What Is Terminal Anti-Spoofing?
Terminal anti-spoofing is a terminal detection, management and control technology. It learns the traffic characteristics of authorized terminals, forms a traffic behavior model, and uses that model to identify spoofed terminals. Once it identifies spoofed terminals, it automatically delivers policies to isolate them.
Why Do We Need Terminal Anti-Spoofing?
Dumb terminals such as IP phones, IP cameras, and printers are often connected to the network using less secure methods such as IP address whitelisting and MAC address authentication. In addition, there is no mechanism to periodically scan and remove viruses from the terminals. Therefore, unauthorized terminals can easily falsify IP addresses or MAC addresses of authorized terminals to attack the network.
To prevent such problems, the device provides the terminal anti-spoofing function. This function implements terminal information management, anomaly detection, and anomaly management and control, reducing the risk of unauthorized terminal spoofing on the network.
What Are Application Scenarios of Terminal Anti-Spoofing?
For instance, as shown in the following figure, dumb terminals such as printers, IP cameras, and IP phones connect to the network through switches.
Unauthorized terminals may falsify IP addresses or MAC addresses of authorized terminals to attack the network. Therefore, you can deploy the terminal anti-spoofing function on the access switches (for example, SwitchA and SwitchB in the figure) to identify spoofed terminals and control their network access rights.
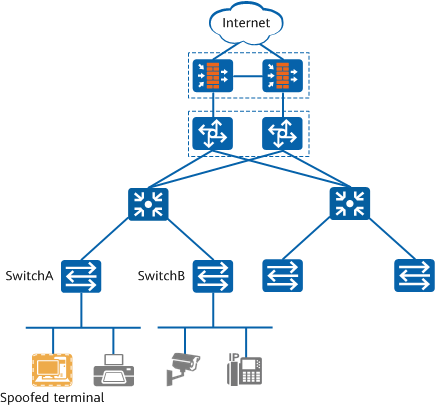
Application scenario of terminal anti-spoofing
Interaction Process for Terminal Anti-Spoofing?
The following uses printers as an example to describe how information management, anomaly detection, and isolation policies are implemented on terminals for anti-spoofing. The following figure shows this process.
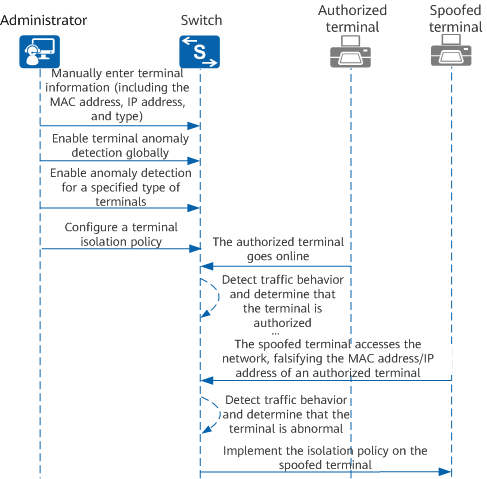
Interaction process for terminal anti-spoofing
The basic interaction process is as follows:
- The administrator configures the terminal anti-spoofing function on the switch, including entering terminal information, enabling terminal anomaly detection globally, enabling anomaly detection for a specified type of terminal, and configuring a terminal isolation policy.
- An authorized terminal accesses the network through the switch. Therefore, the switch receives ARP packets from the authorized terminal. The switch compares the terminal information manually entered by the administrator with the ARP packets sent by the authorized terminal. If they match, the switch generates the corresponding terminal entry because terminal anomaly detection has been enabled globally on the switch.
- The switch determines that the authorized terminal matches the configured terminal type for terminal anomaly detection. Therefore, the switch collects traffic behavior characteristics of this terminal, analyzes the characteristics using related algorithms, and determines that the traffic behavior of this terminal is normal.
- After a period of time, an unauthorized terminal falsifies the MAC address or IP address of this authorized terminal, accesses the network through the switch, and attempts to launch an attack.
- The switch collects the traffic behavior characteristics of the spoofed terminal, analyzes the characteristics using related algorithms, and determines that the traffic behavior of this terminal is abnormal. The switch implements the configured isolation policy on this spoofed terminal. The spoofed terminal is isolated and cannot access the network.
- Author: Fu Li
- Updated on: 2022-05-07
- Views: 2318
- Average rating:






