What Is Web Filtering?
Web filtering technology controls users' web access, involving the control over which websites users can access, what content users can view, and which files users can download. For example, a system can prevent users' access to gambling websites, filter out web pages containing illegal content, and control search engines to filter out inappropriate search results.
Web filtering can restrict access to work-irrelevant websites to improve productivity and regulate online behaviors of employees in enterprises. It also acts as the first line of defense against web threats to prevent users from accessing malicious websites or downloading malicious files. Web filtering is the most commonly used web access control measure for enterprises and organizations.
Why Is Web Filtering Important?
Quickly accessing information by browsing web pages has become the main means for people to work, stay informed, and entertain themselves. The Internet itself is not secure. Network resources bring us convenience as well as unprecedented threats. The threats include network security issues and impacts on services stemming from network abuse:
- Enterprise employees at work access non-work-related websites, such as social networking websites and video websites, which severely affects productivity, consumes network bandwidth, and even poses a risk of breach of law if they access illegal websites.
- Access to inappropriate websites in public institutions, such as schools and libraries poses risks to breach laws.
- Employees' unintentional access to malicious and phishing websites may disclose confidential information about enterprises or individuals, and even bring threats, such as viruses and Trojan horses.
- Employees may disclose confidential information and their terminals become infected with viruses when they post on social media and upload or download files.
Web filtering is an important method to tackle the preceding issues. It helps regulate online behaviors and reduce security risks by limiting web access, as shown in the following figure. You can prevent access to websites by category, such as phishing, social networking, and video websites; prohibit access to web page content that contains specified invalid keywords; control the search engines to filter out inappropriate search results.
Preventing access to unauthorized websites
How Does Web Filtering Work?
Web filtering helps administrators easily implement comprehensive web access control. As shown in the following figure, web filtering provides control modes applicable to different Internet access phases.
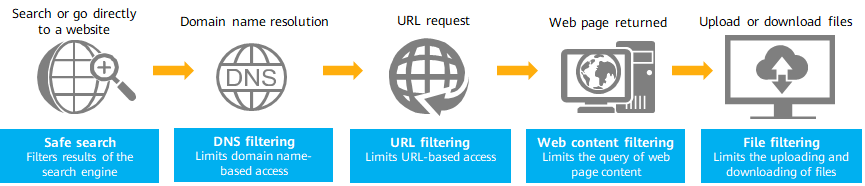
Web filtering for comprehensive web access control
Safe Search
When search engines are used to search web pages, the search engines, such as Google, YouTube, and Bing, provide a safe search extension to automatically filter out search results containing inappropriate content. Without manually enabling the safe search extension on a browser, web filtering can force the search engine to perform safe search, which is suitable for public organizations, such as schools and libraries.
DNS Filtering
The first step for a user to access a website is to send a DNS request to a DNS server to obtain an IP address corresponding to a domain name. For instance, a user attempts to access https://example.news.com/entertainment. The domain name is example.news.com.
At this time, the DNS filtering function can be used to filter the specified domain name in the DNS request to control user access to the entire domain name. For a prohibited domain name, all network addresses under the domain name, such as https://example.news.com/entertainment and https://example.news.com/sports, cannot be accessed.
DNS filtering can be implemented in either of the following modes:
- Pre-defined category database-based filtering
A firewall maintains a dynamically updated database locally or on the cloud. The database includes a large quantity of categories corresponding to common domain names. An administrator only needs to specify actions for various domain name categories, such as social networking, shopping, and news, to implement unified control over the domain names of each category.
- Blacklist- and whitelist-based filtering
An administrator manually specifies actions for specific domain names. For example, known malicious domain names are added to a blacklist, and domain names of self-built websites are added to a whitelist.
URL Filtering
After the preceding domain name resolution phase, the URL request phase follows up. That is, a request is sent to access a specific web page URL, for example, https://example.news.com/entertainment.
In this phase, the URL filtering function is used to filter the specified URL in the URL request to control user access. More refined than DNS filtering, URL filtering controls web access by URL.
Similar to DNS filtering, URL filtering is implemented through the URL category database and blacklist/whitelist modes. Administrators can easily control URL access by specifying URL categories (such as phishing and social networking websites) and URL addresses.
Web Content Filtering
After the URL is accessed, a specific web page is displayed. The user starts to view the web page content and submits information.
In this phase, the web content filtering function is used to control user operations that involve illegitimate keywords, for example, gambling. This function can be used in the following scenarios:
- Prevent users from browsing web pages containing illegitimate keywords.
- Prevent users from sharing on social media or writing posts that contain illegitimate keywords.
- Prevent users from entering illegal keywords in the search box.
- Prevent users from submitting content containing illegitimate keywords (for example, when applications are submitted during network user registration).
Content-level control is effective to ensure appropriate Internet surfing and prevent information breach. In addition to manually specified keywords, some common feature codes, such as bank card numbers, identity card numbers, and mobile phone numbers, are preset on the device. Administrators can directly prohibit such content to prevent information leakage.
File Filtering
Users often upload to and download files from the Internet. Uncontrolled file transfer may cause internal information leakage and virus infection on an internal network. For example, a downloaded executable file may contain hidden viruses, and uploading internal source code files may leak the enterprise's confidential information.
The file filtering function can be used to control the types of files to be transferred, for example, to prevent the transfer of EXE files and C language code files. File filtering can help identify real file types, not only by file name extensions, so that file type information is no longer hidden.
What Is Web Filtering on a Firewall?
Huawei firewall products provide various fine-grained web filtering functions to help enterprises and organizations manage and control web access.
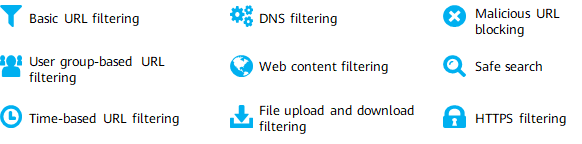
Web filtering functions provided by Huawei firewalls
The basic functions mentioned previously are not described here. In addition to supporting basic URL filtering functions, the firewall provides user group- and schedule-based URL filtering. For example, a school allows teachers to access social networking websites at any time and students to access the same websites only in spare time. As security requirements increase, encrypted websites become increasingly popular. The firewall also provides the web filtering function for HTTPS-encrypted traffic.
Web Filtering Is Not Sufficient to Defend Against All Web Attacks
Web filtering blocks access to known malware and phishing websites to reduce web attack events. However, web filtering alone cannot defend against all web attacks. Enterprises and organizations require a complete web security solution to defend against both known and unknown threats. Multiple security functions must be used together to effectively defend against various web attacks. The common deployment solution is as follows:
- Deploy an NGFW that is integrated with multiple security functions. On the NGFW, enable the IPS function to detect attacks (such as Trojan horses and malware) and the antivirus function to detect file viruses.
- Synchronize the NGFW with the cloud to obtain the latest threat information in real time and defend against unknown threats. Huawei firewalls can interwork with cloud sandboxes to detect advanced persistent threat (APT) attacks. They can reversely use detection results to update the local malicious URL and file list to improve subsequent detection efficiency.
- Security software, such as antivirus software, is installed on intranet terminals.
- Author: Liu Shui
- Updated on: 2023-11-16
- Views: 7277
- Average rating:







