What Is IPS?
An intrusion prevention system (IPS) is a security mechanism. It detects intrusion behaviors (such as Trojan horses, worms, botnets, and spyware) based on behavior detection, signature database matching, and threat modeling, and terminates intrusion behaviors in real time through certain response methods. In recent years, network intrusions are becoming more diverse and covert. Enterprises need to face threats from hidden malicious traffic while processing massive traffic. IPS technology can be utilized to proactively detect and quickly process intrusion behaviors, protecting enterprise information systems and network architectures from intrusions.
Why Is IPS Required?
Intrusion refers to a series of behaviors that make the information system unreliable or unavailable, such as accessing, stealing, and damaging information system resources without authorization. Common intrusion tactics include Trojan horses, worms, injection attacks, botnets, DDoS attacks, cross-site scripting (XSS) attacks, and brute force cracking. In recent years, the amount of grayware such as spyware and adware is on the rise. Intrusion increasingly focuses on interest-driven and multi-faceted penetration. According to the 2020 Cybersecurity Report released by the National Computer Network Emergency Response Technical Team/Coordination Center of China (CNCERT/CC), in 2020, more than 42 million malicious program samples were captured, and more than 50 million IP addresses were attacked by malicious programs.
A typical enterprise may encounter the following intrusion behaviors:
- Launching of injection attacks to obtain the database modification permission of the server, causing enterprise data leakage or corruption.
- Exploitation of system software vulnerabilities to propagate Trojan horse software within enterprises.
- Launching of large-scale DDoS attacks on the target website in a short period of time to maliciously consume network resources, adversely affecting the normal services of the enterprises.
- Implanting of malicious code on external websites frequently accessed by enterprise employees. When an enterprise employee accesses such a website, the malicious actor can obtain information such as the employee's account and cookie and forge the employee's Internet access operations.
- Sending of phishing emails to enterprise employees to trick them into clicking on fake website links in the emails or download infected attachments. Phishing emails may cause information breaches, malware implantation, information system intrusion, and many more severe consequences, resulting in direct economic losses.
One of the important factors that lead to the success of these intrusions is the security vulnerabilities in various systems. Security vulnerabilities refer to defects in hardware, software, protocol implementation, or system security policies. Attackers can exploit these defects to maliciously access or damage the target system. Historically notorious security vulnerabilities, such as Heartbleed and EternalBlue, have resulted in major security breaches. Although system vendors could identify security vulnerabilities from security incidents and release patches or new versions to fix these vulnerabilities, the updates from the system vendors take a certain period of time. The main task of IPS is to detect and defend against attacks exploiting various security vulnerabilities, as well as provide security protection capabilities before the system vendor updates the system. Therefore, IPS has become an important part of an enterprise's basic network security construction.
How Does IPS Work?
IPS can guard against intrusion behaviors and typically uses the following technologies to detect intrusion behaviors:
- Signature-based detection technology: This method matches network traffic against signatures of known threats. A signature represents the characteristics of an intrusion behavior. If the traffic matches the signature, it is regarded as malicious traffic of the intrusion behavior. However, this method can only identify intrusions with existing signatures, and not new intrusions.
- Anomaly-based detection technology: This method collects random samples of network activities and compares them with baseline standards to determine whether they are intrusion behaviors. This technology delivers a wider identification scope than the signature-based detection technology, but also increases the risk of false positives.
- Security policy-based detection technology: This method is less frequently used than the first two methods, and requires the network administrator to configure security policies on the device. Any access behavior that violates these policies will be blocked.
After an intrusion behavior is detected, IPS can automatically handle it based on the configured response action, including generating an alarm, discarding data packets, blocking traffic from the source address, or resetting the connection.
The following uses Huawei IPS technology as an example to describe the detailed working process of IPS. As shown in the following figure, Huawei IPS uses signature-based and security policy-based technologies to identify intrusion behaviors.
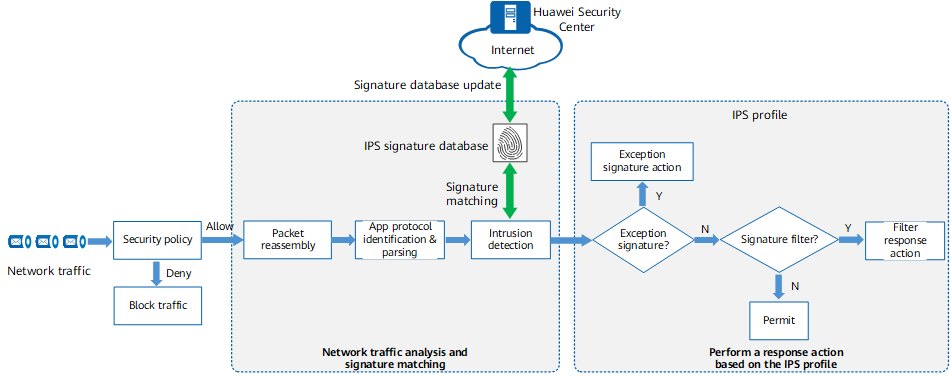
Working process of IPS
- Security policy matching: When traffic matches a security policy with the permit action and the security policy has an IPS profile referenced, the IPS process starts. The device performs intrusion prevention on the traffic.
- Packet reassembly: The device reassembles IP fragments and TCP flows to ensure data continuity at the application layer. In this way, the device can effectively detect attacks that evade IPS detection in the subsequent process.
- Application-layer protocol identification and parsing: The device identifies the application-layer protocol based on the packet content and performs in-depth parsing on the protocol to extract packet features. Compared with the traditional way of identifying protocols, which is based only on IP addresses and ports, application protocol identification greatly improves the detection rate of application-layer attacks. In addition, in this phase, the device can identify protocol anomalies and filter out data packets that do not comply with the protocol format and specifications.
- Signature matching: The device matches the parsed packet features against the signatures in the IPS signature database. If a match is found, the device further responds to it. Signatures represent the characteristics of intrusion behaviors. Huawei security researchers continuously track cyber security posture, analyze intrusion behavior features, and update the features to the IPS signature database. The device periodically downloads the IPS signature database from the Huawei Security Center to effectively defend against network intrusions in a timely manner.
- Response: After a packet matches a signature, the IPS profile determines whether to respond to the packet and how to process the packet (alert or block). An IPS profile consists of two elements: signature filter and exception signature.
Types of IPS
Currently, mainstream IPSs are classified into the following types, which can be deployed in different scenarios:
- Network intrusion prevention system (NIPS): installed at the network egress to detect all network traffic and proactively scan threats.
- Host-based intrusion prevention system (HIPS): installed on an endpoint to detect only the incoming and outgoing traffic of the endpoint. It is usually used together with the NIPS.
- Network behavior analysis (NBA): used to analyze network traffic and discover new malware or zero-day vulnerabilities by detecting abnormal traffic.
- Wireless intrusion prevention system (WIPS): used to scan Wi-Fi networks for unauthorized access and remove unauthorized devices from the networks.
Huawei focuses on NIPS. The NIPS-capable AI firewalls launched in recent years include HiSecEngine USG6000E series and HiSecEngine USG6000F series, as well as high-performance HiSecEngine USG12000 series. The IPS provided by Huawei has the following advantages:
- Offers 12,000+ vulnerability signatures, covering 8000+ CVE IDs and 2000+ botnet, Trojan horse, and worm families.
- Uses in-house dedicated security-purpose acceleration engine, which delivers the pattern matching acceleration capability and fast detection speed.
- Provides more than 400 anti-evasion methods, such as packet reassembly and application content identification.
- Delivers an 85% default blocking rate using signatures, which is industry-leading. Only a few alarms need to be analyzed, reducing costs incurred in log analysis by operation personnel.
Moreover, Huawei integrates the IPS function into AI firewalls. Therefore, compared with a standalone IPS device, an AI firewall provides other security functions such as firewall, VPN, and Antivirus in addition to IPS. This reduces device costs and management difficulties while providing users with more choices.
IPS vs IDS
The intrusion detection system (IDS) is proposed at the early stage of intrusion detection technology development. The differences between IDS and IPS are as follows:
- Deployment mode: The IDS is usually deployed in off-path mode and does not forward data flows. All involved traffic must be mirrored to the IDS port. The IPS is usually deployed in in-path mode on the network. Data flows must be processed by the IPS before being forwarded.
- Function: The IDS is only a detection device. It cannot block attacks and can only generate alarms. To defend against attacks, the IDS needs to interwork with the firewall. The security policies on the firewall block attacks. The IPS can directly detect and process attacks without cooperating with other network devices.
- Response speed: The IDS detects attacks by mirroring data flows. During the detection, the data flows have been or are being forwarded by network devices. No matter whether the IDS processes attacks through alarm reporting or firewall interworking, it is considered as post-event processing. The IDS cannot handle single-packet attacks. In contrast, the IPS performs security check on data packets, and then determines the processing status of the data packets based on the security check result. In this way, the IPS can respond to and process the data packets in time.
In a word, the IDS device does not take any action on intrusion behaviors. Rather, it is a security mechanism that focuses on risk management. Currently, the AI firewalls coming with the IPS function provided by Huawei has both the IDS and IPS functions. You can select desired AI firewalls based on the actual networking requirements.
- Author: Fang Wei
- Updated on: 2022-12-19
- Views: 7516
- Average rating:







