What Is Smart Application Control (SAC)?
Leveraging service awareness (SA) technology, Smart Application Control (SAC) detects and identifies Layer 4 to Layer 7 information in packets and dynamic protocols such as HTTP and RTP through a smart application protocol identification and classification engine. This allows it to implement fine-grained QoS management according to the identification result. In this way, SAC implements application-based traffic control.
Why Do We Need SAC?
Traditional traffic classification technologies only check the content at Layer 4 and lower layers in packets, for example, source IP address, destination IP address, source port number, destination port number, and service type. They cannot analyze applications in packets. Leveraging service awareness (SA) technology, Smart Application Control (SAC) detects and identifies Layer 4 to Layer 7 information in packets and dynamic protocols such as HTTP and RTP through a smart application protocol identification and classification engine. This allows it to implement fine-grained QoS management according to the identification result. In this way, SAC implements application-based traffic control.
What Are Application Scenarios of SAC?
As shown in the following figure, to ensure network quality and ensure acceptable employee online behavior, configure SAC to identify various applications on networks and control packets of application protocols. For example, SAC can be used to achieve the following:
Permit certain network browsing behaviors so that office services of users can be correctly transmitted on the internal network.
Block instant messaging applications or limit the rate of traffic matching these applications to ensure acceptable employee online behavior.
Limit bandwidth of P2P applications such as BT and eDonkey_eMule to ensure network quality.
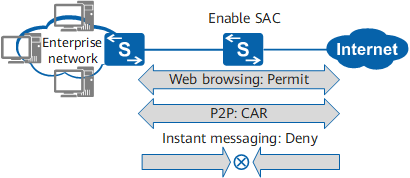
Networking of SAC
How Does SAC Work?
Huawei analyzes the signatures of common applications and develops an application signature database file. After the application signature database file is loaded on a switch, the switch classifies traffic of all applications that can be identified. For example, P2P file sharing applications such as BT and eDonkey_eMule fall into the FileShare_P2P category.
The system analyzes traffic flowing through the device, and compares the analysis result with the signature database file loaded on the device. It identifies an application by detecting signatures in data packets, and implements fine-grained QoS management according to the identification result. The following figure shows the working mechanism of SAC.
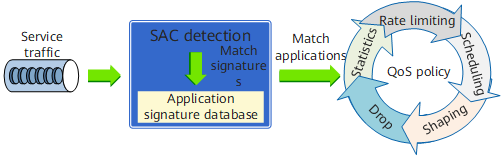
SAC working mechanism
- Author: Li jiyuan
- Updated on: 2021-09-30
- Views: 4722
- Average rating:






