What Is URL Filtering?
URL filtering technology controls the Internet access based on user URL requests. It allows or rejects users' access to certain web pages to regulate Internet access behaviors and reduce security risks.
URL filtering restricts URL access based on URL categories and specific URLs. URL filtering provides the following functions:
1. Restricts access to business-irrelevant websites, improving enterprise employee productivity and reducing bandwidth abuse.
2. Restricts access to the websites that contain illegal or inappropriate content to ensure legal and compliant online behavior.
3. Restricts access to insecure websites containing malware and phishing to prevent network attacks.
Why Is URL Filtering Important?
Quickly accessing information by browsing web pages has become the main means for people to work, stay informed, and entertain themselves. The Internet itself is not secure. Network resources bring us convenience as well as unprecedented threats. The threats include network security issues and impacts on services caused by network abuse:
- Enterprise employees at work access non-work-related websites, such as social networking websites and video websites, which severely affects productivity, consumes network bandwidth, and even poses a risk of breach of law if they access illegal websites.
- Access to inappropriate websites occurs in public institutions, such as schools and libraries, breaching laws.
- Employees' unintentional access to malicious and phishing websites may disclose confidential information about enterprises or individuals, and even bring threats, such as viruses and Trojan horses.
Therefore, online behavior must be controlled. URL filtering is one of the methods to solve the preceding problems. This method restricts URLs to which users can access. You can prevent access to phishing, social networking, and video websites by website category. You can also specify specific URLs that are rejected or allowed for access.
How Does URL Filtering Work?
The basic working process of URL filtering is to compare the URL carried in a URL request with entries in a URL database or URL list. If a match is found, the device performs a corresponding action (permit or deny). If a user manually enters a URL or clicks on a search engine link of the URL and the URL is blocked, the browser will redirect the user to a web page, similar to that in the following figure.
Preventing access to unauthorized websites
URL databases or lists can be deployed locally or on the cloud. Generally, frequently accessed URLs are cached locally, and more URLs are supported on the cloud. If no URL is found locally, the device searches for one on the cloud to minimize latency. In addition, URL databases or lists can be organized in multiple modes, including the URL category, single URL blacklist, and single URL whitelist. The following figure shows the URL filtering process.
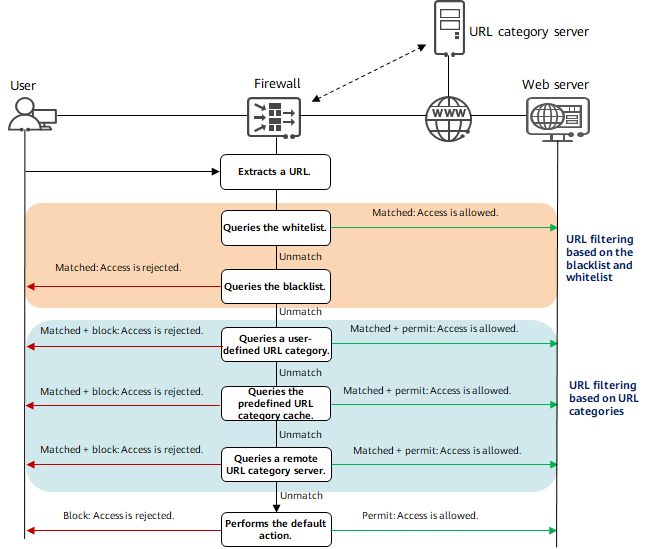
URL filtering process
URL Blacklist and Whitelist
URL blacklists and whitelists are used to allow or reject specific URLs. The processing is simple and straightforward. The whitelist allows access, and the blacklist prohibits access. This method is usually used to control access to known websites, for example, by whitelisting the IT websites that are normally used by enterprises and blacklisting the forums that are forbidden browsing during working hours.
URL Category
URL category is the core management and control method of URL filtering. An administrator specifies response actions based on URL categories, for example, barring access to shopping websites and social networking websites. If a URL that a user accesses matches a specific URL category, the device takes a specific action corresponding to the URL category.
URL categories are classified into predefined and user-defined URL categories.
Predefined URL Categories
Predefined URL categories are sorted out by URL filtering providers and updated periodically. Massive URLs, such as gambling, phishing, and shopping, are classified in advance.
A predefined URL category contains a huge number of URL entries. Searching for URL entries one by one adversely affects efficiency. Generally, a two-step approach is adopted. The first step is to store common URLs and corresponding URL category information on a local device and query the URLs. If no URL category information is found, perform the next step to remotely query the URL category information on a URL category server deployed on the cloud. The URL category server provides more information.
In addition, the URL information is saved locally and continuously learned updated. URLs that are not frequently accessed are aged, and the query results obtained from the URL category server are added locally. This mechanism helps reduce remote queries and speed up URL filtering processing.
User-Defined URL Categories
URLs are frequently added, and the speed at which predefined categories are updated may not meet enterprise requirements. In addition, enterprises may have their own URL category policies and want to implement control based on customized URL categories. In this case, an administrator can create a user-defined URL category and add URLs to the category.
Formulating URL Filtering Policies
Based on the preceding working mechanism, an administrator can customize URL filtering policies for an enterprise as needed. The common procedure is as follows:
- Determining allowed websites: Maintain a list of websites that an enterprise can access through a whitelist or user-defined URL category. Such websites include enterprise portal websites and software upgrade websites. Ensure that URL filtering does not accidentally block websites required for proper business.
- Explicitly prohibited websites: Use blacklists or user-defined URL categories to restrict access to the websites that are prohibited by enterprises. Prevent failures to disable access to such websites because the websites are not in URL categories or are in incorrect URL categories.
- Category-based control: Use predefined URL categories to control the allowed and prohibited categories of websites. In particular, malware and phishing websites must be prohibited to reduce security risks. Predefined URL categories can also be used to control employees' online behavior based on enterprise requirements and prohibit inappropriate websites and websites that adversely affect productivity.
- Refined control: Control website access based on time segments and user identities. For example, control websites that are not allowed for access during working hours and websites that are allowed for access only by employees of a certain department.
URL Filtering vs. DNS Filtering
Both URL filtering and DNS filtering are web filtering methods, but their control granularities and implementation methods are different. URL filtering is implemented by extracting URL information from a user's URL request, which can be used to control access to web pages. DNS filtering, however, is implemented by extracting domain name information from a user's DNS request, which can only control access to an entire domain with a specified name. Their application scenarios differ.
For example, if you want to prohibit employees from accessing an entire website with the domain name example.news.com, you can select DNS filtering. If you just want to ban the entertainment part example.news.com/entertainment in this domain, you need to use URL filtering.
For another example, if an enterprise identifies a malicious website example.malicious.com/index that often lures employees to visit, it is recommended that you use DNS filtering to disable the domain name example.malicious.com because all web pages may be insecure.
URL filtering can also restrict website access by domain name. However, DNS filtering is controlled in the DNS query phase prior to the URL request phase and has little impact on device performance. In addition, DNS filtering is irrelevant to service protocols, whereas URL filtering is restricted to HTTP/HTTPS.
URL Filtering vs. Application Control
The application control function uses the application identification technology to identify various applications in traffic and implement refined traffic control. Applications also include some web applications. For example, the Facebook application is hosted on www.facebook.com. What is the difference between application control and URL filtering?
For web applications, application control identifies and controls web page access traffic; URL filtering controls web page URLs. That is, application control is directed to an application program, and multiple web pages may correspond to the same application program. URL filtering applies to web page-level access behavior.
Application control is better suited for fine-grained control over applications. For websites such as Facebook, you are more familiar with the names of applications such as Facebook browser, Facebook videos, and Facebook games. If it is difficult to collect URLs corresponding to the applications, because one application may correspond to multiple URLs. In this case, it is more convenient to use application control. You only need to configure application names such as Facebook videos and Facebook games.
URL filtering is better at controlling users' access to a certain type of website or a batch of URLs under the same domain name. For example, to allow users to access only the Facebook social networking website but not to other social networking websites, using URL filtering is more convenient. If application control is used, you need to specify all applications corresponding to the websites.
Therefore, application control and URL filtering have different application scenarios and complement each other.
URL Filtering Is Not Sufficient to Defend Against All Web Attacks
URL filtering blocks access to known malware and phishing websites to reduce web attack events. However, URL filtering alone cannot defend against all web attacks. Enterprises and organizations require a complete web security solution to defend against both known and unknown threats. Multiple security functions must be used together to effectively defend against various web attacks. The common deployment solution is as follows:
- Deploy an NGFW that is integrated with multiple security functions. On the NGFW, enable content filtering to filter web page content; enable file filtering to control file uploading and downloading; enable the IPS function to detect attacks (such as Trojan horses and malware); enable the antivirus function to detect file viruses.
- Synchronize the firewall with the cloud to obtain the latest threat information in real time and defend against unknown threats. Huawei firewalls can interwork with cloud sandboxes to detect advanced persistent threat (APT) attacks. They can reversely use detection results to update the local malicious URL or file list to improve subsequent detection efficiency.
- It is used with the SSL-encrypted traffic detection function to detect encrypted HTTPS traffic.
- Security software, such as antivirus software, is installed on intranet terminals.
- Author: Liu Shui
- Updated on: 2021-09-30
- Views: 11083
- Average rating:







