What Is Endpoint Security?
Endpoint security is a network protection technology used to protect users' endpoints from malicious threats and cyber attacks. Traditional endpoint security involves placing each workstation or server within the internal zone of the border firewall for protection. However, as the scope of endpoint devices expands and the number and complexity of network security threats increase, there is a growing need for new endpoint security solutions. Modern endpoint security, such as EDR, is designed to rapidly detect, analyze, prevent, and contain ongoing attacks, and safeguard various endpoints regardless of their location on the network.
Why Is Endpoint Security Important?
To ensure endpoint security, enterprises only need to place workstations and servers within the defense scope of border firewalls and adjust firewall security policies. Firewalls serve as the first line of defense against network threats. As remote and hybrid working continue to develop, endpoints connected to enterprise networks are gradually moved outwards, creating a larger attack surface. New endpoints are emerging faster than ever, requiring access to internal office networks that allow users to access sensitive enterprise information at any given time. Common endpoints include any device that can be connected to the company's network, such as:
- IoT-enabled smart devices
- ATMs
- Industrial machinery
- Laptops
- Medical devices
- Mobile phones
- Printers
- Servers
- Tablets
- Wearable devices, such as smart watches

Common endpoints
The growing number and variety of endpoints provide hackers with entry points to infiltrate enterprise networks and systems. By exploiting vulnerabilities in endpoint devices, hackers can carry out various known and unknown attacks, including ransomware, viruses, and Trojan horses. This enables hackers to gain access to enterprise intranets and systems, and potentially compromise or steal sensitive data. As a result, endpoint security technologies are crucial in safeguarding enterprises against the escalating threats posed by network environments.
How Does Endpoint Security Work?
Endpoint security technologies work by examining files, processes, and systems for suspicious or malicious activities. At the network level, enterprise network firewalls can still be used to restrict access to enterprise networks through security policies and permission control. With the advancement of cloudification, a hybrid solution is gradually emerging, which combines the local management and control center with cloud-based remote automatic control and management. Endpoint security technologies must have the following capabilities:
- Endpoint identification and management
- Automatic endpoint identification: provides the automatic endpoint asset inventory capability. After the endpoint protection software is installed, endpoints can be automatically identified.
- Asset information management: automatically and centrally manages endpoint asset information such as the host list, processes, ports, and components.
- Endpoint security management: intelligently analyzes endpoint security and displays endpoint asset security analysis scores and risk overview.
- Threat detection and handling
- Intrusion detection: offers endpoint behavior detection capabilities based on the behavior detection engine to detect malicious behaviors such as brute-force attacks, abnormal login, and privilege escalation.
- Event aggregation: aggregates discrete ransomware-related alarm events into ransomware events based on the process call chain and supports one-click handling.
- Virus scan and handling
- Virus scan: leverages the antivirus engine to update the antivirus signature database every day, update critical viruses in real time, and offer high-quality malware file detection capabilities.
- Threat analysis: supports threat analysis on detected malware files and displays detailed threat information, such as malware identifiers, risk values, and confidence levels.
- Proactive defense
- Bait capture: places bait files based on ransomware signatures to detect and report abnormal behaviors in real time.
- File anti-tamper: performs access permission control and real-time detection on key files to detect tampering in a timely manner.
- Real-time protection: scans all directories in real time, identifies malware files in a timely manner, and blocks their transmission.
- Source tracing analysis
- Forensic analysis: collects and stores endpoint information, and performs forensic analysis on threat events through data mining and correlation analysis.
- Attack visualization: uses EDR digital modeling and source tracing inference algorithms to visualize attacks and accurately restore threat attack paths.
Types of Endpoint Security
Endpoints of different types and purposes can be protected by distinct endpoint security approaches.
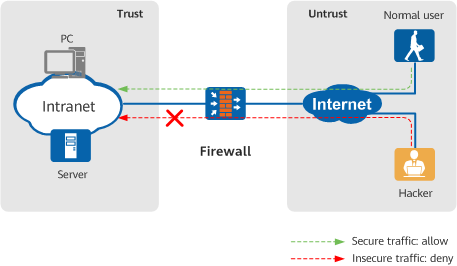
- Network Admission Control (NAC)
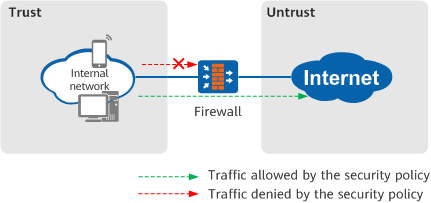
Based on the blacklist/whitelist or security policy, the border firewall can control which users and endpoints can access sensitive network resources and the operations that can be performed by them on the intranet.
Controlling user access to the network through firewall security policies - Data Filtering
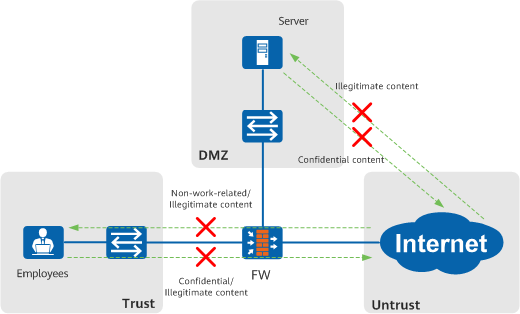
The firewall inspects the data sent by endpoints, identifies specific risky content, and blocks malicious traffic. Data filtering reduces the risk of confidential information leaks, and prevents illegitimate data from spreading and employees from searching for and browsing non-work-related content.
Protecting endpoints through data filtering - Internal Threat Prevention (Zero Trust)
Zero trust is a security model that continuously authenticates and dynamically authorizes all users based on as many trust elements as possible, such as the identity of the access subject, network environment, and endpoint status. The zero-trust solution provides unified identity management, builds identity boundaries, detects risks in real time, and implements dynamic and fine-grained authorization.
- Application Behavior Control
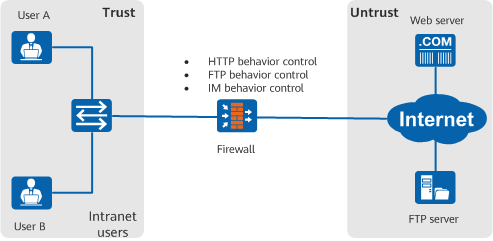
The firewall deployed on the enterprise network can implement fine-grained control over endpoint users' behaviors through protocol detection. For example, the application behavior control function can be used to prohibit FTP file upload and deletion while allowing FTP file download, or control social logins.
Controlling endpoint users' access to applications through protocol detection - URL Filtering
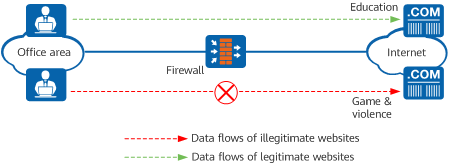
URL filtering regulates online behaviors by controlling which URLs users can access, thereby permitting or denying users' access to specified web page resources. URL filtering can also reference configuration items, such as schedules or users/user groups, to implement targeted URL access control. This delivers more refined and accurate control on employees' Internet access permissions.
- DNS Filtering
DNS filtering precisely manages users' online behaviors by implementing domain name access control for users or user groups based on information such as users or user groups, schedules, and security zones.
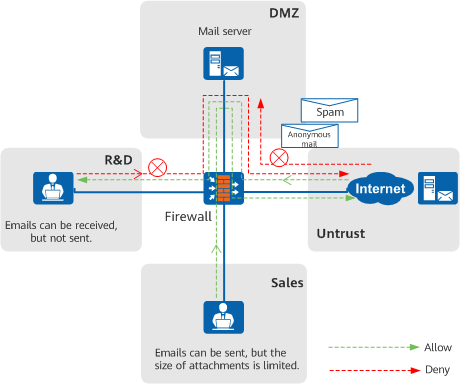
Controlling the network access scope of endpoint users through URL or DNS filtering - Mail Filtering
Mail filtering primarily depends on IP address checks and email content filtering technologies to enhance the security of LAN users' mail system. Mail filtering restricts email sending permissions and sizes to prevent information leakage.
Controlling the email permissions of endpoint users through mail filtering - File Blocking
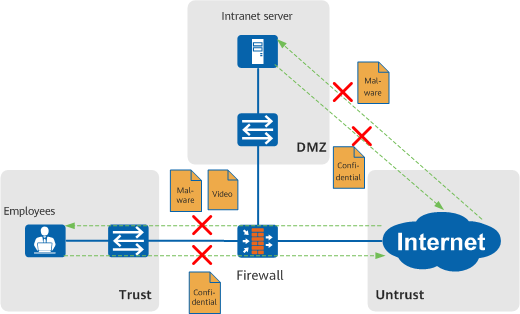
Confidential information and viruses usually exist in certain types of files. For example, confidential information is generally stored in documents, and virus information is generally attached to executable files. Therefore, file blocking blocks the transmission of specified types of files to reduce confidential information leakage and virus infection risks on the intranet.
Protecting endpoint security through file blocking - IPS
Intrusion prevention system (IPS) is a security mechanism that analyzes network traffic to detect intrusions (such as buffer overflow attacks, Trojan horses, and worms) and uses certain response actions to prevent these intrusions in real time, protecting enterprise information systems and network architectures.
Defending against external threats and intrusions through IPS - Antivirus
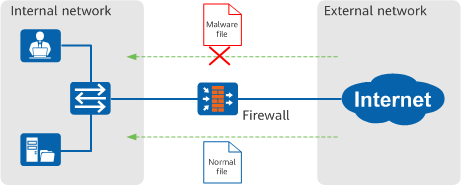
The antivirus function can identify and process malware files to ensure network security and prevent data corruption, permission change, and system crashes caused by these files.
Identifying malware files to protect endpoints by using the antivirus function - Sandbox (APT Defense)
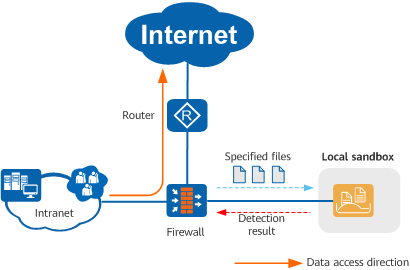
The firewall can use sandboxing to construct an isolated threat detection environment, send network traffic to the sandbox for analysis, and finally determine if any threats exist. If malicious traffic is identified by the sandbox, it updates the cached malicious file and URL list accordingly. If any subsequent traffic with the same characteristics matches the malicious file or URL list, the sandbox blocks the traffic or generates an alarm.
Interworking with the sandbox to detect malicious files and protect endpoints - Cloud Access Security Awareness
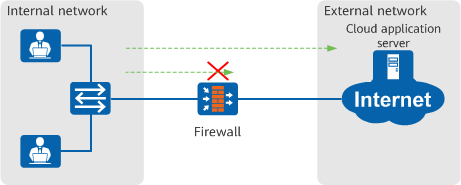
In an enterprise, the use of cloud applications by employees needs to be managed and controlled. This can involve implementing differentiated management for users accessing the same cloud application, or refined management for users using different applications. The cloud access security awareness function is designed to meet these specific requirements.
Restricting different endpoints to access cloud applications through cloud access security awareness
Endpoint Security vs Antivirus
Endpoint security differs from traditional antivirus software in the following key aspects:
- Endpoint security and network security: Traditional antivirus software is typically installed on a single endpoint device, such as a laptop, to protect it from potential threats. However, endpoint security technologies regard the enterprise network as a whole and aim to protect all endpoint devices connected to the enterprise network.
- Management: Traditional antivirus software relies on users to manually update the database or allow the database to be updated at a specified time. Endpoint security technologies transfer management responsibilities to enterprise IT or network security teams and are automatically updated by connecting to the cloud.
- Protection: Traditional antivirus software uses signature-based detection to identify viruses and other types of malware. This means that if the antivirus software is not up to date, your endpoint is still at risk of being attacked by malware. Endpoint security leverages technologies like data encryption and access control to enhance protection, thwart risks such as data loss and breach, and restrict unauthorized access to data. Additionally, advanced techniques such as behavior analysis can be used to identify potential threats based on suspicious activities.
- Author: Zhang Na
- Updated on: 2023-11-15
- Views: 915
- Average rating: