What Is Edge Computing IoT (EC-IoT)?
IoT is developing rapidly and advancing towards the Internet of Everything (IoE). In the fully connected era, the surge in the number of device connections and amount of IoT data has spurred the development of edge computing technology. Edge Computing IoT innovatively brings the edge computing architecture to the IoT field, and provides data processing, storage, and application at the edge close to things. It addresses the "last mile" issue of IoT communication and implements smart connection and efficient management of IoT devices.
Why Do We Need Edge Computing IoT?
Nowadays, IoT has become a critical force driving a new round of global technological revolution and industrial transformation.
What is IoT? To put it simply, IoT enables things to connect to the Internet, and its ultimate goal is to connect everything.
As IoT technologies develop rapidly, diverse industries are starting digital transformation to connect more and more devices to the Internet. According to the prediction of statistical authorities, the number of connections of global IoT devices will reach 100 billion by the year of 2025. Under this trend, enterprises will face the following challenges:
- When massive amounts of data are migrated to the cloud for processing, the lack of real-time data analysis and processing capabilities greatly increases the data processing burden on the cloud.
- It is difficult to centrally deploy and manage numerous IoT devices and applications as well as diversified interfaces and protocols.
Edge Computing IoT: Combination of Edge Computing and IoT
Edge computing greatly simplifies processing for massive amounts of terminal data on the cloud.
Edge computing is deployed at the network edge close to things or data sources, and provides edge intelligence services through an open platform that integrates network, computing, storage, and application capabilities. The data collected by terminal devices is directly analyzed and processed locally at the network edge in real time, without the need to be uploaded to the cloud for processing. Edge computing meets the key requirements of industry digitalization for agile connection and real-time data optimization.
The combination of edge computing and IoT technologies gives birth to edge computing IoT. Edge computing IoT introduces the edge computing architecture to the IoT field. An edge computing gateway that integrates network, computing, storage, and application capabilities is deployed at the network edge close to devices or data sources, so that it can provide device management and control services on network edge nodes. As such, edge computing IoT solves the "last mile" issue of industry IoT communication and implements smart connection and efficient management of IoT devices.
What Is Edge Computing IoT Used for?
Edge computing IoT is dedicated to meeting the following requirements:
- Adapts to diversified physical interfaces and protocols to enable IoT terminals to quickly and smoothly access the Internet.
- Implements unified management of a large number of terminal devices.
- Enables local processing of local traffic and implements quick response.
- Opens systems for industry collaboration.
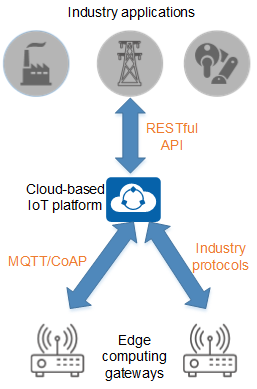
The following figure shows the edge computing IoT architecture, which features edge intelligence and cloud management. Through open edge computing capabilities of gateways, edge computing IoT quickly adapts to intelligent data processing requirements of diverse industries, implementing quick response to key services within milliseconds, local aggregation and optimization of data, and proactive backhaul of high-value data to the cloud.
Edge computing IoT architecture
The edge computing IoT architecture uses two core components: edge computing gateway and cloud-based IoT platform.
- The edge computing gateway is an IoT gateway with edge computing capabilities and implements local analysis and processing for massive amounts of terminal data.
- It supports abundant industrial IoT interfaces (such as PLC, RF, RS-485, and DI) and protocols, allowing flexible access of various sensors and terminals.
- It opens up software and hardware resources, and supports container deployment. Industry applications can be deployed in containers on demand, so that data of access terminal devices can be locally processed.
- The cloud-based IoT platform can interconnect with various industry application systems to implement smart connection of terminal devices:
- It uses a cloud management architecture to centrally manage a large number of terminal devices, reducing O&M costs.
- It uses an open architecture and opens up standard northbound application programming interfaces (APIs) for interconnection with third-party industry application systems.
Key Features of Edge Computing IoT
Cloud Platform Openness
In the edge computing IoT solution, the cloud-based IoT platform leverages cloud computing technologies to implement unified management of networks, devices, containers, and applications on the cloud. The platform also provides open northbound APIs to support flexible interconnection with third-party industry application systems, as shown in the following figure.
- Open architecture
The cloud-based IoT platform uses an open software architecture and provides standard RESTful northbound APIs for interconnection with various industry application systems, implementing value-added application services.
- Service convergence
The cloud-based IoT platform manages gateways, containers, and applications in a unified manner, and supports installation of containers and applications.
- Cloud-based deployment
The cloud-based IoT platform supports distributed cluster deployment, seamless capacity expansion, and centralized management for a large number of IoT gateways.
Cloud-based IoT platform
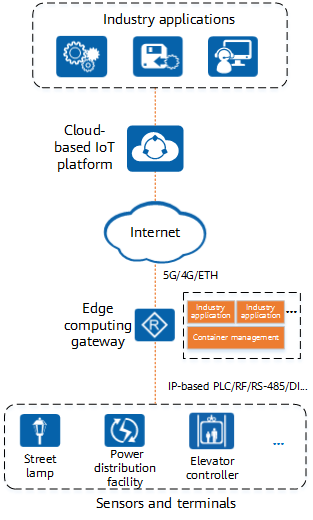
Gateway Openness
As shown in the following figure, an edge computing gateway supports container deployment, and allows users to install their own service applications in containers. In addition, it provides various eSDK interfaces for containers and applications to invoke resources.
Container is a Linux-based lightweight virtualization isolation method. A traditional VM consists of CPUs, memory, disks, and peripherals, and is used as a real machine. In contrast, a Linux container implements resource isolation and allocation based on the Linux kernel, making applications in it consider that they run on an independent machine.
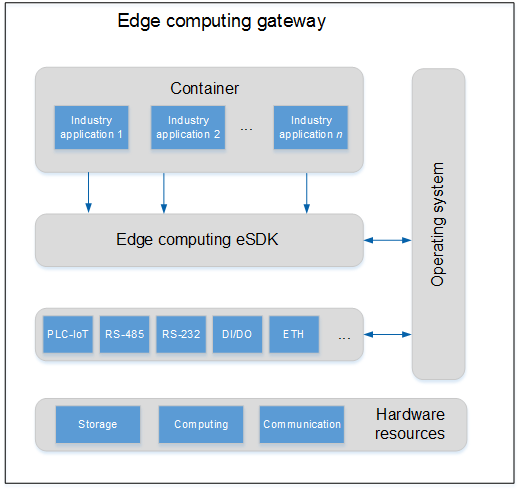
Gateway openness
Typical Applications of Edge Computing IoT
Edge computing IoT has been widely used in fields such as power distribution, smart city, and smart Integrated Energy Service (IES). It has become an important driving force for digital transformation across industries. The following describes how edge computing IoT is applied in the power distribution and smart IES scenarios.
Power Distribution IoT
The power distribution IoT combines traditional power distribution automation technologies with IoT technologies to implement digital transformation of power distribution networks. This solves many long-standing problems beyond the reach of traditional industrial control technologies, such as management of numerous terminal devices as well as service management and control. As such, the power distribution IoT delivers better user service experience and improves service operational efficiency.
In power distribution IoT scenarios, edge computing IoT uses the "cloud-pipe-edge-device" architecture to implement full connections and smart management.
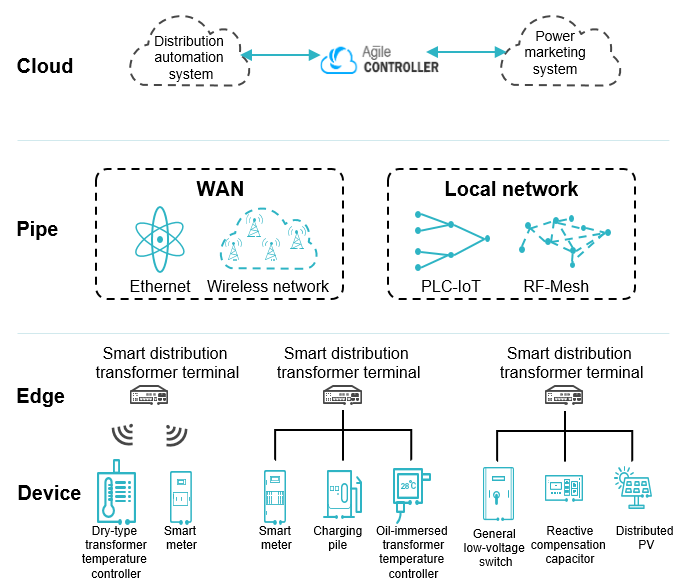
Power distribution IoT
- Cloud: refers to a cloud master station. It consists of a next-generation power distribution automation master station, a micro-application management and control center, and Agile Controller-IoT. These components collaborate to provide various services and functions, including distribution terminal unit (DTU) management, online device monitoring, fault rectification upon power outages, asset management, big data analytics, and artificial intelligence (AI) applications.
- Pipe: refers to communication networks for implementing data exchange between the cloud and edge. WAN communication networks include Ethernet and wireless networks. Local communication networks mainly use PLC-IoT, RF-Mesh, and other communication technologies to transmit data between terminal devices and the edge.
- Edge: An edge computing gateway is deployed at the network edge to provide a container platform that allows users to install service applications in containers to meet service requirements. In addition, the edge computing gateway provides open APIs in containers for applications to invoke.
- Device: Low-voltage distribution devices use intelligent core communication modules to implement communication between intelligent terminal devices and the edge computing gateway. Huawei offers intelligent core communication modules and open APIs for third-party vendors to perform secondary integration of low-voltage devices.
Smart IES
The following figure shows the core architecture of edge computing IoT used in smart IES scenarios. In this architecture, a cloud-based smart IES platform is used to provide data perception, edge processing, and smart applications. This platform displays the alarm status, site status, and device status of network-wide terminal devices (such as electricity, water, and gas meters), and supports remote visualized management, implementing real-time network-wide status monitoring.
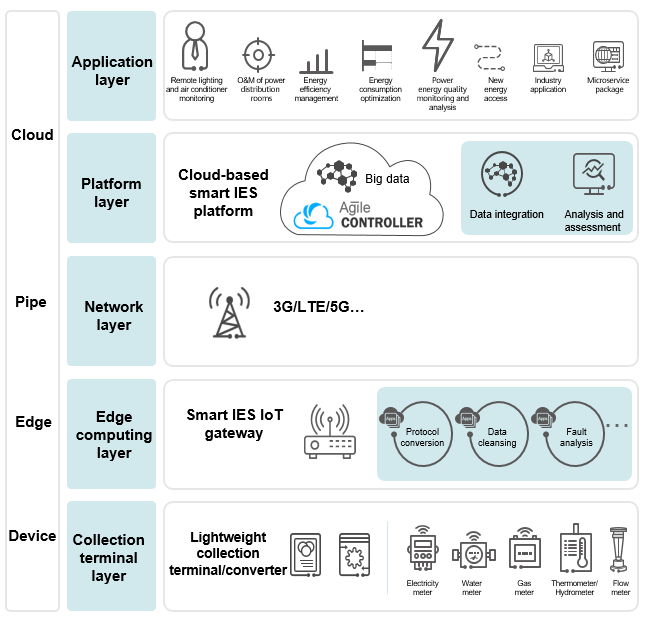
Smart IES
- Platform layer and application layer: The cloud management architecture is used to implement remote full-lifecycle visualized management of a vast number of devices as well as analysis and processing of massive energy consumption data.
- Network layer: Wired and wireless communication modes are supported and can be flexibly selected based on site requirements in diverse application scenarios.
- Edge computing layer: Based on edge computing technology, this layer redefines a smart IES IoT gateway (edge computing gateway) and makes the gateway intelligent. Functions of the smart IES IoT gateway can be customized or loaded on demand, and their data can be flexibly shared, so that they can interconnect with different service ecosystems. As such, one smart IES IoT gateway can be used for multiple purposes, eliminating repeated development of hardware systems.
- Collection terminal layer: Collection terminals or converters adopt PLC-IoT technology and connect terminal devices (such as electricity, water, and gas meters) to the smart IES IoT gateway over existing power lines to reliably and efficiently collect various energy consumption information, providing data basis for integrated energy services.
Edge Computing IoT Products
Agile Controller-IoT
Huawei Agile Controller-IoT provides multi-tenant management, device management, openness management, and system O&M to implement end-to-end automatic management of IoT devices.
For more information about Agile Controller-IoT, see the Agile Controller-IoT Product Documentation.
Edge Computing Devices
Huawei offers AR-CORE series edge computing core cards and AR502H series IoT gateways to manage PLC-IoT central coordinator (CCO) and station (STA) modules.
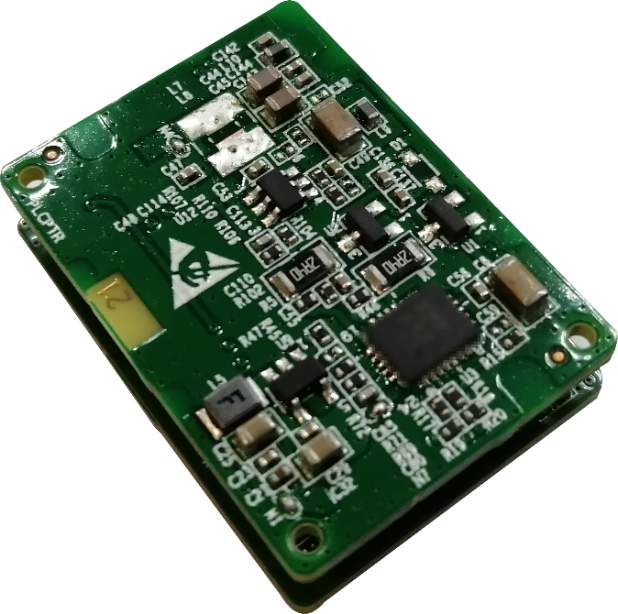
- AR-CORE series edge computing core cards: The AR-CORE-220E, as shown in the following figure, provides an open software and hardware resource platform, and supports secondary development and assembling as well as deployment of containers and applications.
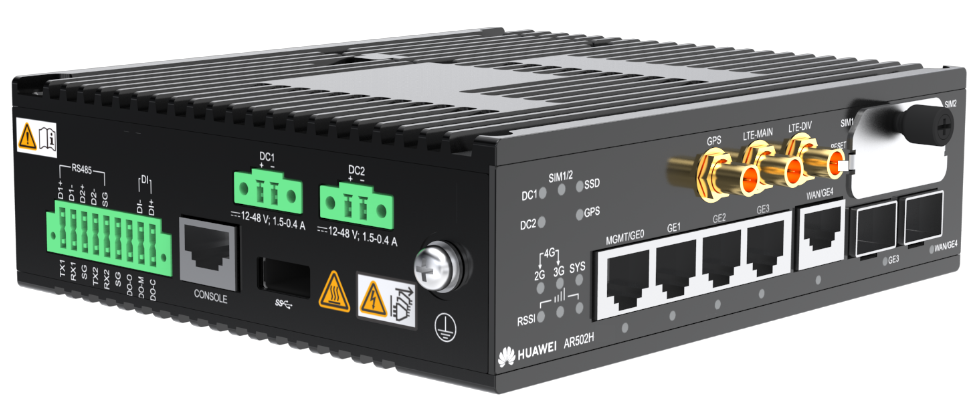
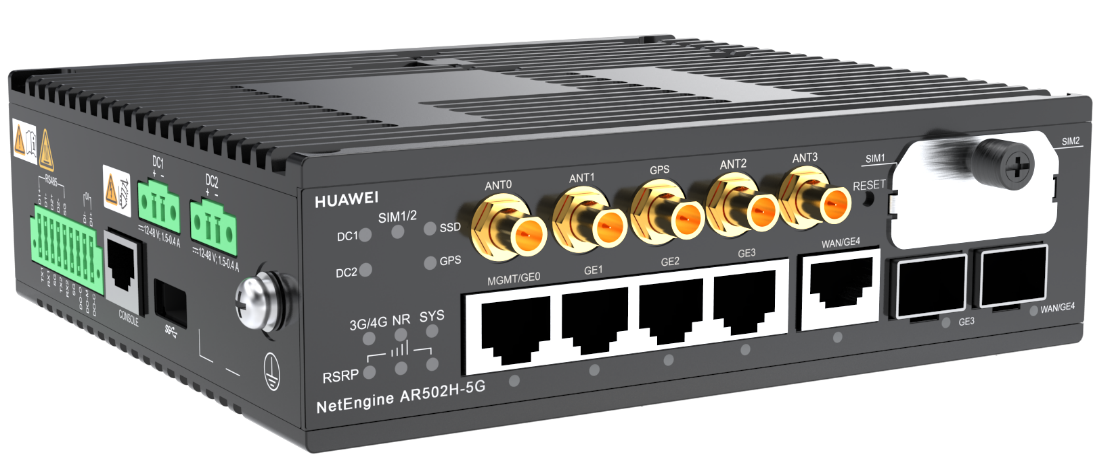
AR-CORE-220E - AR502H series IoT gateways, as shown in the following figures, are next-generation edge computing gateways ideal for industry IoT scenarios. They have powerful edge computing capabilities, provide abundant IoT interfaces for uplink data connections through 3G, LTE, and 5G. They also support lifecycle management of CCO and STA modules. For more information about AR502H series IoT gateways, go to AR502H Series Edge Computing IoT Gateways.
AR502H
NetEngine AR502H-5G
PLC-IoT Communication Modules
Huawei PLC-IoT communication modules include CCO and STA modules. A CCO module is used together with an edge computing core card or gateway, and STA modules are integrated into industry terminals. They work together to reuse power lines for data transmission, making networks available over power lines and ensuring high reliability.
CCO Modules
CCO modules are classified into the following types:
- CCO modules used together with edge computing core cards, including the PLC-IH-1 and PLCh-Power-1: They are used in Huawei Inside solution, and adopt PLC technology to upload and download data, implementing remote control.
The PLC-IH-1 is applicable to diverse scenarios, such as intelligent traffic lights control scenarios. It adopts PLC technology and reuses resources such as power supplies, poles, pipes, and power lines, facilitating fast deployment of terminal devices.
PLC-IH-1The PLCh-Power-1 is applicable to various scenarios. It helps to implement visibility and controllability of power distribution networks, improve data integration and application capabilities, and achieve convergence between information systems and power distribution systems.
PLCh-Power-1 - CCO modules used together with AR502H series edge computing gateways: The iCUBE-PLC100 adopts PLC technology to upload and download data, implementing remote control. It is ideal for various scenarios, and helps to implement visibility and controllability of power distribution networks, improve data integration and application capabilities, and achieve convergence between information systems and power distribution systems.
iCUBE-PLC100
STA Modules
STA modules are mainly used to collect data. Huawei STA modules come in three models: PLC-IS-1, PLCe-Power-1, and iMOD-PLC121.
- The PLC-IS-1 is used in Huawei Inside solution for data collection. It adopts PLC technology to upload and download data, implementing remote control. It is applicable to scenarios where smart street lamps and smart street lamp systems are used, such as smart transportation scenarios and smart buildings.
PLC-IS-1 - The PLCe-Power-1 is used in Huawei Inside solution. It is miniaturized through circuit re-modularization and has the printed circuit board assembly (PCBA) sealed. This module can be re-welded by integrators. PLC interfaces on this module only receive and transmit signals of analog front ends (AFEs).
PLCe-Power-1 - The iMOD-PLC121 is used in Huawei Inside solution. It is miniaturized through circuit re-modularization and can be re-welded by integrators. PLC interfaces on this module only receive and transmit signals of AFEs.
iMOD-PLC121
For more information about Huawei edge computing IoT devices and PLC-IoT communication modules, see the AR502H Series Product Documentation.
- Author: Cui Yunlong
- Updated on: 2021-09-30
- Views: 6895
- Average rating: