What Is SNR?
SNR refers to the signal-to-noise ratio. SNR, as well as SINR, is used to measure communication reliability. The difference between SNR and SINR is that SINR takes the impact of interference into account and is the ratio of signals to interference and noise.
Classification of SNR
The signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) is a main technical indicator for measuring communication reliability. It applies not only to the communications sector but also to other sectors.
Communication SNR: In modulation signal transmission, the SNR typically refers to the ratio of the average power of carrier signals at the output end of a channel (that is, the input end of a receiver) to the average noise power on the channel, and can be referred to as a carrier-to-noise ratio (CNR). In an analog communications system, the SNR typically refers to the ratio of the average signal power to the average noise power at the output end of the demodulator of a communications terminal. In a digital communications system, the SNR typically refers to the ratio of the average signal energy of each digital waveform (bit) to the noise power in a unit frequency band at the output end of a digital demodulator or decoder of a terminal set. The SNR is also referred to as a normalized SNR or an energy SNR, which is a common indicator.
Audio SNR: The audio SNR refers to the ratio of the normal sound signal strength to the noise signal strength when a sound device is playing. At a low SNR, when small signals are input, the noise is severe and greatly affects the voice quality.
Image SNR: Similar to the image definition, the image SNR is an important indicator for measuring the image quality. The image SNR refers to the ratio of the video signal strength to the noise signal strength. A higher SNR indicates a clearer image. A low SNR may result in static noise in the image.
Web page SNR: It is a concept originated in the electroacoustic field, and refers to the ratio of the maximum undistorted sound signal strength generated by the sound source to the noise strength generated at the same time. This concept also exists in web page optimization. When a search engine obtains pages, it mainly obtains the text content after HTML tags are removed. The content can be considered as undistorted sound signals, and the HTML tag content generated at the same time can be considered as noise. Therefore, the web page SNR can be understood as the ratio of the text content on a web page to the generated HTML tag content when the text is produced. A higher web page SNR indicates more plain text content on the page. In this case, it is easier for the search engine to obtain pages.
This document describes the SNR in the wireless communication sector.
SNR and SINR
SNR
SNR refers to the ratio of signal power to noise power in a system, often expressed in decibels (dB). Decibel can be defined as a unit that expresses relative difference in power or intensity, usually between two acoustic or electric signals, equal to ten times the common logarithm of the ratio of the two levels. A signal is an electronic signal that comes from outside a device and needs to be processed by the device. Noise refers to irregular extra signals that do not exist in original signals generated by a device. Noise signals are related to the environment and do not change as the original signals change. Distortion is also an extra signal that does not exist in the original signals generated by a device. In addition, distortion and noise are actually related. The difference between distortion and noise is that distortion is regular while noise is irregular.
Imagine a large room in which people are crowded. When two persons try to communicate with each other, the communication content is signals, and the voices of other people around them are noise. The SNR indicates the impact of surrounding noise on communication content. Therefore, the two persons must attempt to overwhelm the surrounding noise for better communication.
The SNR is calculated using the following formula:
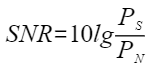
- SNR: signal-to-noise ratio, in dB
- PS: effective power of signals
- PN: effective power of noise signals
SINR
The signal to interference plus noise ratio (SINR) is the ratio of the strength of signals to the total strength of interference and noise.
The SINR is calculated using the following formula:
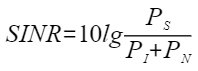
- SINR: signal to interference plus noise ratio, in dB
- PS: effective power of signals
- PN: effective power of noise signals
- PI: effective power of interference signals
Difference Between SNR and SINR
SNR, as well as SINR, is used to measure communication reliability. The difference between SNR and SINR is that SINR takes the impact of interference into account and is the ratio of signals to interference and noise. Interference, such as co-channel interference and multipath interference, is caused by the system and other systems. Similar to the SNR, a larger SINR indicates better signals.
Impact of the SNR on WLANs
The SNR is essentially not a ratio, but a decibel difference between the received signal and the background noise. Background noise is also referred to noise floor. The background noise of a channel is determined by the noise factor, temperature, and channel width of the RF component used in the radio. If the difference between the received signal and the background noise is too small, the data is damaged and needs to be transmitted again. In WLANs, retransmission exerts a negative impact on throughput and delay.
The SNR can be used to determine the quality of radio signals. It also considers the background noise (noise floor) of the radio environment. For example, for a signal of –65 dBm, at a position where the background noise is –90 dBm, the SNR is 25 dB. In this case, the signal quality is good. However, at a position where the background noise is –80 dBm, the SNR is only 15 dB. In this case, larger background noise indicates a lower SNR and poorer signal quality. For a data network, it is recommended that the SNR be at least 20 dB. For a network using voice applications, it is recommended that the SNR be 25 dB or higher. On a WLAN, the SNR must be higher than 30 dB to ensure good user experience.
Improving the SNR on a WLAN
Improving the SNR is a major method for improving the communication quality. On a WLAN, you can perform the following operations to improve the SNR:
- Avoid contention channels with strong signals and high utilization.
- Ensure that an AP is installed as close as possible to the STAs to avoid AP connection through walls.
- Adjust the power of neighboring APs to ensure that each AP covers different areas and does not generate interference to users in adjacent areas.
- Author: Wang Minghui
- Updated on: 2025-04-09
- Views: 10971
- Average rating:







