What Is WAN Data Redundancy Elimination?
WAN Data Redundancy Elimination (DRE) applies data compression technology on data communication networks to compress packets transmitted on WANs. It significantly improves the data transmission volume without requiring additional bandwidth, giving customers a better return on investment (ROI) from their network construction.
Why Do We Need WAN DRE?
Wider roads serve more cars, and likewise, higher WAN bandwidth transmits larger data volumes. Bandwidth resources of WANs are limited and costly. How can more data be transmitted on WANs in the same amount of time without expanding the bandwidth? This is where WAN DRE can help.
WAN DRE applies data compression technology to data communication networks to compress the data packets to be transmitted. In this way, more data packets can be transmitted in the same amount of time, thereby improving the data transmission speed on WANs.
Figure 1 shows a mainstream data compression solution. In this solution, a dedicated compression device is deployed before the egress device (router) to compress data before the data is sent out through the egress device. Figure 2 shows the WAN DRE solution where the egress device has a built-in data compression board or module for compressing data.
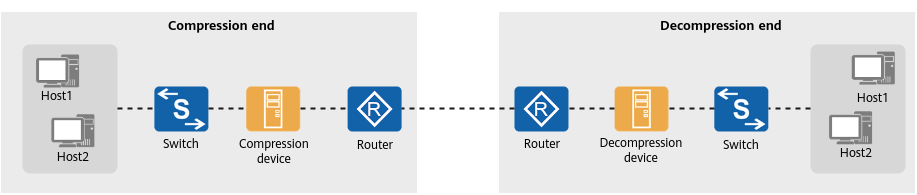
Mainstream data compression solution
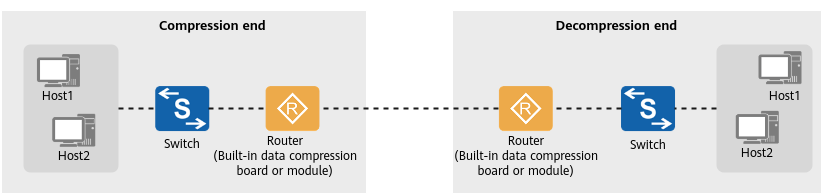
WAN DRE solution
WAN DRE has advantages over mainstream data compression solutions in reliability, transmission performance, compression performance, and networking flexibility.
High Reliability
Huawei's egress device provides the WAN DRE feature through a built-in data compression board or module, which eliminates the need for additional devices and thereby simplifies networking and ensures reliability.
High Performance
Systems with insufficient computing capabilities cannot meet data compression requirements in heavy-traffic WAN scenarios. This will cause a large network latency and deteriorate service quality. WAN DRE uses an industry-leading compression algorithm to implement a compression ratio of up to 30% and ensure less than 0.1 ms latency during compression and decompression.
Lossless Compression
Some 5-tuple information is lost during compression using conventional compression protocols, impeding refined management for service flows. In contrast, WAN DRE retains 5-tuple information of original data packets during compression. This ensures refined identification, proper statistics collection, and Quality of Service (QoS) policy execution for service flows during data forwarding.
Flexible Networking
Mainstream data compression solutions mainly apply to point-to-point leased lines, but not to multipoint-to-multipoint large-scale networking scenarios. In contrast, WAN DRE does not require the compression and decompression ends to establish a session with each other. As such, the compressed data can be sent to any destination based on service requirements, and the destination end simply identifies and decompresses the compressed data. This meets the requirements of distributed multi-point interconnection.
How Does WAN DRE Work?
The WAN DRE process consists of four steps: identifying packets to compress, compressing packets, forwarding compressed packets, and decompressing the packets, as shown in the following figure. Each packet is individually compressed and decompressed, and contains the same data throughout the entire process.
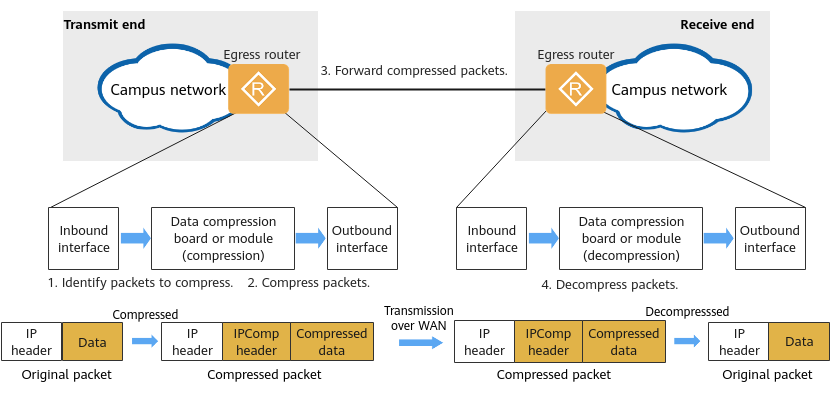
WAN DRE process
- Identify packets to compress.
When WAN DRE is enabled on a device, a compression policy defining the packets to be compressed also needs to be configured. When receiving packets matching the policy, an interface on the device diverts the packets to the data compression board or module.
- Compress packets.
The data compression board or module compresses the packet data using a compression algorithm, encapsulates the resulting packets with an IP payload compression protocol (IPComp) header, and sets the protocol number in the IP header to 108.
- Forward compressed packets to the receive end.
The compressed packets are transmitted over the WAN.
- Decompress packets.
The receive end diverts packets whose protocol number is 108 and that match the compression policy to the data compression board or module for decompression.
Typical Application Scenarios of WAN DRE
Financial Sector
In the financial sector, a large amount of service data is replicated in batches between data centers and between a data center and a disaster recovery (DR) center. With the expansion of financial services, more data needs to be batch replicated, demanding higher WAN bandwidth. To mitigate the WAN bandwidth shortage problem, WAN DRE can be configured on egress devices to effectively utilize WAN bandwidth between data centers and between a data center and a DR center.
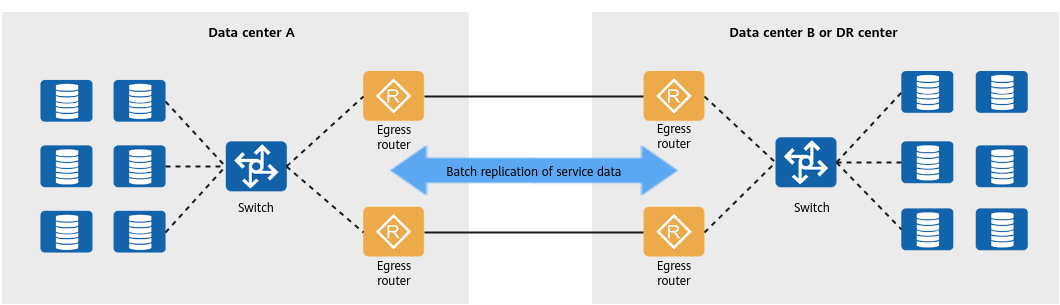
Application of WAN DRE in the financial sector
SD-WAN Solution
In the SD-WAN solution, WAN DRE can apply to the following scenarios:
- If the link bandwidth is insufficient when a branch site accesses the headquarters (HQ) site, WAN DRE can be deployed at the branch and HQ sites to improve the data transmission speed.
- If the link bandwidth is insufficient for mutual access between branch sites, WAN DRE can be deployed at both sites to improve the data transmission speed.
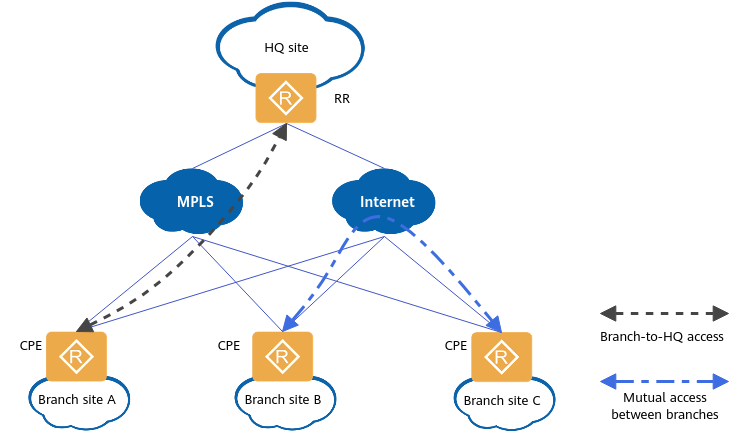
Application of WAN DRE in the SD-WAN solution
- Author: Ling Ziwen
- Updated on: 2023-10-07
- Views: 2531
- Average rating:







