What Is NoF?
NVMe is a storage protocol. A data center includes diverse types of storage and computing devices: NVMe data needs to be transmitted between all of them. NoF falls into three types: NVMe over FC, NVMe over TCP, and NVMe over RDMA.
What Is NVMe?
With the rise of the digital economy, data becomes the single most critical factor of production. The explosive data growth that results is placing ever-higher demands on data center storage performance, leading to the emergence of a range of storage technologies, including NVMe over Fabric (NoF), Non-Volatile Memory express (NVMe), Fibre Channel (FC), and Remote Direct Memory Access over Converged Ethernet (RoCE). How do these technologies relate to each other: where do they all fit in?
In the era of hard disk drives (HDDs), SCSI is used as the storage protocol. However, as HDDs cannot keep up with explosive data growth, all-flash solid-state drives (SSDs) come into being as a replacement for HDDs, and the storage protocol has evolved to NVMe. NVMe is effectively a storage language. SCSI is tailored for HDDs, while NVMe is ideally suited for SSDs.
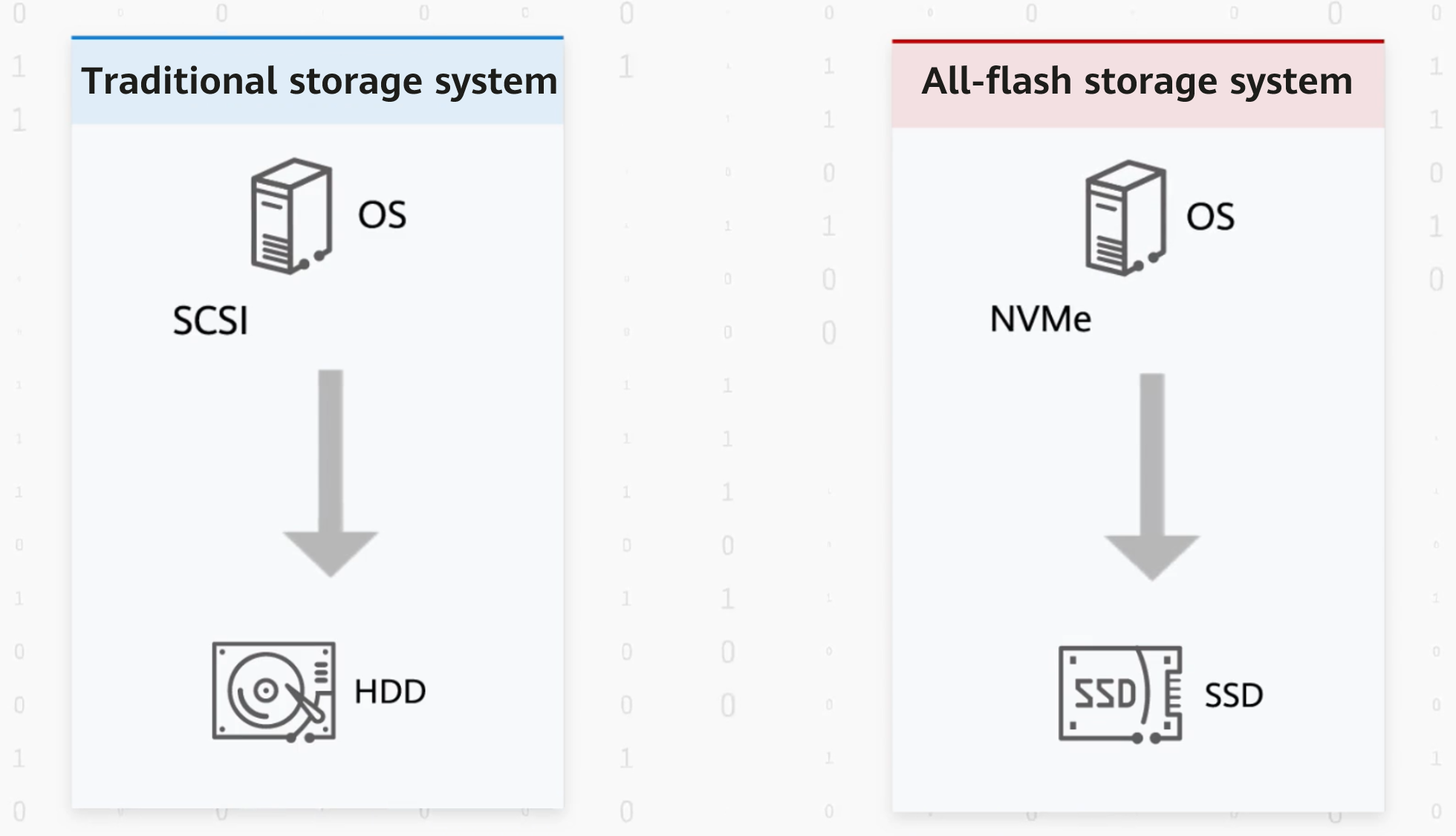
NVMe and SCSI
What Is NoF?
A storage network consists of many storage devices. NVMe is a protocol running on storage devices. How do devices using different languages communicate with each other?
Typical protocols for communication between devices include:
- Fibre Channel Protocol (FCP): FC has been widely used for storage device interconnection since the HDD era and it supports both SCSI and NVMe.
- Transmission Control Protocol (TCP): TCP is a connection-oriented, reliable, and byte stream-based transport layer communication protocol. It can adapt to the protocol hierarchy of network applications. Devices on the network use TCP to provide reliable communication services.
- Remote Direct Data Access (RDMA): RDMA is a technology designed to solve the problem of long delay and packet loss during network transmission. It can directly extract data from storage devices to the storage area of computing devices over the network, without affecting the operation and response of the computing devices.
When NVMe adapts to different types of networks, different technologies come into place, specifically, NVMe over FC for FC networks, NVMe over TCP for TCP-based IP networks, and NVMe over RDMA for RDMA-based networks. All these technologies are collectively called NVMe over Fabric (NoF). The most mainstream NVMe over RoCE is a type of NVMe over RDMA.
NVMe over FC
FC networks emerge very early. In the HDD era, upper-layer adaptation has been implemented for SCSI based on FCP. As such, many enterprises, universities, and scientific research organizations are well prepared in network devices and lines for FC networks in the course of evolution into all-flash SSDs. With the adaptation of FCP to NVMe, NVMe over FC has natural advantages in reuse and affordable device replacement in many scenarios.
NVMe over TCP
The IP network is the most widely used network type for its convenience, good scalability, and strong compatibility. It adopts the best-effort mechanism and therefore requires TCP to ensure the reliability of end-to-end data transmission over the Internet. With NVMe over TCP, storage protocols can be carried over the IP network, maximizing the reach of a storage network.
NVMe over RDMA
RDMA is mainly used in performance-demanding fields such as RoCE. Due to superior performance advantages, NVMe over RDMA has become the first choice for many supercomputing centers, scientific research institutes, and Internet companies. The NoF+ storage network solution pioneered by Huawei is an enhanced solution based on NVMe over RoCE.
More Information
Huawei CloudFabric Data Center Network Solution Intelligent and Lossless Network Best Practices
- Author: Li Yefan
- Updated on: 2023-08-07
- Views: 1706
- Average rating:






