What Is BMP?
BMP is a protocol used to monitor the BGP running status and BGP route processing trajectory of devices on the network in real time. The BGP running status includes the establishment and termination of BGP peer relationships, as well as route updates. The BGP route processing trajectory indicates how BGP routes on a device are processed, for example, how routes that match an import or export policy are processed.
Without BMP, manual query is required to obtain the BGP running status of devices. This results in low monitoring efficiency. With BMP enabled, a device to be monitored can be connected to a monitoring server and configured to report its BGP running status to the server, significantly improving monitoring efficiency. BMP facilitates the monitoring of the BGP running status and reports security risks on networks in real time so that preventive measures can be taken promptly to improve network stability.
Why Do We Need BMP?
Without BMP, it is not possible to access Local-RIB content of devices or the view of the protocol updates being received using a standard protocol mechanism. Instead, the BGP running status of devices can only be queried manually, which is inefficient. As a network monitoring protocol, BMP eliminates the need for manual query and provides the following benefits:
- More detailed routing information: BMP provides detailed routing information and event notifications in real time, helping network administrators better understand and control the network status. By monitoring all routing information sent from neighboring routers to the local router, BMP can provide comprehensive and accurate information about the routing table.
- Lower impact of network faults: BMP can promptly detect and report various errors and abnormal events, such as connection interruption and retransmission failure. This information helps network administrators quickly identify and handle problems, thereby reducing the impact of network faults on services.
- Higher network performance and security: By analyzing routing information and events, BMP helps network administrators enhance network design and optimize routing policies, improving network performance and security.
- Enhanced network scalability: BMP supports multiple router models and vendors, enhancing network scalability and interoperability.
- Route selection process: BMP can record how each BGP router selects the optimal path and updates the routing table, including the BGP prefix, AS number, and path attributes.
- Routing policy verification: BMP can check and verify the correctness and consistency of routing policies, helping network administrators better manage and optimize the network status.
- Route decision analysis: BMP can compare and analyze the route processing trajectory between different BGP routers to find bottlenecks and problems, improving network stability and reliability.
From a high level perspective, BMP can be considered the result of multiplexing messages received over various monitored BGP sessions. In essence, this provides a more convenient method for monitoring the BGP routing protocol information. BMP helps network administrators better manage and control the network status, improve network performance and availability, and reduce network fault and security risks. As the scale and complexity of networks increase, BMP will become more valuable and have greater application prospects.
How Does BMP Work?
Related Concepts
Adj-RIB-In: Adjacency-Routing Information Base-In, which is the information base that stores the routing information received by the local BGP speaker.
Adj-RIB-Out: Adjacency-Routing Information Base-Out, which is the information base that stores the routing information sent by the local BGP speaker to its peers.
End-of-RIB: a marker and special route attribute used to mark the end of routing information in each address family. This marker indicates that the routing information of the current address family is complete and the routing information of the next address family is about to start. It is used to accurately identify the boundary between different address families.
Local-RIB: Local Routing Information Base. Before the routing information in the Adj-RIB-In is copied to the Local-RIB, the routing information of each address family needs to be marked using End-of-RIB.
Initial table: a collection of the network addresses directly connected to the local router and the corresponding routing information. The information is usually calculated by the router itself and stored in the Local-RIB.
Dump table: a collection of all the routing information received from neighboring routers. The information is stored in the Adj-RIB-In and may be copied to the Local-RIB or Adj-RIB-Out after further processing. If the routing information is lost or damaged, neighboring routers will resend the information to ensure the integrity and accuracy of the dump table.
BMP Message Types
A BMP session involves Initiation, Peer Up Notification (PU), Route Monitoring (RM), Peer Down Notification (PD), Stats Reports (SR), Termination, and Route Policy and Attribute Trace (ROFT) messages, which are sent in packets. Note that BMP sessions are unidirectional. That is, a monitored device reports messages to the monitoring server but ignores any messages from the monitoring server. The functions of these messages are as follows:
Initiation message: reports to the monitoring server such information as the device vendor and software version.
PU message: notifies the monitoring server that a BGP peer relationship has been established.
RM message: reports all routes received from BGP peers to the monitoring server and notifies the server of route addition or deletion in real time.
PD message: notifies the monitoring server that a BGP peer has been disconnected.
SR message: reports router running statistics to the monitoring server.
Termination message: reports to the monitoring server the cause of BMP session closure.
- ROFT message: reports the route processing trajectory to the monitoring server in real time.
Implementation
After a BMP session is established, the monitored device starts to send BMP messages to the monitoring server. The process is as follows:
- A BMP session starts when the monitored device sends an Initiation message.
- The monitored device reports PU and RM messages.
- After the initial table is dumped, the monitored device sends incremental updates encapsulated in RM messages and periodically sends SR messages as configured. It also sends PU or PD messages if a new monitored BGP peer relationship is established or if such a BGP peer relationship exits the established state, respectively.
- The monitored device sends a ROFT message through the BMP session as configured.
- When the TCP session is closed for any reason, the BMP session over the TCP session exits. Before the TCP session is closed, the monitored device can also send a Termination message for proactive disconnection.
Application and Deployment
BMP can be widely used on networks of different scales, such as ISPs, enterprise networks, and data centers. It can be integrated with an existing monitoring system to listen to standard TCP ports and collect BGP information in order to obtain comprehensive details about the network status. As shown in the following figure, a TCP connection is established between the monitoring server and PE1 and another between the monitoring server and PE2. PE1 and PE2 send unsolicited BMP messages to the monitoring server to report BGP running statistics. After receiving these BMP messages, the monitoring server parses them and displays the BGP running status in the monitoring view. By analyzing the headers in the BMP messages, the monitoring server can decide which BGP peers have advertised the routes carried in these messages.
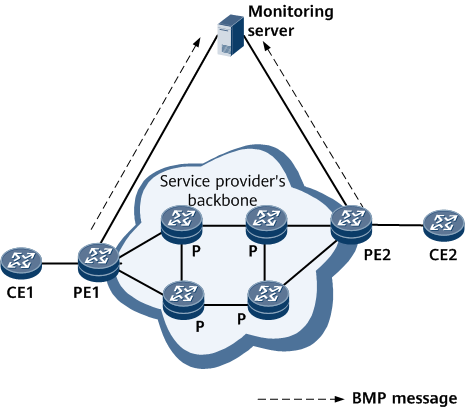
Typical BMP networking
Development Trend
The rapid development of emerging technologies, such as cloud computing, IoT, and 5G, increases the network scale and complexity and consequently imposes higher requirements on network monitoring and management. As a new network monitoring protocol, BMP will develop in the following aspects:
- More efficient data transmission: As network traffic keeps increasing, BMP requires a more efficient data transmission mechanism to ensure that routing information can be obtained and processed promptly.
- More types of data: In addition to basic routing information, BMP supports other types of data, such as AS paths and notification timestamps, and it may support more types of data in the future.
- More flexible configuration options: BMP requires more flexible and easy-to-configure options to adapt to different network environments and requirements.
- Fine-grained routing control: BMP provides more detailed and accurate routing information. In the future, BMP may work with other technologies to implement fine-grained routing control and management.
In general, as a new type of network monitoring protocol, BMP has broad application prospects and development space and will be further optimized to meet increasingly complex and diversified network monitoring requirements.
- Author: Wang Shishi
- Updated on: 2023-07-20
- Views: 2390
- Average rating:







