What Is SOAR?
Security Orchestration Automation and Response (SOAR) is a collection of technologies that helps enterprises and organizations collect various information monitored by security O&M teams, analyze incidents, and classify alarms based on the information. Under the guidance of playbooks, SOAR leverages the human-machine mode to help security O&M personnel define, sort, and trigger standardized incident response activities.
Background of SOAR
With the increasingly fierce attack-defense confrontation of network security, it is not effective to protect networks solely by prevention techniques. Instead, more attention must be paid to detection and response measures. Enterprises and organizations need to build a brand-new security protection system that integrates blocking, detection, response and prevention on the assumption that the network is attacked.
It is against this background that detection and response products have attracted great attention. In China, new detection products are growing in popularity, especially in the field of unknown threat detection. With these products and technologies, users can detect attacks and intrusions more accurately with lower mean time to detect (MTTD). However, most of these products and technologies are unable to help users reduce mean time to recovery (MTTR). From user's perspective, quickly responding to problems is actually more important than quickly detecting them. When improving the security response efficiency, security personnel need to consider not only a single point (endpoint or network), but also the overall security O&M of the entire network. In other words, we need to integrate scattered detection and response mechanisms. This is where SOAR provides a solution to the issue.
Core Capabilities of SOAR
In terms of functions, SOAR has the following core capabilities:
- Alarm classification and priority definition: This function enables the operations team to focus on threat alarms that have a significant negative impact on or cause serious damage to the organizations, reducing alarm fatigue.
- Case set management and collaboration: Case sets contain the experience in response and handling, which can be referenced by security analysts to improve analysis efficiency. Advanced capabilities such as automatic playbook recommendation can be implemented using technologies like feature extraction and machine learning.
- Orchestration and automation: This function integrates different security tools into one process and automatically runs them, which significantly improves operational efficiency and reduces the impact of threats on the network environment. SOAR needs intuitive UI tools so that users can easily orchestrate and design playbooks. It also needs to integrate with a wide range of known and unknown security products, such as firewalls, endpoints, sandboxes, and email and SMS gateways.
- Threat intelligence investigation: This function provides forensic information for threat identification through threat intelligence database, improving the handling accuracy. This process can be orchestrated in a workflow and the best handling method can be selected based on the forensic result.
In terms of architecture, SOAR ensures high reliability and availability through redundancy and elastic scaling, focuses on the orchestration execution performance, provides comprehensive permission management, and supports on-premises and cloud-based deployment.
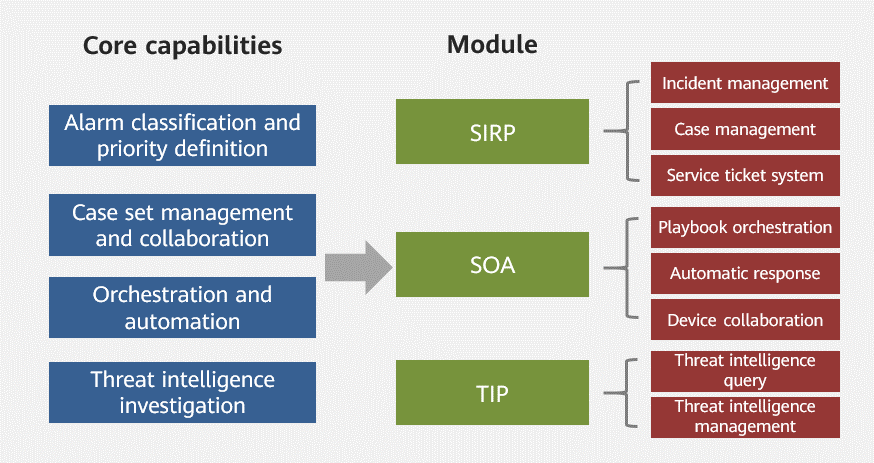
The corresponding product modules to SOAR core capabilities include security incident response platform (SIRP), security orchestration and automation (SOA), and threat intelligence platforms (TIP).
- SOA
As the core of the entire service, SOA shapes a brand-new security response mode which supports both the manual and automatic handling of the security incidents. SOA orchestrates various response actions and associates related device instances to execute threat response actions when a specific incident occurs.
If the orchestration process depends on the APIs of related systems, the orchestration can be automatically executed. In addition to automatic orchestration, manual orchestration and partial automatic orchestration are provided. Both automatic and manual orchestration can be executed in playbooks. The engine that generates the playbook is typically the workflow engine. To make it easier to maintain the playbooks, SOAR usually provides a visualized playbook editor.
- SIRP
SIRP is a platform for responding to and handling security incidents, and has been around before SOAR. However, SOAR greatly improves the response capability. Generally, security incident response includes alarm management, work order management, and case management.
- TIP
TIP is a marketing segment defined by Gartner in 2014. It collects, associates, classifies, shares, and integrates multi-source threat intelligence, and integrates with other systems to help users block, detect, and respond to attacks. Threat intelligence exists mainly in the form of services rather than platforms. Currently, the TIP market is small and has few vendors. Some TIPs exist independently, some depend on threat intelligence services, and some are packaged with security response into SOAR offerings.
What Are the Differences Between SOAR and SIEM
Both SOAR and Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) collect information and mark exceptions. However, there are significant differences between them:
- SIEM initially functions as a compliance reporting tool, mainly used to record and manage a large amount of security incident data.
- SOAR aims to add security-oriented functions, such as orchestration, automation, and response, which are lacking in most standard SIEM offerings. SOAR performs automatic responses through automated playbooks or workflows and machine learning.
With the development of the global security industry, the SOAR market has become increasingly mature. SOAR has been integrated into other security products as a capability, such as security operations center (SOC), SIEM, and managed detection and response (MDR). SIEM vendors have been building SOAR through acquisitions or self-development to improve incident response capabilities. There is also some market space for independent SOAR products. Compared with integrated SOAR products, users attach more importance to their flexibility and neutrality.
Benefits of SOAR
The benefits of SOAR are reflected in the following aspects:
- Reduce alarm fatigue
Gartner defines SOAR as a solution that combines incident response, orchestration and automation, and threat intelligence. These technologies were once provided to customers as independent products. However, too many single-point solutions bring pressure on budget and workforce, and the complexity and repeatability of tools can inundate administrators with a large number of daily alarms, resulting in alarm fatigue. Through integration and automation, SOAR can effectively reduce unnecessary alarms.
- Improve response speed
As attacks spread at an increasingly rapid pace, merely sending alarms and notifications after detecting potential threats is no longer enough. Customers now demand security services that can quickly and proactively prevent threats from causing harm to their network environment. To achieve this, SOAR plays a crucial role in proactive threat response and handling.
- Improve security operational efficiency and incident resolution rate
Through orchestration, SOAR integrates multiple phases — such as forensic investigation, handling, and notification — into one workflow, and automatically schedules and runs the workflow. This reduces the need for operations personnel to switch between different tools. In the face of increasing threats, the automation capability of SOAR helps improve the overall security operational efficiency.
- Accumulate security operational experience
Through playbook orchestration, the threat handling process can be converted into a workflow that can be saved for future reference. This allows for accumulation and consolidation of security operational experience. In addition, the case set summarizes the historical threat handling experience and supplements features, which can be referenced by security experts.
- Improve integration capabilities
SOAR can integrate existing security products in the network environment to implement effective human-machine and machine-machine collaboration.
- Accelerate the requirement implementation
In hard coding mode, customers' new service requirements can be implemented only after version upgrades. In the on-premises deployment, the long iteration periods of versions negatively affect customer satisfaction. However, the inherent low-code orchestration capability of SOAR makes the system open. With this capability, security operations teams can easily create and improve workflows, helping customers rapidly implement requirement changes.
SOAR Practice in Huawei HiSec Insight
HiSec Insight is a security situation awareness product launched by Huawei, and functions similarly to SIEM products. Based on the big data platform, HiSec Insight security situation awareness system integrates threat detection, threat blocking, forensics, source tracing, response, and handling, helping customers resolve threat incidents throughout the entire process.
The resolution capability of HiSec Insight is attributed to the integration of Huawei-developed SOAR components in 2019. With SOAR, the incident handling period of HiSec Insight is shortened from days to minutes, MTTR is greatly reduced, and the incident resolution rate and handling rate are significantly improved.
In addition, the response and orchestration capabilities provided by SOAR make HiSec Insight the only Chinese product listed in Gartner's MQ for two consecutive years. Therefore, SOAR is of great importance.
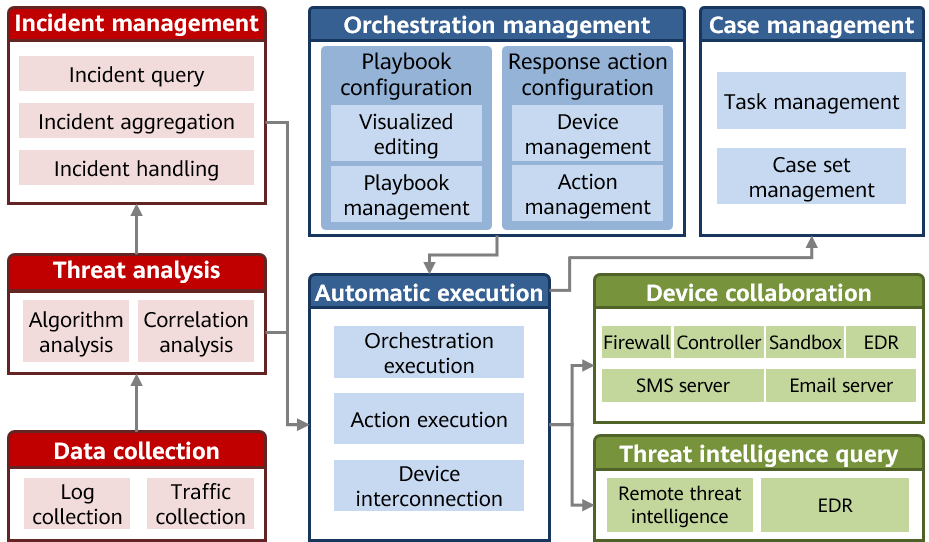
The following figure shows the basic architecture of HiSec Insight SOAR.
- Data collection
HiSec Insight can collect mirrored traffic and security logs in multiple formats. After preprocessing the collected data, HiSec Insight sends it to the threat detection module for analysis.
- Threat analysis
The threat analysis engine uses technologies such as correlation analysis, AI detection, and threat identification to discover and classify threat incidents, as well as set incident priorities. If a playbook matches the incident, SOAR immediately handles the incident according to the playbook process.
- Incident management
In HiSec Insight, incident management is an independent service that provides incident query and management capabilities. Users can select playbooks to orchestrate specific aggregated incidents.
- Orchestration management
Orchestration management includes response action configuration and playbook configuration.
- Response action configuration is used to encapsulate security products, including device configuration information such as the authentication mode, access credentials, and access address, as well as APIs. HiSec Insight has a large number of preset security device types (mainly Huawei devices) and response actions, and supports the interconnection with third-party devices.
- Playbook configuration includes the playbook editing and management. HiSec Insight SOAR provides a visualized playbook editing tool that allows users to create playbooks through drag and drop operations. The editing tool adopts the mainstream vertical typesetting mode. It has multiple built-in nodes such as response action, filtering, condition judgment, aggregation, manual decision-making, and data formatting, and gradually supplements capabilities such as sub-process nesting and looping.
Through a large number of preset playbooks and actions, HiSec Insight transfers security experience to customers and provides them with out-of-the-box capabilities.
- Automatic execution
HiSec Insight SOAR provides two methods of triggering playbook execution: automatic execution and manual execution. Automatic execution is triggered by matching the incident type. Manual execution is triggered by selecting a proper playbook for incident handling.
During playbook running, the execution engine calls the threat intelligence system for forensics, and then determines the subsequent process based on the forensic result. According to the preceding description, the key to orchestration is calling different security tools, which is also implemented by the orchestration execution engine. HiSec Insight SOAR interconnects with various security tools, systems, and services, including users' third-party devices, based on the configured actions.
- Case management
The playbook execution result is generated as a task for archiving and viewing. Tasks of the same incident type are automatically aggregated to form a case set, which provides references for analysis by security experts.
- Author: Jiao Cuicui
- Updated on: 2023-09-05
- Views: 1254
- Average rating: