What Is SSL-Encrypted Traffic Detection?
SSL-encrypted traffic detection, also known as SSL decryption, is an important security technology. It decrypts encrypted traffic so that the firewall can perform content security check (such as URL filtering, intrusion prevention, and antivirus) on the decrypted traffic. This helps to effectively detect network threats that may be hidden in encrypted traffic, preventing malicious actors from stealing confidential data or spreading malware through encrypted channels.
Popularity of SSL-Encrypted Traffic
In recent years, to ensure secure and private data transmission, more and more network traffic is encrypted by using Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) and Transport Layer Security (TLS). In fact, 95% of traffic is transmitted using encryption protocols. Encryption protocols are increasingly used for the following reasons:
- Easy-to-obtain certificates: Encryption protocols require certificates to work. Website or application developers can easily obtain free certificates from certificate authorities (CAs) such as Let's Encrypt.
- "Not Secure" warning: Mainstream browsers mark websites that are not encrypted using SSL/TLS as insecure.
- Enhanced public awareness: A large number of recent data breaches have turned public attention to data security. EU General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA), and other laws and regulations also compel service providers to use SSL/TLS encryption.
- Search engine ranking: Some search engines provide higher rankings of search results for websites encrypted using SSL/TLS.
- Service continuity: TLS 1.0 and TLS 1.2 are less secure and may be discontinued at any time. Modern protocols, such as TLS 1.3 and HTTP/2, are more secure and widely used.
Why Is SSL-Encrypted Traffic Detection Required?
The wide use of encryption protocols presents new challenges to network security. Traditional security detection firewalls are unable to detect encrypted traffic, yet over 70% of attackers currently utilize encryption protocols to transmit malicious software, conceal attack activities, and pilfer confidential data. This results in the following security incidents:
- Viruses are hidden in executable files downloaded by intranet users through encrypted traffic.
- An intranet user inadvertently accesses a malicious website using HTTPS.
- Unauthorized internal confidential information is leaked to the external network through encrypted data transmission.
As shown in the following figure, after SSL-encrypted traffic detection is configured on the firewall, the firewall can decrypt encrypted traffic. After decryption, the administrator can configure content security detection services as required based on the network status and service characteristics. After the detection is complete, the firewall encrypts normal traffic and sends it to the peer end, securing data.
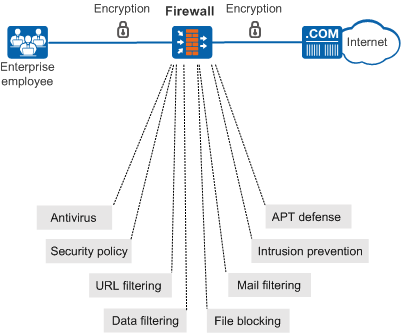
Content security detection services
Typical Scenarios of SSL-Encrypted Traffic Detection
Depending on the objects to be protected, SSL-encrypted traffic detection of the firewall is classified into outbound detection and inbound detection. In outbound detection, the device detects Internet access traffic of intranet users and protects intranet user clients. For this reason, this scenario is also called client protection. Accordingly, in inbound detection, the device detects the traffic destined for intranet servers and protects these servers, and so this scenario is also called server protection.
Outbound Detection: Client Protection
Client protection is typically used when an intranet client accesses an external website.
The website depicted in the following figure has been compromised, with the attacker having implanted Trojan horses. As intranet users access the website, malware enters the intranet, surreptitiously implanting itself on some user hosts without their knowledge.
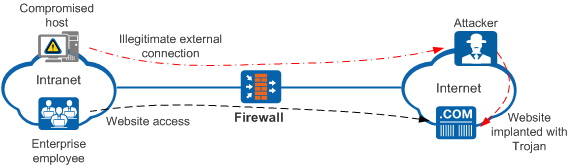
Outbound detection scenario
To safeguard intranet users against external malicious websites, SSL-encrypted traffic detection can be configured on the firewall. With this function configured, upon receiving users' access requests, the firewall decrypts them, and detects and blocks any malicious websites, thereby protecting intranet users.
Inbound Detection: Server Protection
Server protection is used when external network clients access intranet websites. The firewall is deployed on the network where the web server resides. When a browser sends a request to access the web server through the firewall, the firewall functions as a proxy to establish communication with the client, decrypts the traffic, and performs security check. The firewall only permits the access traffic after ensuring that the traffic is secure, thereby protecting the server.
As shown in the following figure, a malicious actor on the Internet uploads malware files to the web server through the browser client.
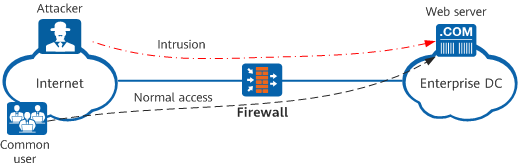
Inbound detection scenario
To protect the web server from external malware, the firewall decrypts the access data and performs content security check on the decrypted data. If the firewall detects any threats in the traffic, it blocks the traffic to protect the intranet server.
Working Principles of SSL-Encrypted Traffic Detection
The following uses the client protection scenario as an example to describe the working principles of SSL-encrypted traffic detection.
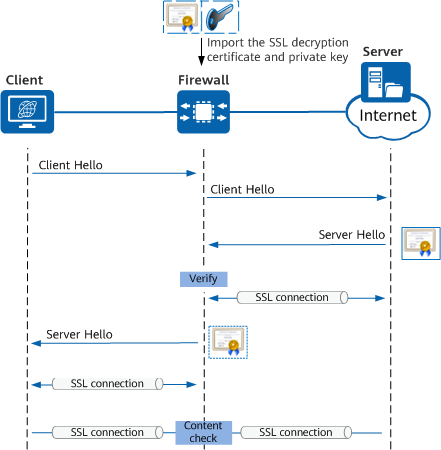
SSL-encrypted traffic detection process
- When a user attempts to access a website, the browser client sends an access request to the server, expecting to establish an SSL connection.
- The firewall parses and caches the access request sent by the user client. Then, the firewall functions as a proxy to send the access request to the server.
- Upon receipt of this access request, the server sends its own certificate.
- After verifying that the certificate is valid, the firewall establishes an SSL connection with the server.
- The firewall re-issues the certificate sent by the server to establish an SSL connection with the user client.
- The client considers the firewall to be the target web server, and then establishes an SSL connection with the firewall.
- Then, SSL connections are established between the client and the firewall as well as between the firewall and the server. The firewall filters out malicious traffic based on the content security check result, encrypts valid traffic, and sends the encrypted traffic to the peer end.
How Do I Configure SSL-Encrypted Traffic Detection?
SSL-encrypted traffic detection only encrypts and decrypts traffic. Therefore, when configuring SSL-encrypted traffic detection, you also need to configure security policies and specific content detection services to implement content security detection on encrypted traffic. The following uses URL filtering as an example to describe how to configure SSL-encrypted traffic detection on Huawei HiSecEngine USG6000E and USG6000F series AI firewalls and build a security defense system for website access through security policies and URL filtering.
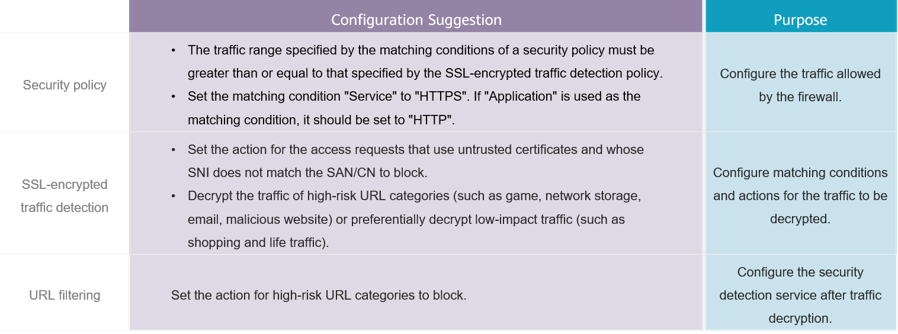
Configuration suggestions for Huawei SSL-encrypted traffic detection
In addition, SSL-encrypted traffic detection requires a large number of encryption and decryption operations. If SSL decryption is performed on all SSL traffic, the forwarding performance of the firewall is affected. Therefore, you need to configure an SSL-encrypted traffic detection policy to decrypt only the SSL-encrypted traffic that meets certain conditions.
- Author: Fang Wei
- Updated on: 2023-09-04
- Views: 986
- Average rating:






