What Is ECA?
To ensure the security of data and application services, more and more traffic is encrypted for communication. Despite the fact that encryption ensures communication security to some extent, it also brings many problems. More and more malware launches network attacks and spreads viruses through encrypted traffic, and 99% of IT personnel consider encrypted traffic as a possible source of security threats.
ECA is a new technology for analyzing encrypted traffic. Instead of decrypting encrypted traffic, ECA uses the machine learning algorithm to train a model based on the handshake information before traffic is encrypted, statistics of encrypted traffic, and background traffic of encrypted traffic, and then uses the model to classify encrypted traffic and identify malicious encrypted traffic. Moreover, ECA protects user privacy and helps users detect potential threats in encrypted traffic to avoid, prevent, or mitigate threats in a timely manner.
Why Do We Use ECA?
With the fast ongoing pace of digital transformation, more and more network traffic is encrypted to ensure communication security and privacy. For example, the HTTPS service is used instead of the traditional HTTP service. However, hackers can use encryption technologies to hide malicious software and commands in encrypted traffic to evade detection and ensure that malicious activities can be implemented properly.
Currently, the solution for detecting encrypted traffic mainly uses the man-in-the-middle (MITM) technology to decrypt traffic, analyze the behavior and content in the traffic, encrypt the traffic again and send the traffic. However, this solution has the following limitations:
- The encryption technology aims to guarantee data privacy. The MITM decryption breaks the original intention of privacy protection, and has risks in channel integrity.
- If the encrypted traffic keeps increasing, decryption consumes a large amount of resources and deteriorates the performance of the existing network.
Based on the analysis and research of encrypted traffic, researchers find that there are many obvious differences between normal encrypted traffic and malicious encrypted traffic both on the client and server. For example, normal encrypted traffic usually uses new and strong encryption algorithms and parameters, whereas malicious encrypted traffic usually uses outdated and weak encryption algorithms and parameters. We can extract such distinguishing features, use the machine learning algorithm to train a model, and then use the model to distinguish between normal and malicious encrypted traffic.
This is where ECA technology comes in. Instead of decrypting encrypted traffic, ECA uses the machine learning algorithm to train a model based on the handshake information before traffic is encrypted, statistics of encrypted traffic, and background traffic of encrypted traffic, and then uses the model to classify encrypted traffic and identify malicious encrypted traffic. The core function of ECA is to detect C&C traffic which is encrypted by the TLS protocol.
How Does ECA Work?
ECA Solution Architecture
The Huawei ECA solution consists of the ECA probe and ECA analysis system. The ECA probe extracts features of encrypted traffic, encodes the features in metadata format, and sends them to the ECA analysis model for analysis. There are two types of ECA probes: independent flow probe and built-in probes on switches or firewalls.
The ECA analysis system detects malicious encrypted traffic based on the Huawei-developed detection model, and is integrated into Huawei's powerful HiSec Insight system. Huawei HiSec Insight system extracts the features of handshake information before traffic is encrypted, time sequence relationship of data packets, flow statistics, and background traffic of encrypted traffic, and uses machine learning to model key features. Then, the system can use the model to classify encrypted traffic and identify malicious encrypted traffic effectively. The following figure shows the solution.
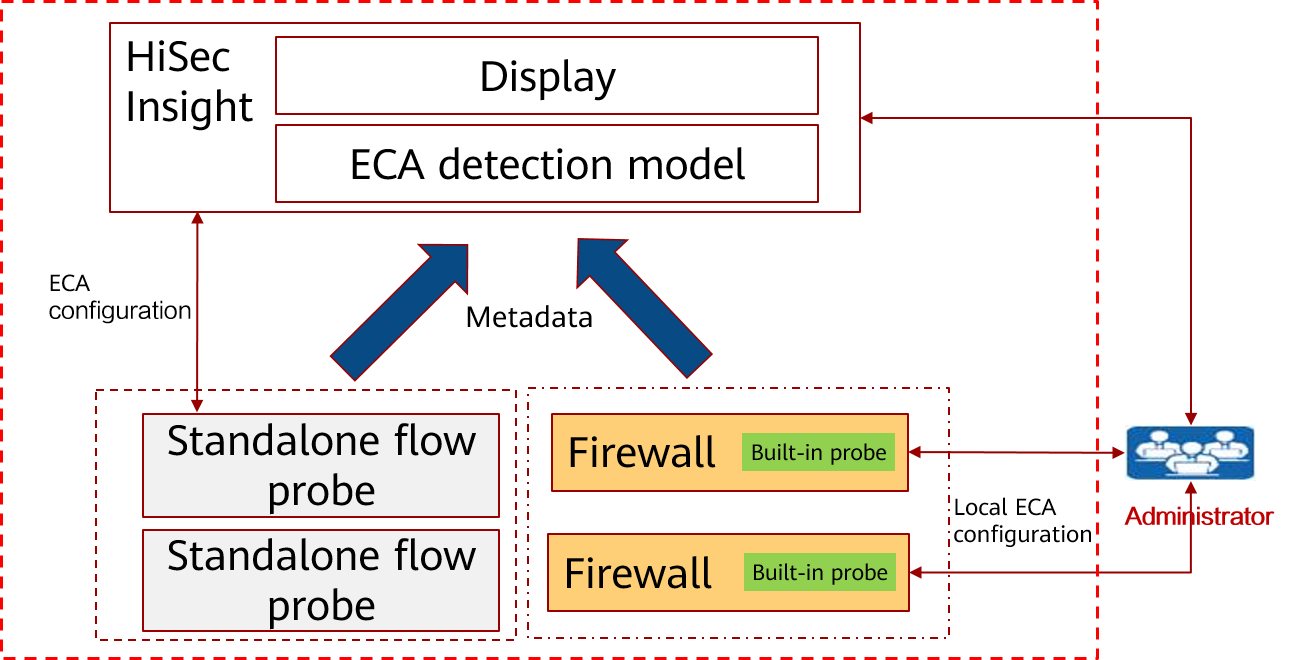
ECA solution
ECA Process
The working process of ECA for analyzing encrypted traffic consists of three parts, as shown in the following figure.
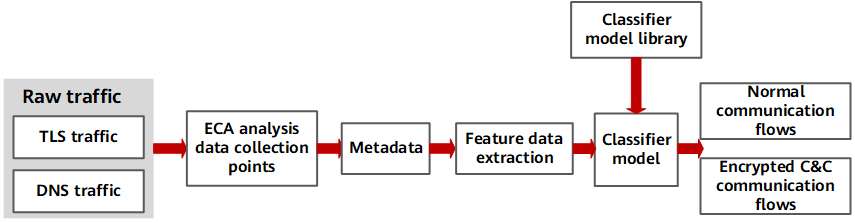
ECA process
1. Mark the samples based on the obtained malware and non-malware sample sets, and queried threat information (including the domain name, IP address, and SSL certificate information). Feature vectors are extracted from handshake information between the server and client of malware and non-malware samples, TCP flow statistical features, and DNS features. The client signature and server certificate signature of malware and non-malware samples are analyzed. Based on the preceding feature vectors extracted from sample data, a classifier model is generated using a machine learning algorithm. This model is the ECA detection model, which is the core of HiSec Insight.
2. Extract features from encrypted network traffic using the ECA probe, including TLS handshake information, TCP statistics, and DNS/HTTP information, and send the data to HiSec Insight.
3. Based on the big data correlation analysis capability, HiSec Insight processes various feature data sent by the probe and uses the ECA detection model to identify abnormal C&C connections in encrypted traffic, thereby detecting abnormal behavior of zombie hosts or APT attacks in the C&C phase.
- Author: Zhu Wenjuan
- Updated on: 2022-08-05
- Views: 2188
- Average rating:






