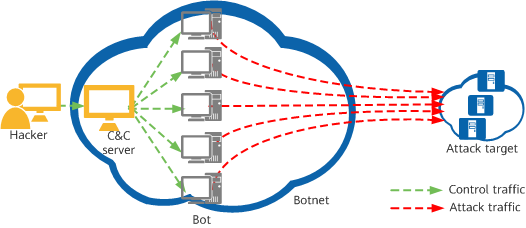
What Is a Botnet?
A hacker uses one or more means to infect a large number of hosts with bot programs. The infected hosts receive instructions from the hacker through a control protocol. In this way, the controller and bots form a 1-to-N control network. The name botnet conveys the fact that many computers are controlled and instructed to form a network of bots, which are used as tools by hackers.
Components of a Botnet
A botnet typically consists of a hacker, control protocol, C&C server, and bots. The hacker (controller) can remotely control the bots by communicating with their clients through a specific control protocol.
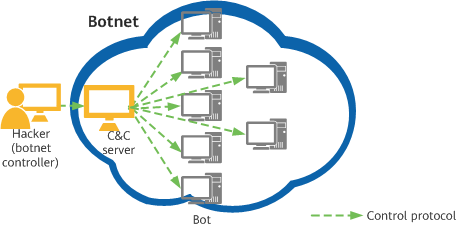
Components of a botnet
- Hacker
Controller of bots on the botnet.
- C&C server
A computer used to control bots. A hacker uses the C&C server to deliver control instructions to control a large number of bots on the botnet.
- Control protocol
Medium used by a hacker to control the bots on the botnet. A common communications protocol is IRC, which allows a hacker to send control commands to all bots through the created IRC channel.
- Bots
Hosts that have been controlled by a hacker. They perform malicious tasks under remote control.
Construction Process of a Botnet
Constructing a botnet can be simplified into the following three steps:
- Exposure: A hacker exposes a user to malicious software by exploiting system vulnerabilities.
- Infection: The user unconsciously infects its device with malicious software that can control it.
- Activation: Exploiting the infected device to launch attacks, the hacker organizes all infected computers into a botnet and remotely manages them using a control protocol.
Common Propagation Paths of a Botnet
Botnets spread through the following ways:
- Operating system vulnerabilities: A hacker obtains the permission to access the operating system of a host by exploiting the vulnerabilities in the host operating system. The hacker infects the attacked computers, which become bots when the shellcode is used to execute bot programs. They also combine bot programs (such as AgoBot) with worms, so that bot programs can spread automatically.
- Emails: Hackers often use emails to spread bot programs in attachments or links. They send a large number of such emails to users, and exploit social engineering techniques to induce email receivers to execute programs in the attachments or click links. Sometimes, they exploit the vulnerabilities on the mail clients to automatically execute bot programs. As a result, the mail receivers' hosts are infected and become bots.
- Instant messaging software: A hacker exploits instant messaging software to send links to users in the friend list, using social engineering techniques to trick them into clicking the links to execute the bot programs. As a result, their hosts are infected. An example is Worm.MSNLoveme, which broke out in early 2005.
- Malicious website scripts: Hackers bind malicious scripts to HTML pages of websites that provide web services. When visitors access these websites, malicious scripts are executed to download bot programs to hosts. The programs run automatically. As a result, the visitors' hosts become bots.
Harms Caused by a Botnet
A botnet can function as an attack platform. The number of bots can be in the hundreds, tens of thousands, or even millions. The botnet can be used to launch various attacks, which paralyze the entire basic information network or important application systems, and leak a great amount of confidential or personal information. Common attacks through botnets are as follows:
- DDoS attacks
DDoS attacks are one of the major botnet threats. A hacker can instruct all controlled bots to continuously send access requests to a specific network target at a specific time. A large number of bots can launch DDoS attacks simultaneously, making DDoS attacks more harmful and difficult to defend against.
DDoS attack
- Spam
Hackers use botnets to send a large amount of spam. The spam senders are bots, so hackers can hide their IP addresses easily.
- Personal information leakage
Botnet controllers can steal sensitive user information, such as personal account passwords and confidential data, from bots.
- Abuse of resources
Hackers use botnets to perform various activities that consume network resources, deteriorating network performance and even resulting in economic loss. Examples include implanting adware, using bots to store large-scale or illegal data, and using bots to build fake bank websites for phishing.
- Cryptocurrency mining
Hackers control a large number of bots to perform mining activities, thereby consuming the computing resources of the victim hosts, increasing the host temperature, and consuming extra power.
How Do We Prevent a Botnet?
- Create a secure password.
In many cases, creating a secure password can effectively prevent botnet intrusion. Creating a secure password makes brute force cracking difficult, and creating a sophisticated and secure password makes it almost impossible.
- Closely monitor the network status.
Closely monitor the abnormal activities on your network. If there are abnormal activities on the network, handle them in time and check whether your devices are attacked by malicious software.
- Check system files regularly.
Regularly review files in the system and delete unnecessary junk files to prevent botnet intrusion through malicious programs.
- Execute only authenticated software services.
Run only authenticated software services and do not open unknown software. This effectively prevents hackers from infiltrating hosts through malicious software.
Huawei HiSecEngine USG6000E and USG6000F series AI firewalls help large and midsize enterprises as well as data centers effectively defend against common botnet attacks. A device with the attack defense function enabled begins to differentiate traffic after being deployed at the egress of an enterprise network, permitting legitimate traffic and blocking attack traffic. This function ensures that intranet servers and PCs run properly, thereby providing uninterrupted services for authorized users.
- Author: Huang Xunwei
- Updated on: 2024-01-18
- Views: 1367
- Average rating: