, requesting the upstream device to stop sending traffic for a period of time.
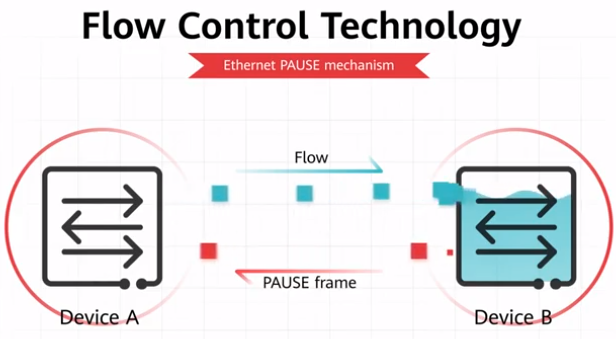
Implementation of the Ethernet Pause mechanism
- Burst traffic of one type cannot affect forwarding of other types of traffic.
- A large amount of one type of traffic in a queue cannot occupy buffer resources of other types of traffic.
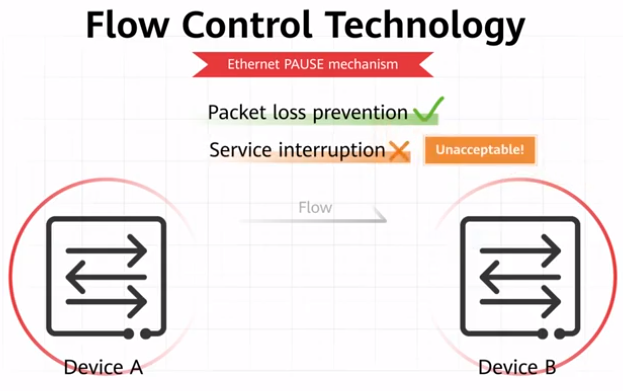
Disadvantages of the Ethernet Pause mechanism
What Is PFC?
PFC is the most widely used flow control technology that can effectively prevent packet loss and serve as the basis for intelligent lossless networks. A PFC-enabled queue is a lossless queue. When congestion occurs in such a queue on a downstream device, the downstream device instructs the upstream device to stop sending traffic in the queue, implementing zero packet loss.
How Does PFC Work?
As shown in the figure, eight priority queues on the transmit interface of DeviceA correspond to eight receive buffers on the receive interface of DeviceB. When a receive buffer on DeviceB is congested, DeviceB sends a backpressure signal "STOP" to DeviceA, requesting DeviceA to stop sending traffic in the corresponding priority queue.
PFC addresses the conflict between the Ethernet Pause mechanisms and link sharing. It controls traffic only in one or several priority queues of an interface, rather than on the entire interface. What's more, PFC can pause or restart any queue, without interrupting traffic in other queues. This feature enables traffic of various types to share one link.
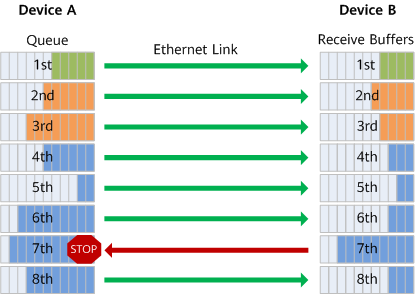
PFC working mechanism
- Author: Ma Shuai
- Updated on: 2024-02-27
- Views: 15543
- Average rating:






