What Is the CloudWAN Solution?
The CloudWAN solution provides a cloud-based WAN. It is optimized for use on backbone networks between enterprise campuses and clouds, between enterprise campuses, and between clouds, connecting enterprise branches, campuses, traditional data centers, public clouds, and private clouds. This implements agile cloudification of enterprise services, industrial interconnection between enterprise campuses, and inter-cloud interconnection, providing abundant computing power and momentum for accelerating enterprise digital transformation.
Why Do We Need the CloudWAN Solution?
A WAN is an interconnection network used for long-distance communication between enterprises or organizations. With coverage ranging from tens to thousands of kilometers, WANs enable information and resource sharing over vast distances. Typically, enterprises lease links from carriers or build their own links for long-distance communication.
Global digitalization is accelerating as the fourth industrial revolution — characterized by the use of intelligent technologies — continues to gather pace. More than 50 countries have developed digital strategies and plans, such as China's new infrastructure initiative and the EU's recovery plan, to boost their digital economy development and social transformation. The new infrastructure (such as that involved in China's "east-to-west computing resource transfer" project) covers information, convergence, and innovation. The WAN is not only an important part of the information infrastructure, but also a key enabler of the convergence infrastructure and innovation infrastructure. As a link, the WAN connects enterprise factories, branches, cloud platforms, intelligent products, and users. At the same time, it breaks data silos, supports quick implementation of innovative services and applications, and enables efficient collaboration between various fields. The key to the digital transformation of enterprises is data value mining, and the prerequisite to this is efficient data circulation. Indeed, the WAN is the foundation for data connection and convergence. In order to achieve more efficient collaboration and connection in various fields, and to accelerate digital transformation of numerous industries, it is imperative that the flow of data be made more robust and efficient. While enterprise digital transformation improves production efficiency, it also brings the following challenges to WANs:
Challenge 1: Segment-based O&M of traditional WANs results in inefficient network provisioning and non-agile enterprise cloudification.
Enterprise cloudification changes the connection mode of traditional enterprise WANs. Traditional enterprise applications are mostly deployed on local servers in the headquarters. In this case, the WAN only needs to implement communication between branches and the headquarters, typically adopting the Point-to-Point (P2P) connection mode. As enterprise applications are deployed on clouds, the WAN is used to connect branches and the headquarters to these clouds in Point-to-Multipoint (P2MP) or Multipoint-to-Multipoint (MP2MP) mode.
Traditional WANs typically use MPLS and maintenance is conducted by multiple departments. Service deployment is based on manual segment-based configuration, which is time-consuming and cannot match the cloud deployment speed. The following figure illustrates segment-based service deployment using a bank's information center as an example. While the cloud deployment of a new outlet takes less than 1 hour, the entire deployment takes more than 30 days. This is because the network connection involves the collaboration of multiple departments, such as outlets, tier-2 branches, provincial branches, and headquarters. Consequently, the overall service rollout is severely delayed. Due to the lack of a unified WAN backbone network, an enterprise needs to lease multiple site-to-cloud private lines based on the deployment locations of different clouds. Building a new cloud data center means that all network and cloud connections need to be established from scratch. This results in complex connections, difficult segment-based deployment, and lengthy service monetization.
How to implement agile cloud migration for enterprises and on-demand flexible connection of any cloud has become one of the key challenges for WANs.
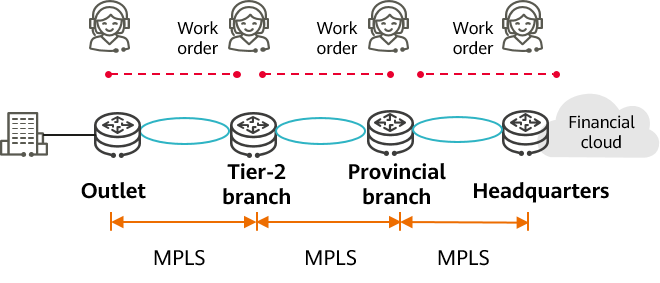
Segment-based service deployment
Challenge 2: Production networks are IP-based, meaning that the network SLAs cannot be guaranteed.
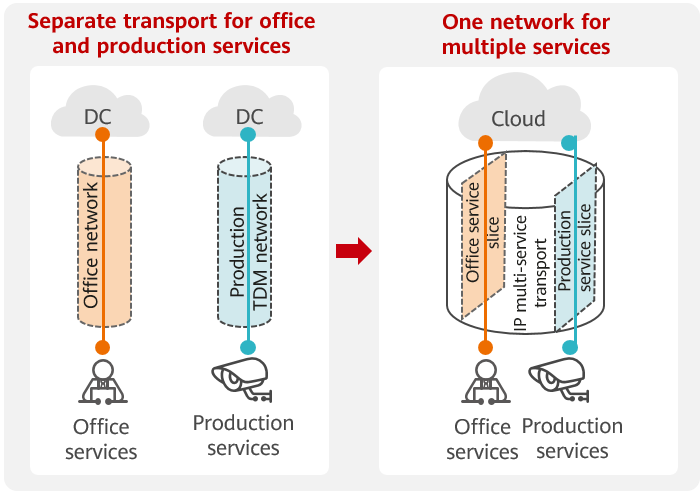
Production, manufacturing, and interaction are core services of an enterprise and have strict requirements in terms of security and stability. To ensure that these services are not affected by other services, production networks are typically dedicated Time Division Multiplexing (TDM) networks, which are isolated from office networks and traditionally use protocols of different standards. Because multiple networks need to be constructed independently, costs are high, bandwidth is low, and openness is poor. Furthermore, many data silos are created. This not only restricts the efficient flow of data and control streams, but also makes it difficult to develop emerging services.
For example, in China's energy sector, the total length of oil and gas pipelines is expected to exceed 160,000 km, making it difficult to continue using conventional manual inspection. As such, drone inspection will become a new security assurance method. Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs) need to access different base stations for remote control and signal backhaul. However, traditional production networks cannot meet the requirements of UAVs for anywhere, anytime access and flexible connection due to poor openness. And in the transportation sector, as trains run quicker on high-speed railways, the train control and dispatching mode gradually shifts from manual monitoring to over-the-horizon monitoring. Cameras and sensors are used to transmit information about safety conditions around trains to edge gateways for processing so that hazards and faults can be predicted, greatly improving traveling safety. However, over-the-horizon monitoring requires the network bandwidth to be greater than 100 Mbit/s, which exceeds what a traditional production network can deliver.
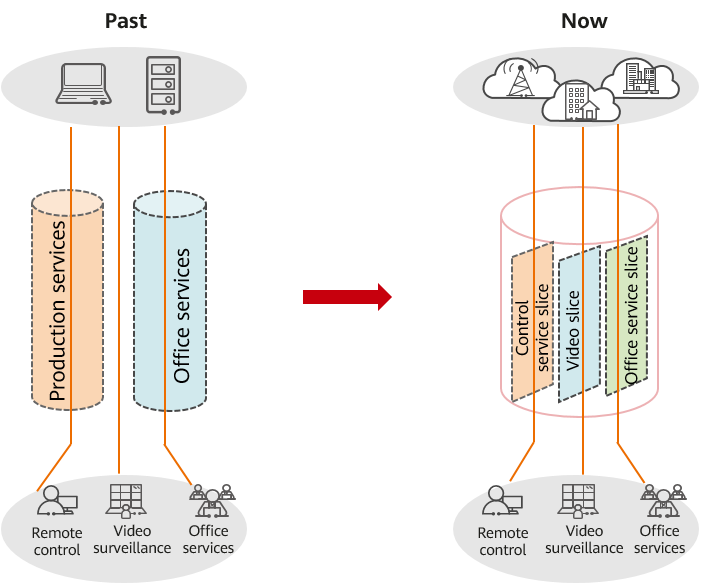
As core production systems are migrated to the cloud, it is an inevitable trend for enterprise digital transformation to carry multiple services on one IP WAN due to factors such as construction costs, O&M, and rapid service expansion. Different services have different requirements on network latency and bandwidth. How to carry multiple services on a single network and meet the SLA requirements of different services is also a key challenge for WANs.
Network convergence trend
Challenge 3: Cloud-network resource utilization is unbalanced, and enterprises frequently perform passive capacity expansion.
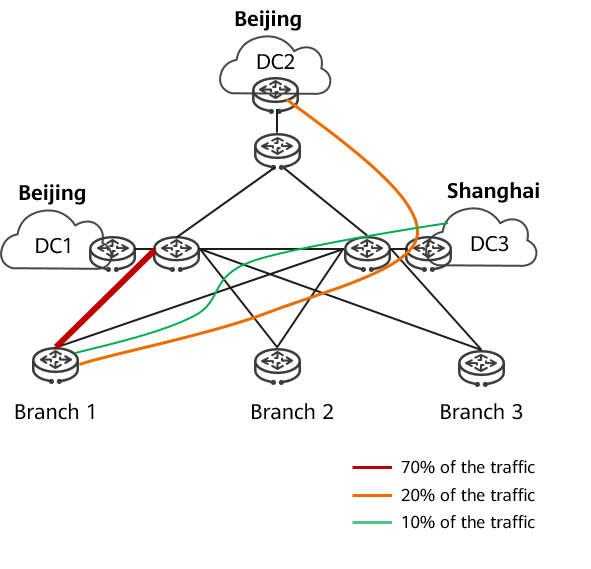
Traditional WANs forward packets based on the shortest path. As a result, the resource utilization of both the cloud and the network is unbalanced. Some nodes are full of resource data while some nodes are idle or their resource utilization is low. As the overall network traffic increases year by year, enterprises passively invest in capacity expansion of some nodes or links, leading to waste. An example of this can be seen in the following figure. 70% of traffic sent from enterprise branch 1 is to the primary data center in Beijing, 20% is to the backup data center in Beijing, and 10% is to the data center in Shanghai. As time goes by, the capacity of the primary data center in Beijing will be expanded continuously, while the resources of the other two data centers will be idle. Furthermore, cloud data center construction leads to a sharp increase in traffic between the enterprise and cloud data centers and between cloud data centers, exacerbating this problem. How to effectively balance cloud-network resource utilization is also a major challenge for WANs.
Unbalanced traffic distribution
Challenge 4: In the cloud era, the number of network connections increases by hundreds of times, and connections are complex and difficult to maintain.
Traditional O&M lacks E2E automation capabilities and instead responds passively to customer complaints. Manual fault locating, segment-by-segment troubleshooting, and path adjustment are time-consuming and labor-intensive, resulting in low O&M efficiency. And with the development of technologies such as the Internet of Things (IoT) and 5G, various smart terminals and applications emerge one after another. Furthermore, enterprise access terminals change from a single type of office PC to various types of smart terminals, and the quantity increases 100-fold. The applications of smart terminals, such as video protection and drone inspection, greatly improve the production efficiency of enterprises. However, massive terminal connections make services more diversified and network connections more complex, posing severe challenges to traditional O&M modes. How to improve O&M efficiency and implement intelligent O&M is a must for WANs.
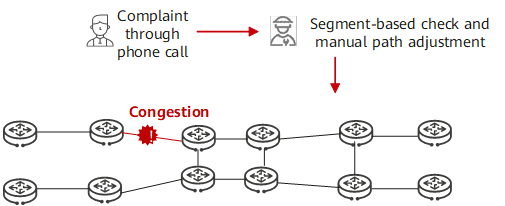
Traditional O&M modes
To address these challenges, the CloudWAN solution is launched. This solution is a next-generation agile, intelligent, and secure WAN solution based on IPv6 Enhanced — a digital infrastructure intelligent foundation. The CloudWAN solution uses key technologies such as SRv6, network slicing, intelligent cloud-map algorithm, and In-situ Flow Information Telemetry (IFIT).
What Are the Key Capabilities of the CloudWAN Solution?
The CloudWAN solution uses key technologies such as SRv6, network slicing, intelligent cloud-map algorithm, and IFIT. It also uses iMaster NCE-IP for unified control and management to implement automatic deployment of enterprise cloud services, SLA assurance for key services, intelligent network traffic optimization, service visualization, fast O&M, and more. The solution offers the following key capabilities:
Intelligent Connectivity
The CloudWAN solution enables the construction of a cloud WAN backbone network, to which various cloud resources and enterprise sites are connected through cloud PEs and network PEs, respectively. In this solution, SRv6 is used to overcome process barriers and implement flexible cloud-network connections, solving the problem of time-consuming service cloudification caused by multi-level cross-domain collaboration. In the entire process, services are automatically provisioned through iMaster NCE-IP. Configurations need to be performed only on the enterprise and cloud sides, meaning that services can be provisioned within minutes. The CloudWAN solution also meets the different cloudification requirements imposed by diverse user services. For example, bank services need to access different clouds, office services need to be migrated to the public cloud, and production services need to be migrated to the industry cloud. The CloudWAN solution enables cloud paths with different latency and bandwidth to be generated for different services, assuring the SLA of the services. Cloud paths are configured for services instead of nodes or ports, helping users quickly and agilely access cloud services and implementing cloud access upon network access, as shown in the following figure.
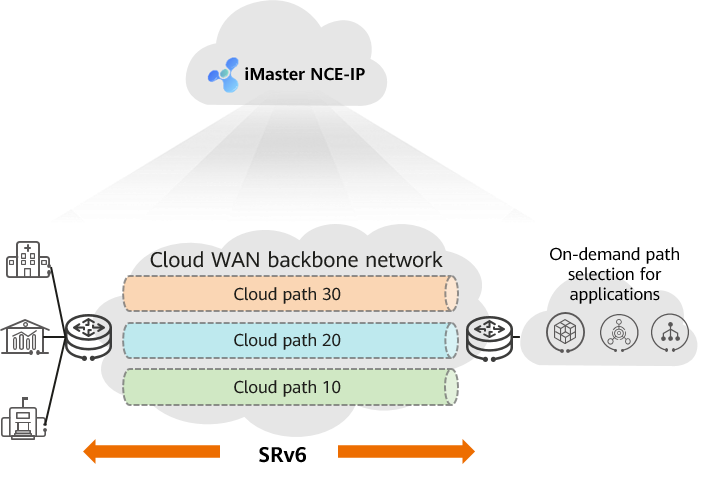
Differentiated cloud paths of the cloud WAN backbone network
Deterministic Experience
The CloudWAN solution uses the hierarchical slicing technology to divide a physical network into multiple slices, enabling one network to carry multiple services. For example, control, video, and office slices respectively carry control, video, and office services. This achieves full security isolation of production and office services, refined SLA assurance, and deterministic service experience.
Hierarchical slicing
Unified O&M
The CloudWAN solution uses IFIT to monitor service SLAs, enabling automatic demarcation of disconnection faults. More than 80,000 network KPIs are collected in real time to implement in-depth service quality awareness and real-time visualization of network-wide service SLAs, including the latency, jitter, packet loss, and perceived bandwidth. The knowledge graph algorithm is used to intelligently associate massive volumes of network data (which is often discrete and fragmented) and historical fault information to predict network exceptions, slashing the time required to locate the root cause from days to minutes. In addition, many typical network risks can be proactively identified, with the success rate reaching 90% (up from 60%).
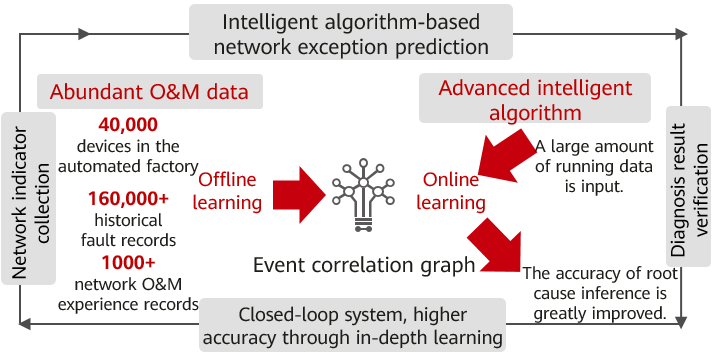
Intelligent O&M
Secure Services
The CloudWAN solution provides protection for the forwarding, protocol, and control planes, enabling all-round security protection. In forwarding plane, the high-performance IPsec subcard VSUI-100 is supported. In addition, the GE/10GE/100GE full-rate MACsec subcard is supported to encrypt key services. These subcards can be inserted and used on demand, reducing customer Capital Expenditure (CAPEX). In protocol plane, the Topology-Independent Loop-Free Alternate (TI-LFA) mechanism is supported to protect any-topology networks, and protection switching within 50 ms ensures service continuity in any fault scenario. In control plane, devices support mechanisms such as multi-level CPU-CAR and BGP FlowSpec anti-DDoS to protect against external attacks.
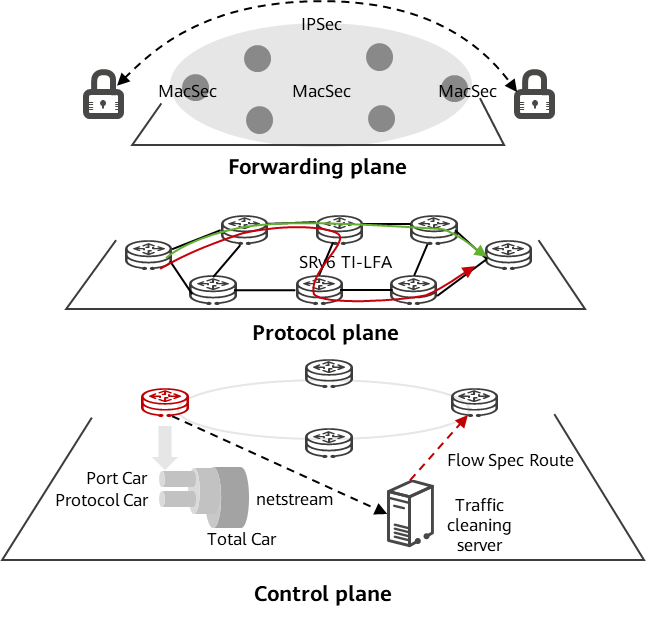
Secure services
Architecture of the CloudWAN Solution
The overall architecture of the CloudWAN solution consists of the management and control layer, virtual network layer, and physical network layer, as shown in the following figure.
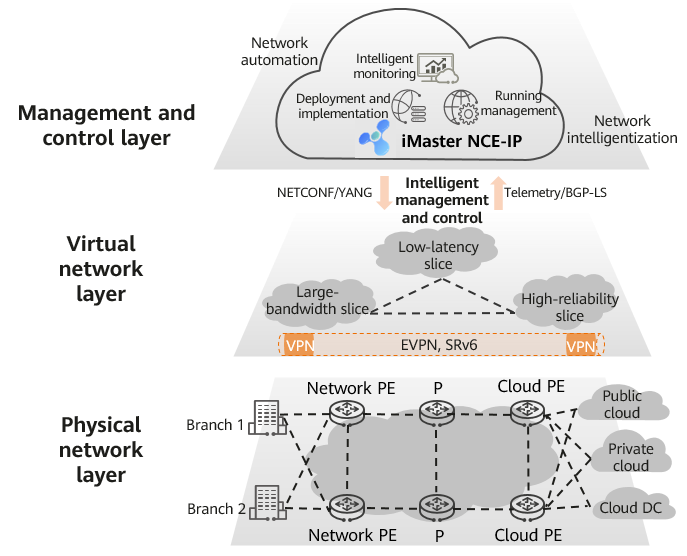
Overall architecture of the CloudWAN solution
Management and Control Layer
The CloudWAN solution uses the automatic and intelligent O&M platform — iMaster NCE-IP — to manage and control the virtual and physical network layers. iMaster NCE-IP uses technologies such as telemetry and BGP-LS to collect network topology, link, service, and other information in real time. It performs in-depth analysis on the quality and traffic data of the entire network, and displays awareness data such as the network topology, device health status, protocol status, and service experience results on GUIs, implementing visualized network management and O&M. iMaster NCE-IP features the following key capabilities:
- Management capabilities: It provides traditional management capabilities for device configurations, alarms, performance, links, and Quality of Service (QoS), in addition to automated E2E service provisioning capabilities for traditional networks.
- Control capabilities: It provides SDN-oriented control capabilities. Based on the NETCONF/YANG model, SRv6 network programmability technology, and SDN path computation technology, iMaster NCE-IP can compute optimal forwarding paths and quickly deliver service configurations.
- Analysis capabilities: It provides real-time data collection, status perception, in-depth analysis, and intelligent prediction capabilities for network traffic and performance. Based on big data analytics and IFIT, iMaster NCE-IP can proactively identify faults, detect potential risks, and provide warnings.
Virtual Network Layer
The CloudWAN solution can virtualize a physical network into multiple network slices, with each slice capable of serving one or more services. While different network slices share devices and links on the physical network, services and bandwidth resources on the network slices are isolated and decoupled from each other. Different EVPN instances can be used to logically isolate services in each network slice.
Enterprise services, such as production, office, video, and Internet access, have different network SLA requirements. During service planning, enterprises can allocate different services to different network slices to implement logical isolation and bandwidth isolation between the services, ensuring application experience of high-value services.
Physical Network Layer
The CloudWAN solution is optimized for use on backbone networks between enterprise campuses and clouds, between enterprise campuses, and between clouds, connecting subnets, campuses, traditional data centers, public clouds, and private clouds.
Typically, the backbone network adopts a hierarchical design consisting of the core, aggregation, and access layers. For small- and medium-sized networks, a flattened design consisting of only the core and access layers can also be adopted. To ensure network reliability, the dual-plane design is used. Specifically, each site uses two devices, and the access, aggregation, and core devices are interconnected in single-homed networking mode.
From the perspective of functions, network devices include network PEs, Ps, and cloud PEs.
- Network PE: a device responsible for network and user access. It connects to lower-level subnets or campus networks.
- Cloud PE: a device responsible for cloud and data center access. It implements access of public clouds, private clouds, and cloud data centers.
- P: a device that provides high-speed connections between cloud and network PEs.
What Key Technologies Are Used in the CloudWAN Solution?
SRv6, Enabling Network Automation
By introducing iMaster NCE-IP and SRv6, the CloudWAN solution implements agile service cloudification in addition to meeting differentiated SLA requirements.
Based on native IPv6, SRv6 integrates the network programming capability of Segment Routing. SRv6 TE Policy leverages the source routing mechanism of Segment Routing to guide packet forwarding based on an ordered list of segments encapsulated by the headend. Thanks to iMaster NCE-IP and SRv6 TE Policy, provisioning end-to-end services in enterprise cloudification scenarios does not require any manual intervention. Consequently, the configuration process can be based entirely on the cloud and SDN. According to enterprises' business requirements, iMaster NCE-IP can generate cloud paths with different service quality, latency, and bandwidth indicators in minutes, thereby implementing quick deployment of cloud services.
Network Slicing, Providing Dterministic SLA Assurance
Using hierarchical slicing, the CloudWAN solution enables multiple logical networks to be created over one physical network for multi-service transport and deterministic SLA assurance. Network SLAs mainly involve latency and bandwidth, which network slicing can control and guarantee, respectively, to safeguard mission-critical services.
In order to create network slices, interface forwarding resources must be partitioned on a physical network. The CloudWAN solution uses Flexible Ethernet (FlexE) as the resource partition technology, which pools physical interface resources based on timeslots to implement flexible and refined management of interface resources. Specifically, this technology flexibly divides a high-bandwidth physical interface into several sub-channel interfaces (FlexE interfaces) through timeslot resource pools. A FlexE interface functions like a physical interface, with its bandwidth resources being strictly isolated from those of other FlexE interfaces. After all physical interfaces of devices along a link are divided using FlexE, network slicing at the physical layer is implemented.
Intelligent Cloud-Map Algorithm, Improving Resource Utilization
The intelligent cloud-map algorithm is a vital part of the CloudWAN solution. In this solution, iMaster NCE-IP is used to collect network-wide information (such as path latency and bandwidth), compute E2E optimal forwarding paths based on the collected information, and steer traffic to these paths. In addition to network factors such as bandwidth and latency, the intelligent cloud-map algorithm considers cloud pool load factors. Based on SRv6 and SDN technologies, the algorithm can quickly match and schedule services to the most appropriate cloud pool.
The path computation result obtained by the intelligent cloud-graph algorithm may not be the shortest path in the physical sense. Instead, the path is the optimal cloud migration one selected based on network and cloud factors. Network factors include bandwidth, reliability, and latency, and cloud factors include cost, computing power, and resource utilization. The intelligent management and control platform iMaster NCE-IP comprehensively computes different service paths of different cloud pools and determines both the optimal cloud migration path and service cloud pool based on the serviceable cloud pool information collected by the cloud management platform.
IFIT, Building a Closed-Loop Intelligent O&M System
Through IFIT, the CloudWAN solution makes it possible to visualize and manage service experience.
IFIT directly measures network performance indicators such as the latency, packet loss rate, and jitter by adding IFIT headers to real service packets. It uses telemetry to report measurement data in real time to iMaster NCE-IP, which then displays network performance indicators through its GUI. After IFIT is deployed on a network, the actual forwarding path of packets can be restored. Thanks to telemetry enabling the collection of data within seconds, network SLAs can be visualized in real time and faults can be quickly demarcated and automatically rectified, building a closed-loop intelligent O&M system.
What Are the Successful Applications of the CloudWAN Solution?
The CloudWAN solution has been applied to the government, finance, transportation, electric power, ISP, and other sectors.
Building a Smart Government Network for the Government Sector
With the digital evolution of society, countries have issued policies to drive the digital transformation of governments.
With a combination of the vertical WAN and horizontal metro network for multi-level governments, a company in Argentina uses the CloudWAN solution to build a next-generation intelligent backbone network based on advanced IPv6 Enhanced technologies, such as SRv6 and IFIT. The solution effectively solves problems — such as slow service provisioning, poor experience, and difficult O&M — that affected the original e-Government network, further consolidates support for the digital government's foundation, and provides strong network assurance for Argentina's government services and governance.
Building an Agile, Stable Financial DCI Backbone Network for the Financial Sector
To interconnect its financial data centers, a bank in Germany uses the CloudWAN solution. This enables the bank to greatly improve its service efficiency and experience, effectively support its financial technology strategy.
The CloudWAN solution meets the bank's current and future requirements for changing single-cloud data centers into multi-cloud data centers, helping the bank build an agile, stable financial DCI backbone network. This implements minute-level rollout and high-reliability provisioning of financial services, and provides customers with convenient, differentiated, and comprehensive scenario-based financial services.
Building an Intelligent Railway Cloud-Network for the Transportation Sector
After analyzing its ICT status, a railway company in Spain decided to abandon the traditional SDH network. It uses the CloudWAN solution to build a highly reliable, flexible, and evolvable railway operational communication network, implementing the digital and intelligent construction of railway data networks. In the solution, the control plane uses iMaster NCE-IP to implement automatic and intelligent network O&M, and the forwarding plane uses slicing technologies to implement soft- and hard-isolation of services.
Building an Intelligent Electric Power Production Network for the Electric Power Sector
An electric power company in Malaysia uses the CloudWAN solution to upgrade the infrastructure of substations and branches in order to replace the current SDH network. In this way, the company will be able to provide a highly reliable and high-bandwidth intelligent electric power production network for all substations and branches. The upgraded production network supports a large number of service links, features high scalability, simplifies service provisioning, and ensures service SLAs, providing optimal service experience for users at any time.
Building a CloudWAN Solution-Based IP Converged Transport Network for the ISP Sector
In the Philippines, an ISP that provides communication infrastructure is facing problems such as severe device and link overloads caused by the increasing number of Internet access users. The ISP uses the CloudWAN solution and technologies such as SRv6, network slicing, and IFIT to provide customers with a CloudWAN solution-based IP converged transport network featuring ultra-high bandwidth, simplified network protocols, deterministic SLAs, and intelligent O&M. This implements smooth network upgrade and fast and high-quality service provisioning.
- Author: Chen Peishan
- Updated on: 2022-11-24
- Views: 19963
- Average rating: