Top Searches
Refresh
Cyclic redundancy check (CRC) is a common data transmission error detection technique commonly used in the data communication field. The transmit end calculates a check code for the data in a data frame based on a certain algorithm, appends the check code to the data frame, and sends the data frame to the receive end. The receive end verifies the correctness and integrity of the received data by repeating the calculation using the same algorithm.
52.1k
WiFi 7 (Wi-Fi 7) is the next-generation Wi-Fi standard to be launched, also known as IEEE 802.11be — extremely high throughput (EHT).
Based on Wi-Fi 6, Wi-Fi 7 introduces technologies such as 320 MHz bandwidth, 4096-quadrature amplitude modulation (QAM), multiple resource unit (MRU), multi-link operation (MLO), and multi-access point (AP) coordination. Drawing on these cutting-edge technologies, Wi-Fi 7 delivers a higher data transmission rates and lower latency than Wi-Fi 6. Wi-Fi 7 is expected to support a throughput of up to 23 Gbps, about three times that of Wi-Fi 6.
51.4k
VXLAN, or Virtual Extensible LAN, is a network virtualization technology widely used on large Layer 2 networks. VXLAN establishes a logical tunnel between the source and destination network devices, through which it uses MAC-in-UDP encapsulation for packets. Specifically, it encapsulates original Ethernet frames sent by a VM into UDP packets. It then encapsulates the UDP packets with the IP header and Ethernet header of the physical network as outer headers, enabling these packets to be routed across the network like common IP packets. This frees VMs on the Layer 2 network from the structural limitations of the Layer 2 and Layer 3 networks.
39.4k
Segment Routing IPv6 (SRv6) is a next-generation IP bearer protocol that combines Segment Routing (SR) and IPv6. Utilizing existing IPv6 forwarding technology, SRv6 implements network programming through flexible IPv6 extension headers.
SRv6 reduces the number of required protocol types, offers great extensibility and programmability, and meets the diversified requirements of more new services. It also provides high reliability and offers exciting cloud service application potential.
39.4k
Internet Protocol Security (IPsec) is a suite of protocols and services that provide security for IP networks. It is a widely used virtual private network (VPN) technology. IP packets lack effective security mechanisms and may be forged, stolen, or tampered with when being transmitted on a public network, such as the Internet. To solve this problem, the communicating parties establish an IPsec tunnel for encrypted transmission of IP packets. This ensures secure transmission of IP packets on an insecure network, such as the Internet.
38.6k
Telemetry is a next-generation network monitoring technology used to remotely collect data from devices at high speed. Devices periodically push device information to a collector, providing real-time, high-speed, and accurate network monitoring. To be specific, telemetry organizes data based on YANG models, encodes data in the Google Protocol Buffers (GPB) format, and transmits data through the Google Remote Procedure Call (gRPC) protocol. This improves data collection efficiency and facilitates intelligent interconnection.
In traditional technologies, a collector and devices interact in pull mode by alternatively sending requests and responses. In contrast to these technologies, telemetry works in push mode and has the following advantages:
- Proactively pushes data, reducing the pressure on devices.
- Pushes data periodically in subseconds to avoid data inaccuracy caused by network delay.
- Is capable to monitor a large number of network devices, improving network monitoring efficiency.
38.4k
Latest Updates
Refresh

WiFi, also known as Wi-Fi, is a trademark owned by the Wi-Fi Alliance (WFA). It is a WLAN technology based on the IEEE 802.11 family of standards. Since the release of the first-generation IEEE 802.11 standard in 1997, it has been evolved to the latest 7th-generation 802.11be standard (Wi-Fi 7). Before the release of Wi-Fi 6, Wi-Fi standards were identified by versions from 802.11b to 802.11ac. Later, the WFA decided to make the Wi-Fi standards easier to understand and remember for Wi-Fi users and device vendors, and therefore renamed the standards using generational numbering.

EVPN is a next-generation full-service bearer VPN solution. It unifies the control planes for various VPN services and uses BGP extensions to transmit Layer 2 or Layer 3 reachability information, separating the forwarding plane from the control plane.
Traditional L2VPN lacks load balancing capabilities and consumes many network resources. EVPN overcomes these drawbacks and introduces IP VPN's advantages of traffic balancing and flexible deployment into the Ethernet. EVPN is widely used for interconnecting Layer 2 networks spanning large data centers. Furthermore, it can carry L3VPN services, thereby reducing protocol complexity.
A public cloud is a cloud service provided by a third-party provider for users through the Internet. Users can access the cloud and enjoy various services, including but not limited to computing, storage, and network services. Public cloud services can be free of charge or charged by usage.

An ACL is a collection of one or more rules. A rule refers to a judgment statement that describes a packet matching condition, which may be a source address, destination address, or port number.
An ACL is essentially a rule-based packet filter. Packets matching an ACL are processed based on the policy defined in the ACL.

Since the birth of Ethernet in 1970s, the network has gone through half a century of development. Now, network has become an inseparable part of our life and work. If we compare a network to a road, information is the car, and car driving relies on various types of guidance information alongside the road. Such guidance information needs to be planned and configured manually. As digital transformation speeds up, service volumes increase explosively, raising higher requirements on network experience, which, however, has gone beyond the limits of manual decision-making and processing capabilities. The question is: Can the network work like an autonomous vehicle to free people's hands?
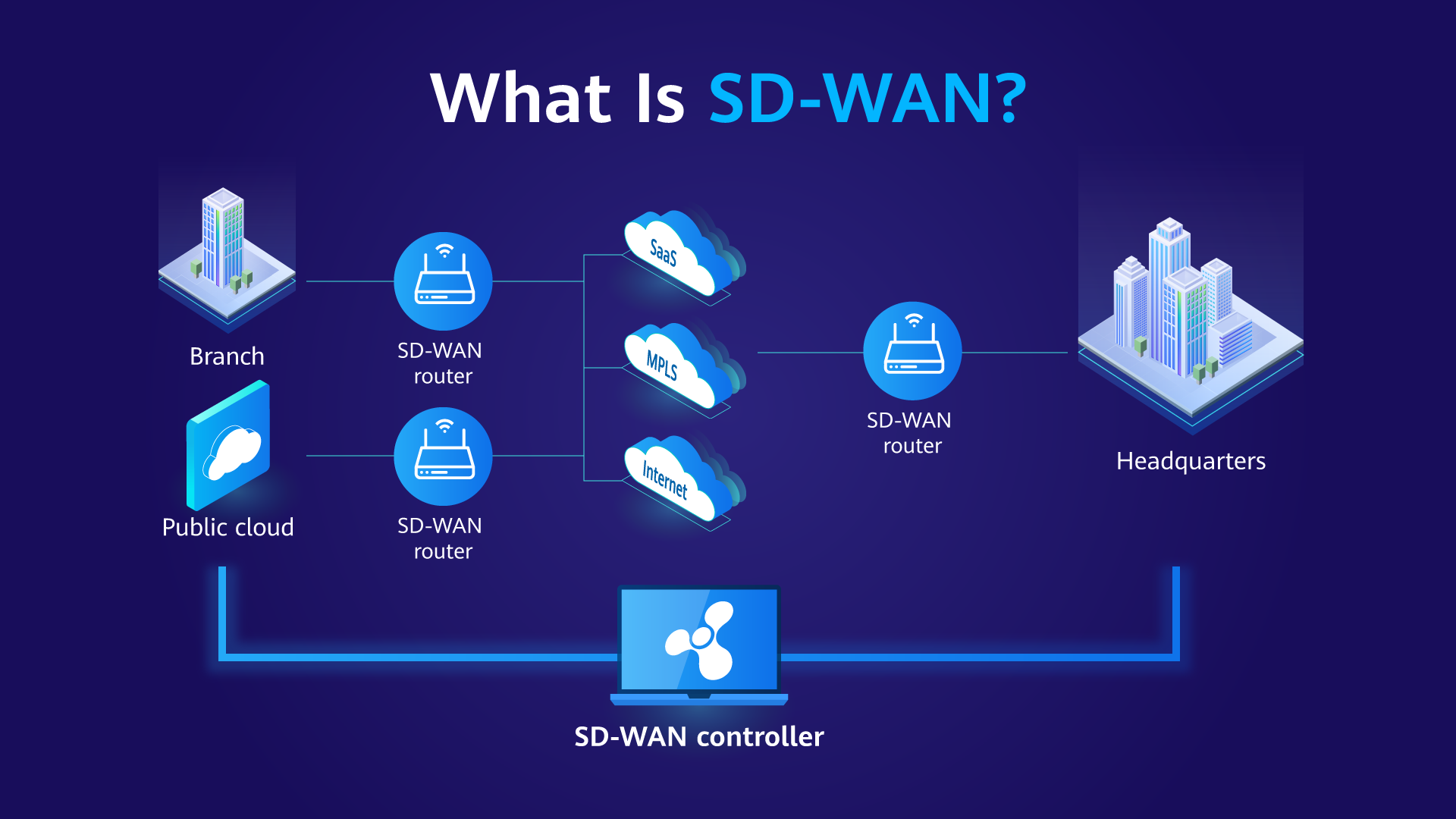
Intelligent traffic steering is a technology that uses intelligent algorithms to dynamically select the optimal path for network traffic. It can dynamically adjust network traffic paths based on the network topology and quality information, reduce network costs, improve network performance and reliability, and improve user experience. It is of great significance for enterprises to build SD-WAN networks.
All Topics
Alphabetical
By Category
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
J
K
L
M
N
O
P
Q
R
S
T
U
V
W
X
Y
Z
0-9
- AAA
- ACL
- Adaptive Forward Error Correction
- Adaptive Routing
- Advanced Persistent Threat
- AI ECN
- AI Firewall
- Air Interface Slicing
- AI Roaming
- Antivirus
- API Gateway
- APN6
- Application Identification
- APS Protection
- ARP
- Autonomous Driving Network
- Channelized Sub-interface
- CloudFabric
- CloudFabric N1 Business Model
- Cloud Managed Network
- CloudWAN
- Combined RF Power
- Command and Control
- Computer Virus
- Computing efficiency
- Computing network
- Computing-network integration
- CoSR
- CPCAR
- CRC
- Cryptocurrency Mining
- CSC
- CSRF
- CSS
- CVE
- DCI
- DDoS Attack
- Deception Technology
- DGA
- DHCP
- DHCP-based deployment
- DHCP Snooping
- DLP
- DNS
- Docker Container
- DPFR
- Dual Fed and Selective Receiving
- EAI
- ECA
- Edge Computing
- Edge Computing IoT
- EDR
- Email-based deployment
- eMDI
- Endpoint Security
- Eth-Trunk
- EVA
- EVPN
- HACA
- Hot swapping
- HQoS
- HSR
- HTTP/2
- HVPN
- Hybrid Cable
- Hybrid Cloud
- Hyper-Converged Data Center Network
- ICMP
- iConnect
- IFIT
- IIoT
- Industrial Internet
- iNOF
- Intelligent Cloud-Network
- Intelligent Lossless Network
- Intelligent network O&M
- Intelligent Traffic Analysis
- Intelligent traffic steering
- Intelligent Wind Power Network
- Intent-driven Deployment
- IOAM
- IoT Aware Network
- IP-based production and broadcasting network
- iPCA2.0
- IPoE
- IP Private Line
- IPRAN
- IPS
- IPsec
- IPSG
- IPv6
- IPv6 Enhanced
- IS-IS
- ISSU
- MACsec
- Malware
- MCE
- MD-CLI
- MFA
- Microsegmentation
- MIMO
- Mirroring
- MITM
- M-LAG
- MPLS
- MTN
- MTU
- Multicast
- Multi-fed and selective receiving
- MU-MIMO
- MUX-VPN
- NAC
- NAT
- NAT66
- NETCONF
- NetStream
- Network digital map
- Network Programming
- Network Slicing
- NFV
- NGFW
- NoF
- NoF+
- NPCC
- NQA
- NSR
- NTA
- NTP
- PAM4
- PCEP
- PFC
- Phishing
- PLC-IoT
- Plug-and-Play
- PoE
- Policy Association
- PPPoE
- Private Cloud
- Private Line + Managed Services
- Public Cloud
- SAC
- Sandboxing
- SBFD
- SDN
- SD-WAN
- SD-WAN EVPN
- Security Policy
- Segment Routing
- SFC
- sFlow
- Simulation and verification
- Situational Awareness
- Smart Antenna
- Smart policy routing
- Smart Upgrade
- SNMP
- SNR
- SOAR
- SOC
- Social Engineering
- Solar System architecture
- SPN
- SPN FGU
- Spyware
- SQL Injection
- SR-MPLS
- SR-TP tunnel
- SRv6
- SSH
- SSID
- SSL
- SSL-Encrypted Traffic Detection
- SSL Offloading
- SSL VPN
- SSO
- Stacking
- STP
- STP loop protection
- STUN
- Super VLAN
- SWG
- SYN Flood
- SZTP