What Is Mirroring?
Mirroring allows packets from a specified source to be copied to a destination port without affecting packet processing on a network device such as a switch or router. The destination port is directly or indirectly connected to a monitoring device on which analysis software is installed to analyze packets.
When an attack or a fault occurs on the network, the network administrator can use the mirroring function to obtain and analyze packets to find out the attack source or fault cause.
Mirroring can be classified into port mirroring, flow mirroring, VLAN mirroring, and MAC address mirroring based on the mirroring source. For example, port mirroring allows packets in the inbound, outbound, or both the inbound and outbound directions of a specified port to be copied to a destination port.
Mirroring can be classified into local mirroring and remote mirroring based on the connection mode between the destination port and the monitoring device.
How Does Port Mirroring Work?
Port mirroring is used to copy the packets received and/or sent by a specified port on a network device to a destination port. The specified port is called a mirrored port, and the destination port is called an observing port.
As shown in the following figure, when the mirrored port on DeviceA receives or sends packets, it copies the packets to the observing port. The observing port then sends the copied original packets to the monitoring device.
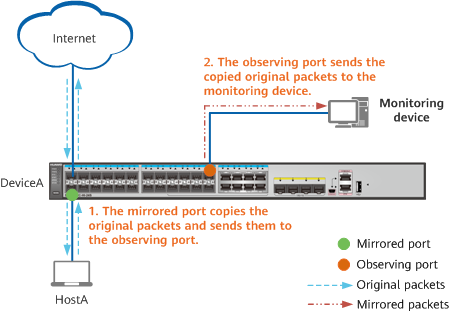
Port mirroring
- Layer 2 remote mirroring Remote Switched Port Analyzer (RSPAN) is used when an observing port is connected to a monitoring device through a Layer 2 network.
- Layer 3 remote mirroring Encapsulated Remote Switched Port Analyzer (ERSPAN) is used when an observing port is connected to a monitoring device through a Layer 3 network.
In the remote port mirroring scenario shown in the following figure, the observing port adds a VLAN tag or performs GRE encapsulation for the copied packets before sending them to the monitoring device. In this way, the copied packets can reach the monitoring device through the intermediate Layer 2 or Layer 3 network.
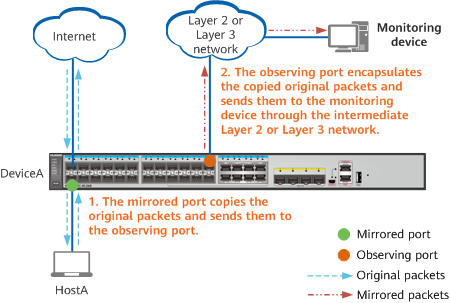
Remote port mirroring
Other mirroring modes are implemented in a similar way as port mirroring as follows:
- In flow mirroring, packets matching a specified rule are copied to an observing port.
- In VLAN mirroring, incoming or outgoing packets on all active ports in a specified VLAN are copied to an observing port.
- In MAC address mirroring, packets with a specified source or destination MAC address in a specified VLAN are copied to an observing port.
What Is Mirroring Used For?
During network maintenance, you may need to obtain and analyze packets. For example, if you suspect that there are attack packets, you need to obtain and analyze the packets without affecting packet forwarding.
Mirroring allows packets on a mirrored port to be copied to an observing port without affecting packet processing. You can use a data monitoring device to analyze the packets copied to the observing port for network monitoring and troubleshooting.
The mirroring function is mainly used for network detection and fault management and may involve some communication information of individual users. Huawei does not independently collect or store user communication information. You are responsible for complying with applicable laws and regulations when enabling related functions used to collect or store user communication information. During user communication information usage and storage, proper measures must be taken to protect user communication information.
Does Mirroring Affect Device Performance?
The mirroring function consumes bandwidth resources of the device, degrading service processing performance and even affecting services. Therefore, disable the mirroring function in a timely manner if it is no longer required, preventing service traffic forwarding performance of the device from being affected.
What Is the Difference Between Port Mirroring and Flow Mirroring?
Both port mirroring and flow mirroring are mirroring functions. In port mirroring, all incoming or outgoing packets on a mirrored port are copied to an observing port. In flow mirroring, incoming or outgoing packets on a mirrored port are filtered, and only the packets that meet the matching conditions are copied to an observing port. In flow mirroring, ACL rules or related configuration commands can be used to specify matching conditions.
- Author: Zhao Fangfang
- Updated on: 2024-01-18
- Views: 11767
- Average rating:






